Hamstring Syndrome Relief for Sciatic Nerve Pain
Individuals dealing with pain in the buttocks and in the back of the thigh, along with numbness and tingling down to the bottom of the foot, may be experiencing hamstring syndrome, a condition caused by pressure on the sciatic nerve. What is the recommended treatment?
Hamstring-Syndrome Relief
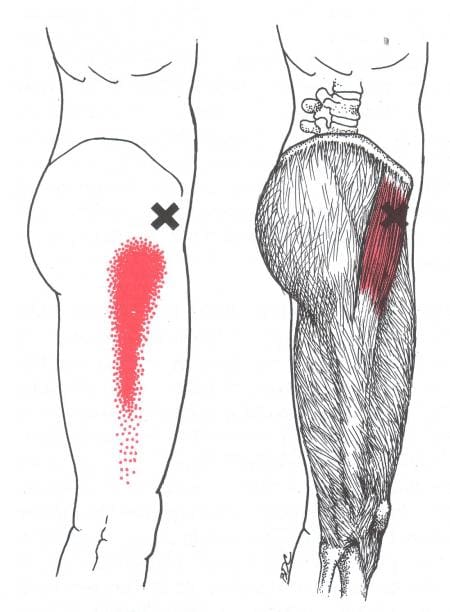
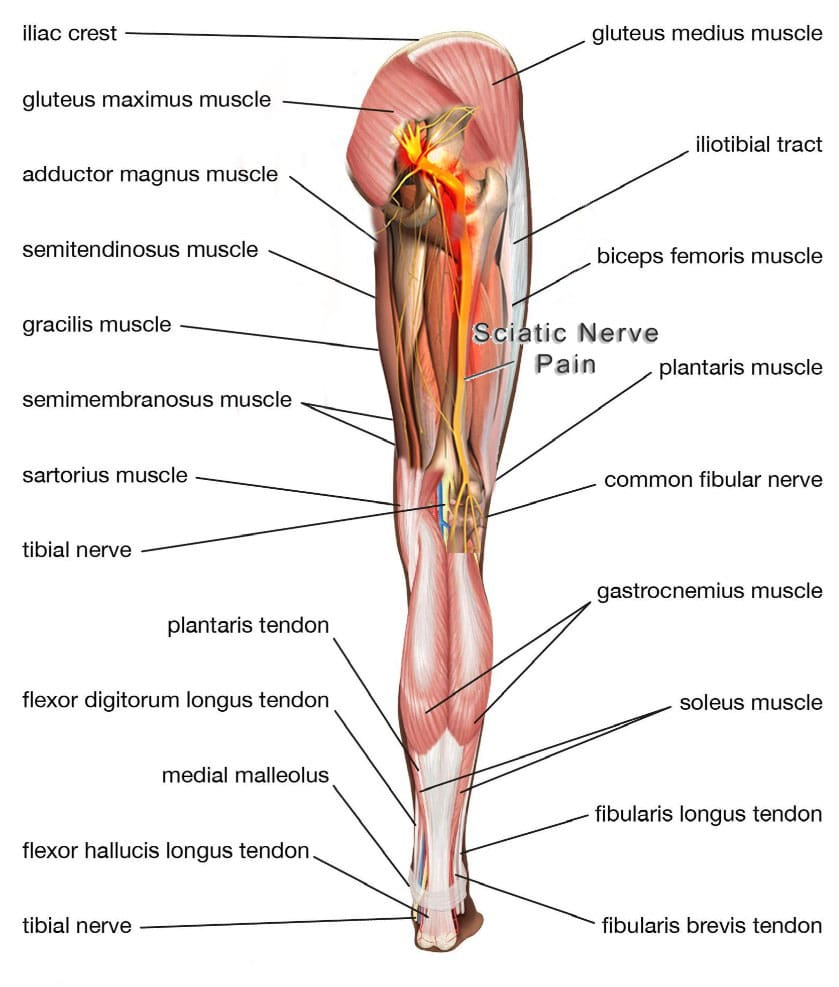
The hamstrings are three muscles in the back of the thigh, extending from the pelvis or upper thigh across the back of the knee to the leg. This muscle group is important for bending the knee, straightening the hip, and stabilizing the knee. The sciatic nerve is a large nerve that runs from the lower back down the legs. It usually passes near or through these muscles, and the pelvis then runs under these muscles in the thigh. Hamstring syndrome refers to pain in the buttock and back of the thigh, often radiating down the leg, caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve at the hamstring-insertion point on the ischial tuberosity, typically due to tight or scarred tissue. (Sakari Orava, 1997)
Pain Location
The pain is primarily felt in the buttock and back of the thigh, sometimes extending down the leg. It’s characterized by pressure on the sciatic nerve, which runs through the buttock and into the back of the thigh, where it supplies the hamstring muscles. (Kaiser Permanente, 2024)
Mechanism
This pressure can occur due to: (Sakari Orava, 1997) (Kaiser Permanente, 2024)
Fibrotic Bands
- Tight, tendon-like, or scarred bands of tissue at the hamstring’s insertion point/ischial tuberosity can irritate the sciatic nerve.
Compression
- These bands can compress the nerve, especially when sitting or during activities that involve hip flexion and knee extension.
Traction
- The sciatic nerve can also be stretched or irritated by the hamstring tendons.
Symptoms
- Pain in the buttock and back of the thigh may radiate down the leg.
- Pain that is worse when sitting, stretching the hamstrings, or during activities like running. (Puranen J. & Orava S. 1988)
- Numbness or tingling in the back of the leg
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to differentiate hamstring syndrome from other conditions that could be causing similar symptoms, including:
- Piriformis syndrome
- Ischiogluteal bursitis
- Hamstring muscle strains
Treatment
Hamstring syndrome relief may consist of the following:
Conservative
- Initial treatment focuses on rest, ice, stretching, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
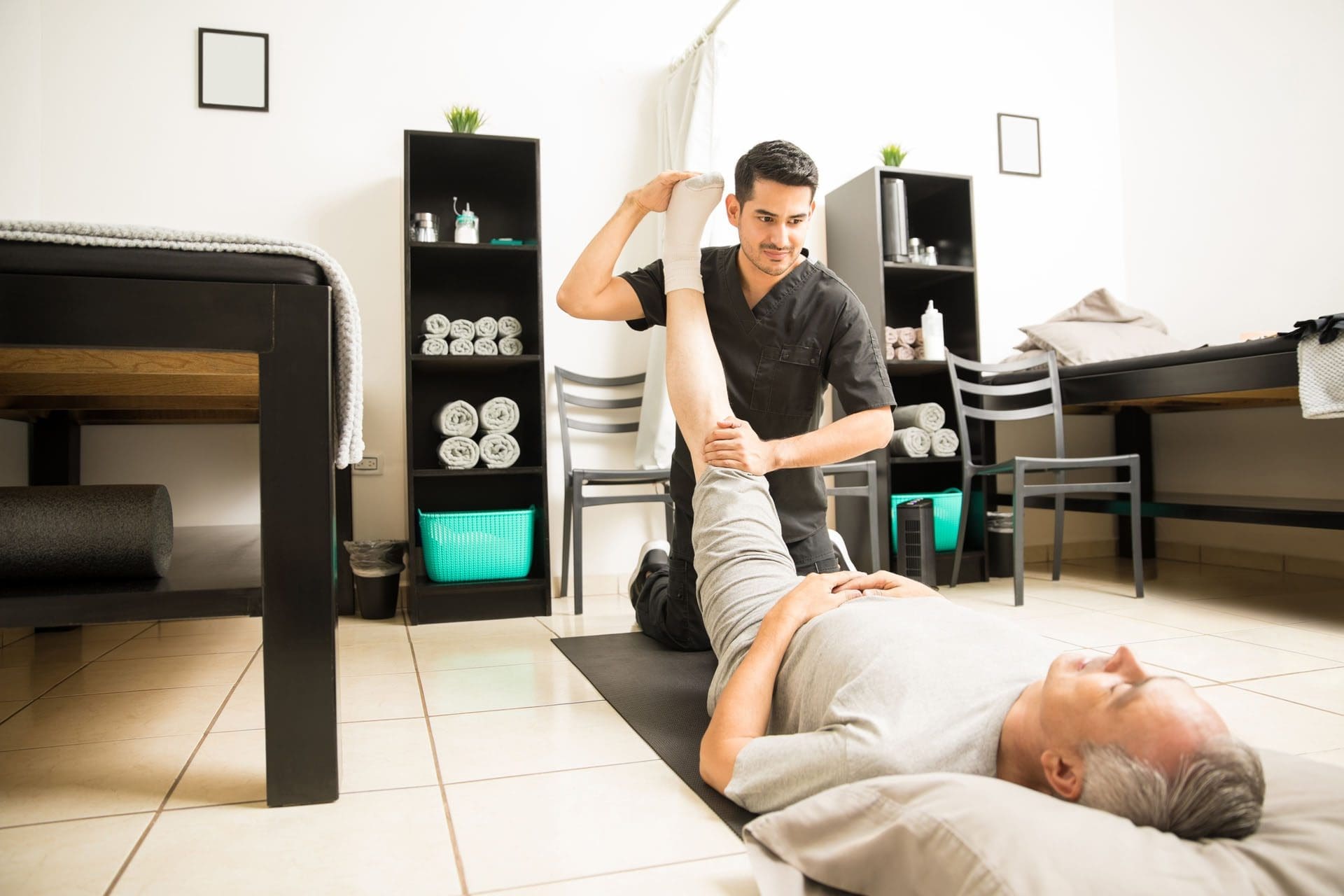
Physical Therapy
- Exercises to strengthen and stretch the hip and hamstring muscles can be beneficial. (Zion Physical Therapy, 2023)
Injections
- In some cases, injections with cortisone and numbing medicine may be used to reduce nerve inflammation and pain. (Lower Limb Surgery, 2024)
Surgery
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to release the compressing bands and free the sciatic nerve. (Lower Limb Surgery, 2024)
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
Talk to a healthcare provider about what interventions would help the most. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms and Tips
References
Orava, Sakari. (1997). Hamstring syndrome. Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine, 5(3). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1060-1872(97)80035-4.
Kaiser Permanente. (2024). Hamstring Syndrome: Care Instructions. https://healthy.kaiserpermanente.org/health-wellness/health-encyclopedia/he.hamstring-syndrome-care-instructions.abr3618
Puranen, J., & Orava, S. (1988). The hamstring syndrome. A new diagnosis of gluteal sciatic pain. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 16(5), 517–521. https://doi.org/10.1177/036354658801600515
Zion Physical Therapy. (2023). Hamstring Tendinitis Vs. Hamstring Syndrome. https://www.zionpt.com/post/hamstring-tendinitis-vs-hamstring-syndrome
Lower Limb Surgery. (2024). Hamstring Syndrome. https://www.lowerlimbsurgery.com/hamstring syndrome#:~:text=General%20Treatment%20Considerations,%E2%80%8B