Understanding Nerve Conduction Velocity in Health Care
Should individuals experiencing nerve pain or various sensations get a nerve conduction velocity study to examine nerve health and function?
Nerve Conduction Velocity
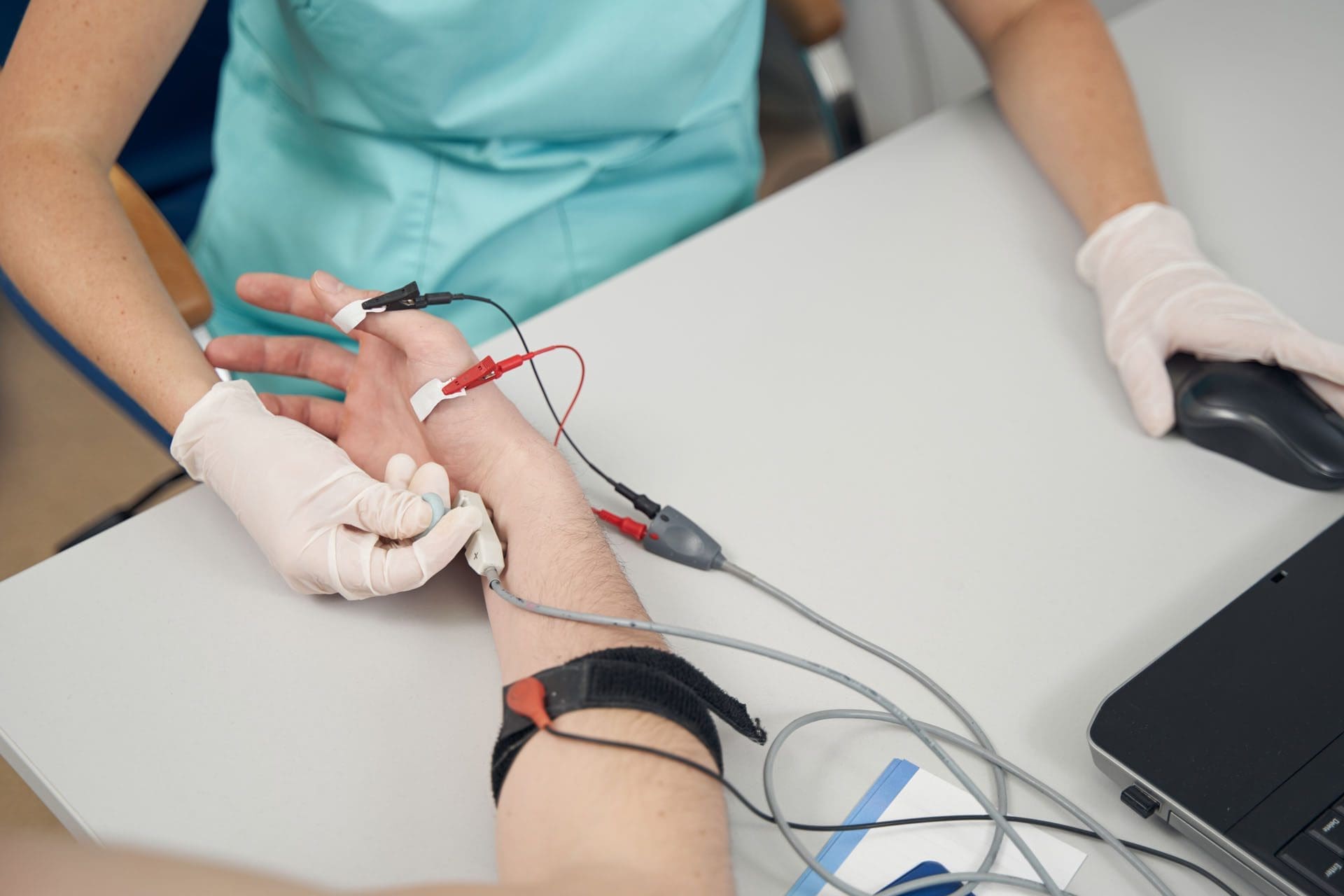
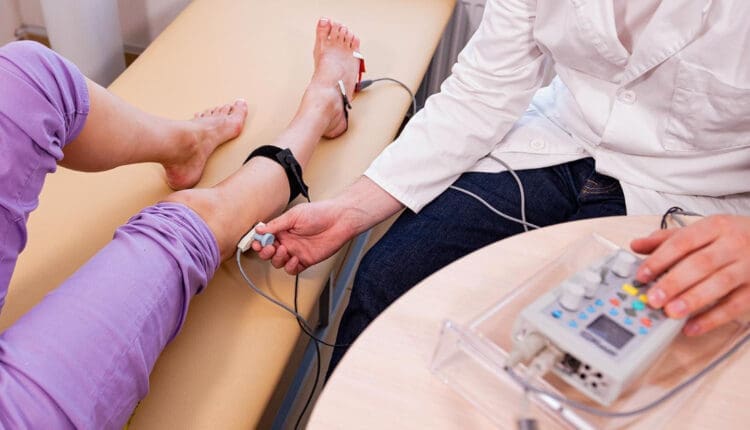
A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a noninvasive test that measures the speed and strength of nerve stimulation using electrical probes placed on the skin. It’s used to diagnose nerve damage or disease, often alongside an EMG (electromyogram) to differentiate between nerve and muscle problems. It can also evaluate sensory issues, pain, and weakness of the extremities.
- This test involves safe electrical shocks that can be slightly uncomfortable but not painful.
- Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) measures the speed at which electrical impulses travel along a nerve fiber, which measures how quickly electrical signals travel through a nerve.
- This information indicates nerve health and function.
- Electromyography (EMG) is a nerve test that involves placing tiny needles into the muscles.
- A slower NCV can indicate nerve injury or dysfunction.
Test Uses
Generally, the test is ordered to assess peripheral nerve diseases, those that connect from the muscles, organs, and skin to the spinal cord or brain. It can help identify the type and location of nerve damage.
- Peripheral nerve conditions typically cause pain, sensory loss, tingling, or burning.
- Mild weakness and diminished reflexes can be detected during a neurological examination.
Conditions
Nerve conduction studies are performed to help diagnose conditions.
- Herniated disc disease
- Sciatic nerve problems
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Nerve damage (neuropathy), such as from diabetes, chemotherapy, or autoimmune disorders
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Nerve compression
- Many different conditions, including trauma, inflammation, and tumors, can compress one or more nerves.
Radiculopathy
- Often described as a pinched nerve, radiculopathy can affect an arm or a leg, causing pain and weakness.
Peripheral Neuropathy
- This nerve damage begins in the most distal nerves, those farthest from the center of the body, such as the toes and fingers. It is often due to chronic alcohol misuse, uncontrolled diabetes, nutritional deficits, and inflammatory diseases. (Ferdousi M. et al., 2020)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Commonly caused by inflammatory diseases or overuse of the wrists, such as from assembly line work, carpal tunnel syndrome causes numbness, pain, and weakness of the fingers and hands. (Tada K. et al., 2022)
Ulnar neuropathy
- This common condition causes arm pain and sensory changes, usually due to repetitive movements or a prolonged position that causes pressure on the ulnar nerve.
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS)
- This inflammatory condition causes demyelination, or loss of the insulating covering around nerves, which results in leg weakness.
- It begins in the motor nerves, which send signals to muscles in the legs. (Shibuya K. et al., 2022)
- The inflammation travels to nerves of the upper body, often affecting the muscles that control breathing.
- Respiratory support is necessary until the condition improves.
Chronic Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- This condition is a chronic, recurrent form of GBS that usually affects the legs and causes episodes of weakness.
ICU neuropathy
- Metabolic changes, severe illness, and not moving enough can cause nerves to develop a pattern of weakness and sensory loss.
Myasthenia gravis (MG)
- This autoimmune condition affects the junction between the nerves and the muscles.
- Myasthenia gravis causes drooping eyelids and weakness of the arms and shoulders.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- ALS is a serious, degenerative disease affecting the spinal cord’s motor neurons.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis progresses rapidly, resulting in substantial weakness of muscles throughout the body.
How it’s Done
- Surface electrodes are placed on the skin over nerves, and a small electrical current is applied to stimulate the nerve.
- The time it takes for the electrical signal to travel between the electrodes is measured, and this time is used to calculate the NCV.
Values
Normal NCV values are generally between 50 and 70 meters per second. However, these values can vary depending on the nerve and the individual.
NCV Factors
Various factors can influence NCV.
- Age
- Sex
- Medical conditions like diabetes
Interpretation
- A slower NCV can indicate nerve damage or demyelination (loss of the myelin sheath, which insulates nerve fibers), while an EMG can help determine if the problem is with the nerve or the muscle.
Results
The results of NCV testing can be used to determine the type, severity, and location of nerve damage. The results will be ready in report form about a week after the test.
- The test measures velocity (how fast a nerve transmits signals) and amplitude (how many nerve fibers were activated). (Tavee J. 2019)
- The measurements are transmitted to a computer and shown as waves and numerical values.
- The values are compared to a standard measurement based on the tested nerve.
- The distance between the electrodes.
- The person’s age.
Compared to the standard, the NCV results can identify certain patterns of nerve damage. (Tada K. et al., 2022) Outcomes include: (Tavee J. 2019)
- If one or more nerves are affected.
- If motor nerves (control movement), sensory nerves (transmit sensory signals), or both are affected.
- Whether a nerve is blocked or damaged.
- The severity of the damage.
- The type of nerve damage
- Axonal (damage to the nerve itself)
- Demyelination (damage to the protective fatty layer around the nerve)
The results can help point to certain diagnoses.
Preparation Before the Test
Individuals will not need to change their diet before having an NCV. However, patients will be asked to avoid lotions or creams on their skin before the test. Individuals who are also having an EMG at the time of their NCV might be asked to stop taking medications or supplements that increase the risk of bleeding and bruising. If a healthcare provider says not to stop taking the medicines for health reasons, the patient might be warned that they could have some bruising after the EMG test.
- NCV may advise against getting the test for those with electrical device implants.
- Make sure your healthcare providers are aware of your whole medical history.
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Peripheral Neuropathy and Chiropractic Care
References
Ferdousi, M., Kalteniece, A., Azmi, S., Petropoulos, I. N., Worthington, A., D’Onofrio, L., Dhage, S., Ponirakis, G., Alam, U., Marshall, A., Faber, C. G., Lauria, G., Soran, H., & Malik, R. A. (2020). Corneal confocal microscopy compared with quantitative sensory testing and nerve conduction for diagnosing and stratifying the severity of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. BMJ open diabetes research & care, 8(2), e001801. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001801
Tada, K., Murai, A., Nakamura, Y., Nakade, Y., & Tsuchiya, H. (2022). In Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Sensory Nerve Conduction Velocities Are Worst in the Middle Finger Than in the Index Finger. Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 851108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.851108
Shibuya, K., Tsuneyama, A., Misawa, S., Suzuki, Y. I., Suichi, T., Kojima, Y., Nakamura, K., Kano, H., Ohtani, R., Aotsuka, Y., Morooka, M., Prado, M., & Kuwabara, S. (2022). Different patterns of sensory nerve involvement in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy subtypes. Muscle & Nerve, 66(2), 131–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.27530
Tavee J. (2019). Nerve conduction studies: Basic concepts. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 160, 217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64032-1.00014-X