Mustard: A Low-Calorie Alternative Packed with Health Benefits
Can mustard be a low-calorie alternative to higher-fat condiments for individuals trying to reduce calorie intake?

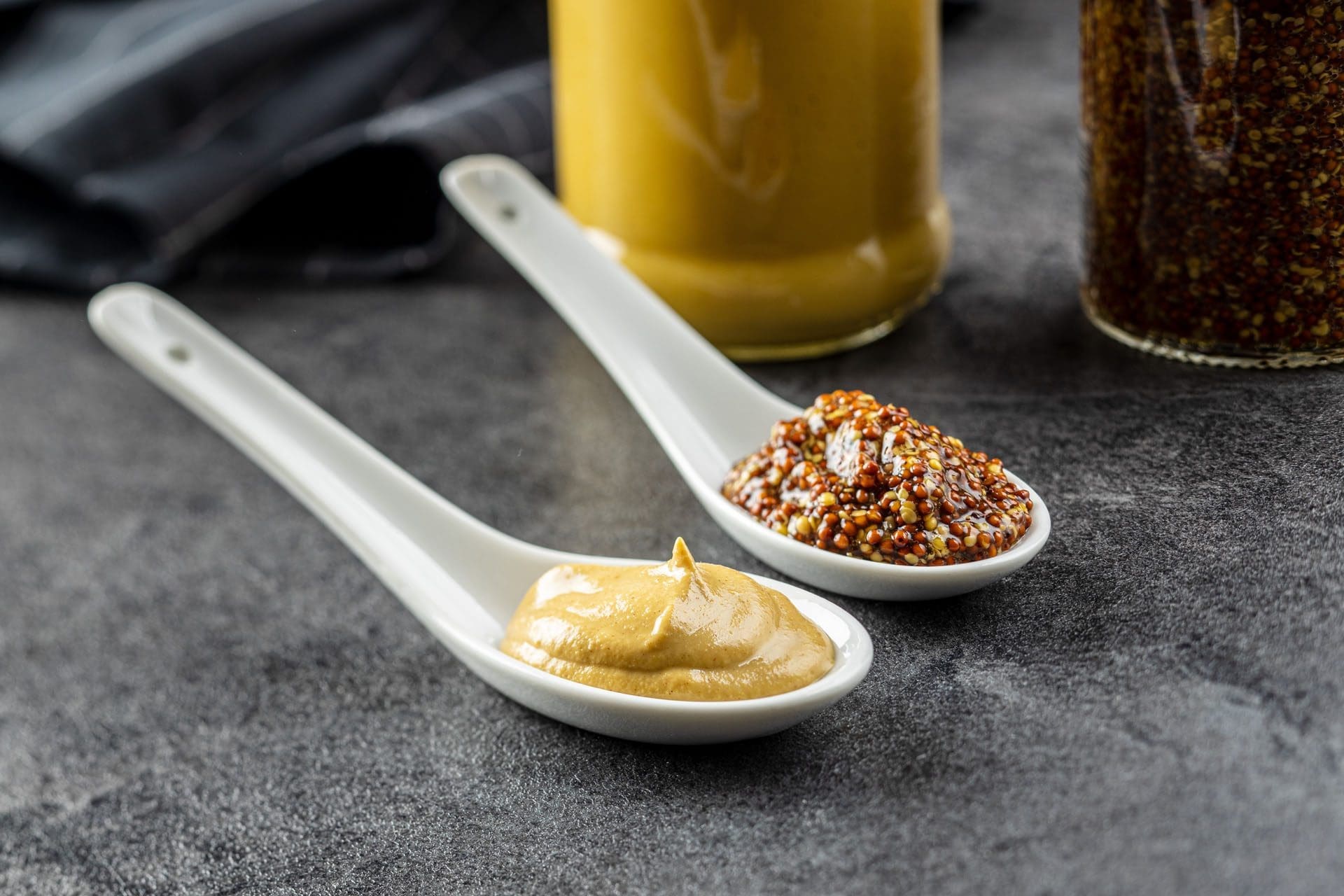
Mustard
Prepared mustard is a common condiment used around the country. It is a low-calorie, highly flavored condiment that can replace more calorie-dense options. The familiar condiment combines mustard seeds with vinegar, salt, lemon, and other ingredients. There are also different varieties made from brown or black mustard seeds.
Health Benefits
Mustard is considered healthy because it contains antioxidants that provide various health benefits, including anti-cancer, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties. (Mazumder A., Dwivedi A., & du Plessis J. 2016) Although not associated with significant health benefits, mustard is a low-calorie alternative to many higher-fat condiments, like mayonnaise. Different types of mustard seeds are used for health purposes. For example, some herbalists use white mustard seeds to clear the throat when mixed with honey (Ewing, Sarah, 1999). Antioxidants include isothiocyanates and sinigrin.
- Isothiocyanates, the oil that gives mustard its pungent taste, have anti-cancer properties for breast, lung, GI tract, and prostate cancers.
- However, the mechanism remains unclear, and more research is needed to determine the efficacy of mustard’s health benefits for cancer.
- Isothiocyanates may also help manage diabetes and reduce unhealthy cholesterol, providing cardiovascular protection and neurological benefits that may help autistic individuals. More research is needed. (Palliyaguru D. et al., 2018)
- Sinigrin is another antioxidant. Research shows this antioxidant has anti-cancer, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties. (Mazumder A., Dwivedi A., & du Plessis J. 2016)
Nutrition
A single serving is usually about a teaspoon. A serving of prepared yellow and spicy mustard provides only about three calories. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, 2019) Its nutritional profile includes a rich supply of essential minerals, including calcium, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It is also a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, tryptophan, phosphorus, iron, and protein. The seeds are also a very good source of selenium. Most calories come from carbohydrates, but because the calorie count is so low, these carbohydrates are not likely to significantly affect daily intake. Dijon mustard may provide more calories. A single serving of Dijon may contain up to 10 calories.
Preparation and Storage
Yellow mustard and Dijon are easy to find. Try course mustard varieties with distinct textures and seeds. Buy in small quantities, as mustard can lose flavor with time. Once opened, store in the refrigerator for up to one year. Mustard imparts a strong, spicy taste that pairs well with meat and seafood and can also be used to make salad dressings.
Side Effects
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recognizes mustard as safe (GRAS). Eating too much can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and gut inflammation. However, mustard and mustard seed allergies are not uncommon. Symptoms may be mild or severe and generally appear shortly after consuming the product. Individuals may experience a rash or a tingly, itchy feeling in the mouth. Difficulty breathing is also possible. Other foods derived from the mustard plant, including leaves, seeds, and flowers, sprouted seeds, oil, and foods that contain these, are likely to cause reactions in those with mustard allergies.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic focuses on and treats injuries and chronic pain syndromes through personalized care plans that improve ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs to relieve pain. Our providers use an integrated approach to create customized care plans for each patient and restore health and function to the body through nutrition and wellness, functional medicine, acupuncture, Electroacupuncture, and sports medicine protocols. If the individual needs other treatment, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them. Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, nutritionists, and health coaches to provide the most effective clinical treatments.
Enhancing Health Together
References
Mazumder, A., Dwivedi, A., & du Plessis, J. (2016). Sinigrin and Its Therapeutic Benefits. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 21(4), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040416
Ewing, Sarah. (1999). Black Mustard (Brassica nigra). https://opensiuc.lib.siu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1421&context=ebl
Palliyaguru, D. L., Yuan, J. M., Kensler, T. W., & Fahey, J. W. (2018). Isothiocyanates: Translating the Power of Plants to People. Molecular nutrition & food research, 62(18), e1700965. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700965
U.S. Department of Agriculture. (2019). Mustard, prepared, yellow. Retrieved from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/326698/nutrients