Gastrointestinal Impact After Motor Vehicle Accidents: Treatment Through Integrative Medicine

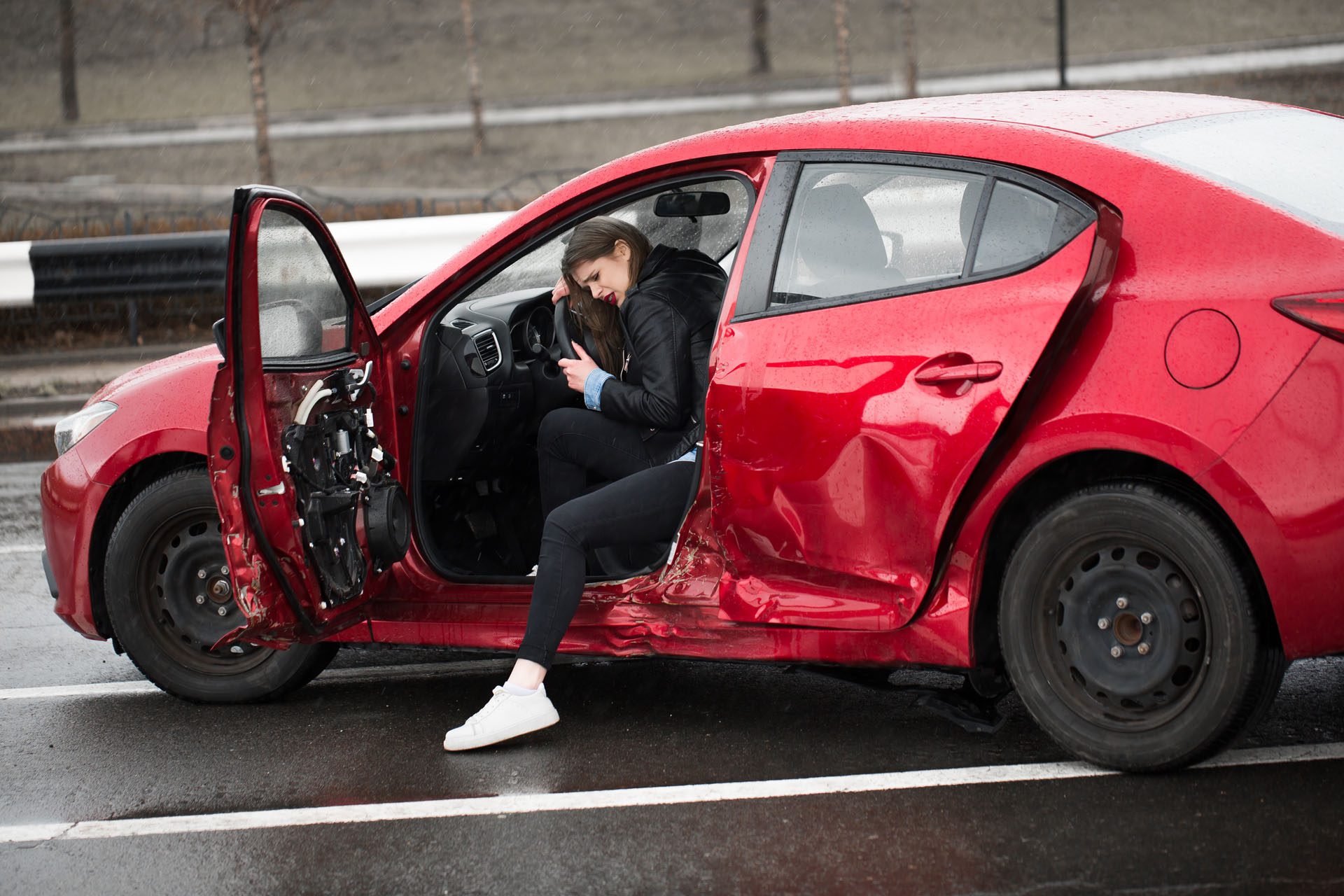
Car accidents, also known as motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), can cause a range of injuries, from visible cuts and bruises to hidden internal damage. One area often overlooked is the gastrointestinal (GI) system, which can suffer significant harm due to blunt force trauma or seatbelt-related injuries. These injuries may not exhibit symptoms immediately, making them difficult to detect without proper medical attention. Fortunately, nurse practitioners, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and integrative medicine specialists can collaborate to diagnose and treat these issues, enabling patients to recover fully. This post examines how MVAs impact the GI system, the specific injuries that can result, and how a combination of medical and holistic treatments can help restore health. We’ll also highlight the importance of dual-scope diagnosis and integrative care in addressing these complex injuries, drawing on clinical insights from Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a nurse practitioner and chiropractor in El Paso, Texas.
How Motor Vehicle Accidents Affect the Gastrointestinal System
The GI system, which includes organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, and pancreas, is vulnerable during a car accident. The sudden force of a crash can cause internal damage, even if there are no external signs of injury. Blunt force trauma—when the body is struck by or slams into an object like a steering wheel or dashboard—can harm internal organs. Seatbelts, while life-saving, can also contribute to abdominal injuries by applying intense pressure to the torso during a collision.
Delayed symptoms are common with GI injuries. For example, stomach pain, nausea, or diarrhea might not appear until hours or days after the accident. This delay can make it hard for victims to connect their symptoms to the crash, which is why medical evaluation is critical. If left untreated, GI injuries can lead to serious complications like internal bleeding, organ rupture, or sepsis.
Common GI Injuries from MVAs
- Abdominal Wall Injuries: Contusions, lacerations, or hernias can occur when the abdominal wall is compressed or struck. These injuries may cause localized pain or swelling but can also mask deeper damage (Plaxen & Adler, 2024).
- Organ Damage: The liver, spleen, and intestines are particularly at risk. Blunt trauma can cause tears or ruptures, leading to internal bleeding. For instance, delayed splenic rupture is a known risk after MVAs (UpToDate, n.d.).
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Even without visible organ damage, the GI system can be disrupted. Symptoms like stomach pain, bloating, or irregular bowel movements may result from inflammation or stress responses triggered by the accident (Maguire Law Firm, n.d.).
- Seatbelt Syndrome: This refers to injuries caused by the seatbelt’s pressure on the abdomen. It can lead to bruising, internal bleeding, or damage to organs like the intestines or pancreas (PMC, 2012).
- Pelvic and Abdominal Injuries: Trauma to the pelvic region can affect the lower GI tract, causing pain or dysfunction in the intestines or bladder (Patterson Personal Injury, n.d.).
Research shows that abdominal injuries are common in MVAs, with one study finding that 10% of front-seat passengers in crashes sustain abdominal trauma (PMC, 2012). Another analysis of 50,000 crash victims reported a significant number of blunt abdominal injuries, particularly among unrestrained passengers (BMC Emergency Medicine, 2024). These statistics demonstrate the value of comprehensive medical evaluations following an accident.
Why GI Injuries Are Dangerous
GI injuries are concerning because they can escalate quickly. A small tear in the intestines, for example, can lead to peritonitis (infection in the abdominal cavity) if bacteria leak out. Similarly, a ruptured spleen can cause life-threatening internal bleeding. Symptoms like a rigid or hard stomach, fever, or severe pain are red flags that require immediate attention (Lorfing Law, n.d.). Even less severe issues, such as chronic stomach pain or disrupted digestion, can significantly impact quality of life if left unaddressed.
References
Maguire Law Firm. (n.d.). Stomach pain after a car accident. Retrieved from https://maguirelawfirm.com/stomach-pain-after-a-car-accident/\
Lorfing Law. (n.d.). Stomach rigid hard after car accident Texas. Retrieved from https://lorfinglaw.com/blog/stomach-rigid-hard-after-car-accident-texas/\
Patterson Personal Injury. (n.d.). Pelvic & abdominal injury. Retrieved from https://pattersonpersonalinjury.com/common-car-injuries/pelvic-abdominal-injury/\
Plaxen & Adler. (2024, July 16). Abdominal injuries from vehicle crashes. Retrieved from https://www.plaxenadler.com/2024/07/16/abdominal-injuries-from-vehicle-crashes/\
PMC. (2012). Abdominal injuries in seatbelt wearers. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3503429/\
BMC Emergency Medicine. (2024). Epidemiology of blunt abdominal trauma. Retrieved from https://bmcemergmed.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12873-024-01002-0\
UpToDate. (n.d.). Blunt abdominal trauma in adults: Initial evaluation and management. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/blunt-abdominal-trauma-in-adults-initial-evaluation-and-management/print
Diagnosing GI Injuries After an MVA
Diagnosing GI injuries requires a combination of clinical expertise and advanced tools. Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a nurse practitioner and chiropractor in El Paso, emphasizes the importance of a dual-scope approach—combining medical and chiropractic perspectives—to effectively identify and treat these injuries. His clinical observations, shared through platforms like dralexjimenez.com and chiromed.com, underscore the importance of thorough assessments to detect hidden damage.
Diagnostic Assessments
- Physical Exams: A healthcare provider will examine the patient for signs of abdominal tenderness, rigidity, or bruising. These can indicate internal bleeding or organ damage (Fletcher Law USA, n.d.).
- Patient History: Understanding the accident’s details (e.g., speed, impact direction, seatbelt use) helps clinicians predict likely injuries. Dr. Jimenez notes that patients often downplay symptoms, so a detailed history is crucial.
- Symptom Monitoring: Symptoms like delayed stomach pain, nausea, or changes in bowel habits are red flags. Nurse practitioners are trained to recognize these as potential signs of GI trauma (Michigan Auto Law, n.d.).
Advanced Imaging
Imaging is essential for confirming GI injuries. Common tools include:
- CT Scans: These provide detailed images of the abdomen, revealing organ damage or internal bleeding. They’re often the first choice in trauma cases (UpToDate, n.d.).
- Ultrasounds: Used to detect fluid buildup or organ injuries, especially in emergency settings.
- X-rays: Helpful for identifying fractures or foreign objects, but less effective for soft tissue damage.
- MRI: Used in complex cases to assess soft tissue or spinal involvement, which can contribute to GI symptoms (Jimenez, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez’s dual training as a nurse practitioner and chiropractor allows him to interpret these tests with a holistic view. For example, he might notice spinal misalignments on an MRI that could be contributing to nerve-related GI issues, which a purely medical approach might miss. His ability to correlate imaging with clinical findings ensures accurate diagnoses.
Challenges in Diagnosis
GI injuries can be tricky to diagnose because symptoms often mimic less serious conditions, like stress or indigestion. Dr. Jimenez stresses the importance of not dismissing vague symptoms, as they could signal serious issues like internal bleeding or organ perforation (Jimenez, n.d.). His integrative approach combines medical diagnostics with chiropractic assessments to address both the injury and its ripple effects on the body.
References
Fletcher Law USA. (n.d.). Stomach pain after a Texas car accident. Retrieved from https://www.fletcherlawusa.com/blog/stomach-pain-after-a-texas-car-accident/\
Michigan Auto Law. (n.d.). Stomach pain & diarrhea after car accident. Retrieved from https://www.michiganautolaw.com/personal-injury-lawyer/stomach-pain-diarrhea-after-car-accident/\
UpToDate. (n.d.). Blunt abdominal trauma in adults: Initial evaluation and management. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/blunt-abdominal-trauma-in-adults-initial-evaluation-and-management/print\
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical observations on auto accident injuries. Retrieved from https://dralexjimenez.com/
Treatment Options for GI Injuries
Treating GI injuries from MVAs requires a multi-faceted approach. While severe cases (e.g., organ rupture) may need surgery, many patients benefit from non-invasive treatments provided by nurse practitioners, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and integrative medicine specialists. Dr. Jimenez’s practice exemplifies this, combining medical care with holistic therapies to address both symptoms and underlying causes.
Nurse Practitioners: Coordinating Care
Nurse practitioners (NPs) play a key role in managing GI injuries. As primary care providers, they:
- Order and Interpret Tests: NPs like Dr. Jimenez order CT scans or blood tests to confirm diagnoses.
- Prescribe Medications: They may use pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, or antibiotics to manage symptoms or prevent infections.
- Coordinate Referrals: If surgery or specialist care is needed, NPs ensure patients see the right providers (Jimenez, n.d.).
NPs also educate patients about their condition, helping them understand why symptoms like diarrhea or bloating persist and what steps can be taken to alleviate them.
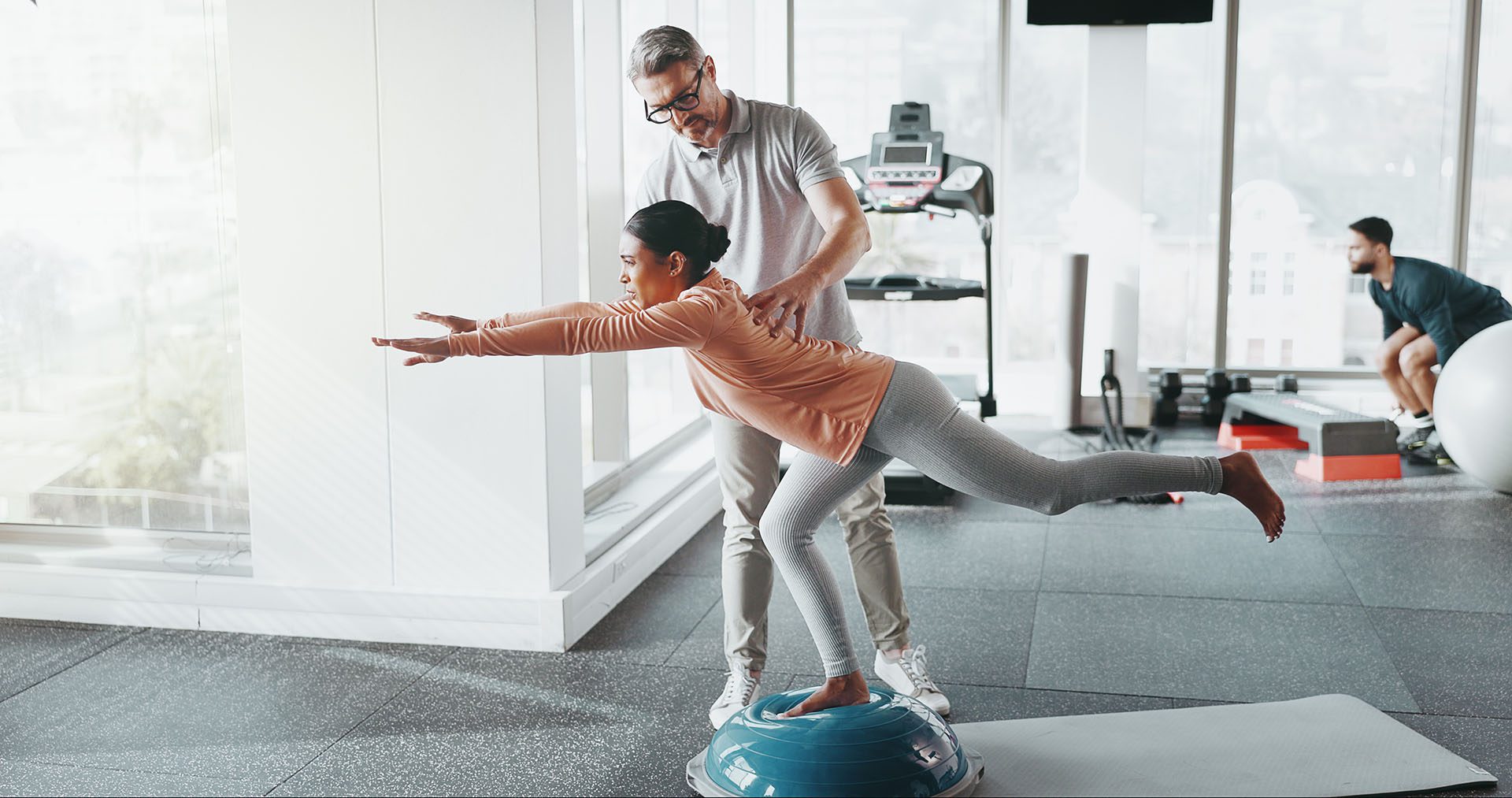
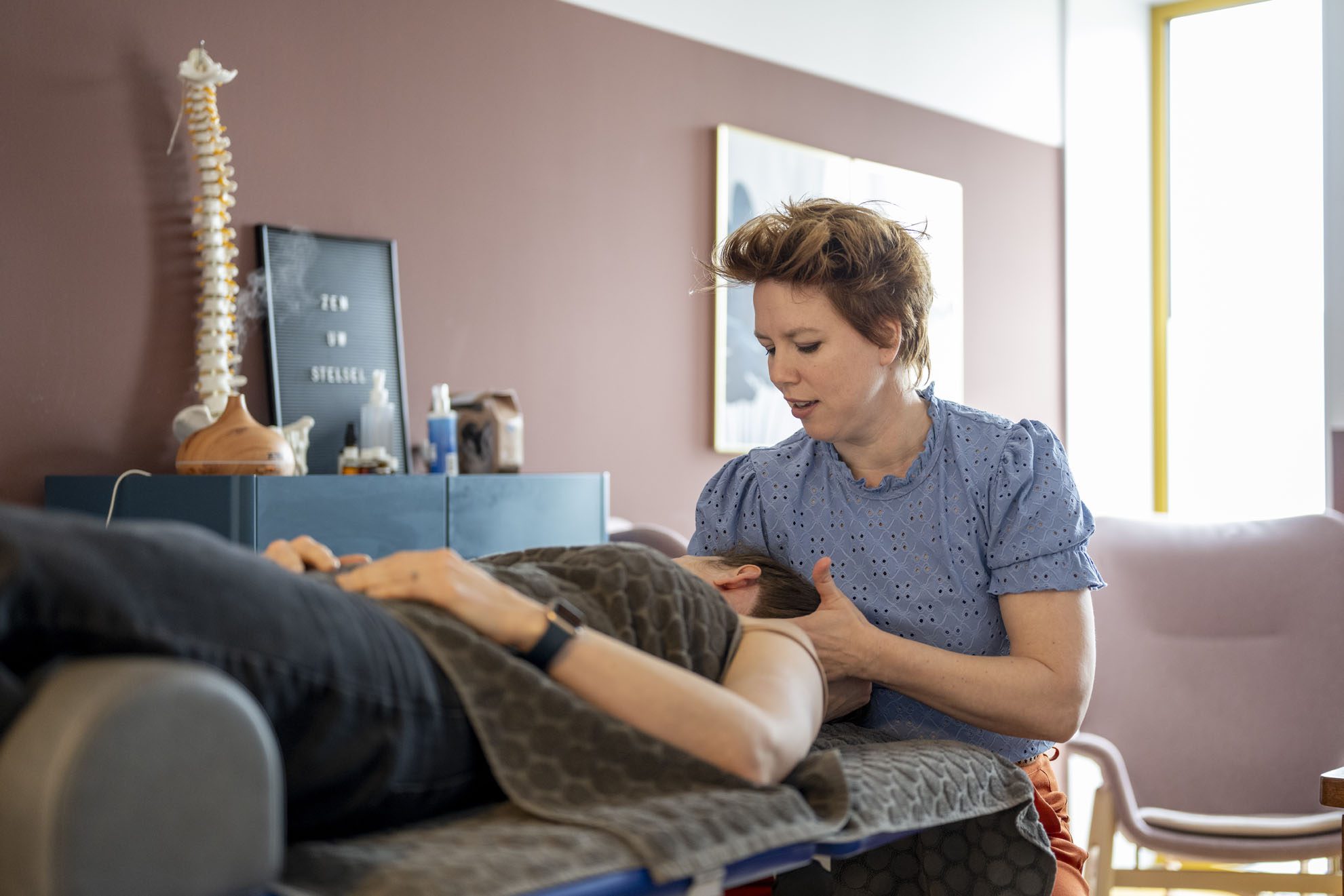
Chiropractic Care: Addressing Structural Issues
Chiropractic care is especially effective for addressing the musculoskeletal and neurological effects of MVAs that contribute to GI issues. Dr. Jimenez explains that spinal misalignments (subluxations) from a crash can disrupt nerve signals to the GI system, causing symptoms like bloating or irregular digestion. Chiropractic adjustments can:
- Restore Alignment: Correcting spinal misalignments improves nerve function, which may alleviate GI distress.
- Reduce Inflammation: Adjustments can reduce systemic inflammation, aiding overall recovery.
- Improve Mobility: Restoring movement in the spine and pelvis can relieve pressure on abdominal organs (Jimenez, n.d.).
A study on chiropractic care for post-traumatic injuries found that it significantly reduced pain and improved function in accident victims (PMC, 2011).
Acupuncture: Managing Pain and Stress
Acupuncture, a cornerstone of integrative medicine, uses thin needles to stimulate specific points on the body. It’s effective for:
- Pain Relief: Acupuncture can reduce abdominal pain by releasing endorphins and calming the nervous system.
- Stress Reduction: MVAs often cause anxiety, which can worsen GI symptoms. Acupuncture helps regulate the body’s stress response.
- Improved Digestion: By targeting points linked to the GI system, acupuncture can ease nausea or bloating (Smith & Hassler, n.d.).
Research supports acupuncture’s role in managing chronic pain and stress-related GI issues, making it a valuable tool for MVA recovery (PMC, 2011).
Integrative Medicine: A Holistic Approach
Integrative medicine combines conventional treatments with complementary therapies like nutrition, herbal remedies, and physical therapy. For GI injuries, integrative approaches might include:
- Nutritional Counseling: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., leafy greens, omega-3s) can support healing. Dr. Jimenez often advises patients to avoid processed foods that irritate the GI tract.
- Herbal Supplements: Remedies like ginger or peppermint can soothe digestion.
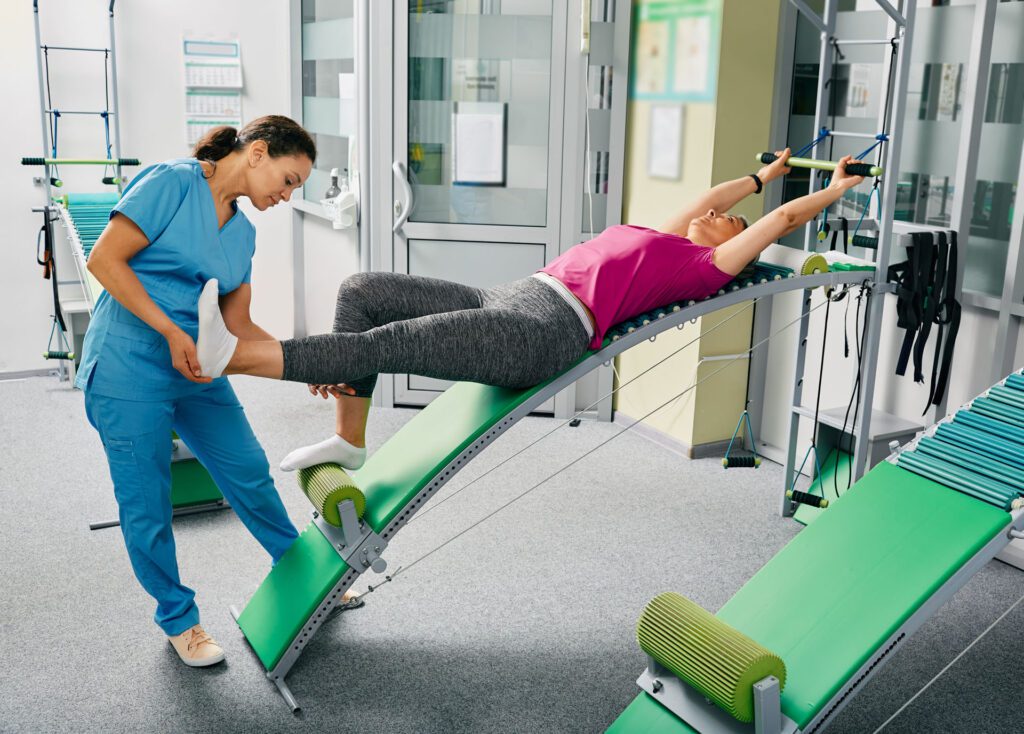
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises can strengthen the abdominal muscles and improve circulation, aiding recovery (Bryant PSC, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez’s practice integrates these therapies, tailoring plans to each patient’s specific needs. His ability to combine medical knowledge with holistic care ensures comprehensive and personalized treatment.
References
Bryant PSC. (n.d.). Stomach pain after car accident. Retrieved from https://www.bryantpsc.com/stomach-pain-after-car-accident/\
Smith & Hassler. (n.d.). Stomach pain after car accident. Retrieved from https://www.smithandhassler.com/articles/stomach-pain-after-car-accident/\
PMC. (2011). Chiropractic and acupuncture in trauma care. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3217390/\
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Integrative care for auto accident injuries. Retrieved from https://chiromed.com/
Dr. Alexander Jimenez: A Unique Approach to MVA Recovery
Dr. Alexander Jimenez stands out in the field of auto accident recovery due to his dual credentials as a nurse practitioner (APRN, FNP-BC) and chiropractor (DC). Based in El Paso, Texas, he specializes in treating MVA victims, with a focus on complex injuries like those affecting the GI system. His practice, detailed on dralexjimenez.com and chiromed.com, combines medical precision with chiropractic expertise, offering a model for integrative care.
Dual-Scope Diagnosis and Treatment
Dr. Jimenez’s dual training allows him to approach injuries from two angles:
- Medical Perspective: As a nurse practitioner, he diagnoses conditions using lab tests, imaging, and clinical exams. He can prescribe medications or refer patients to surgeons if needed.
- Chiropractic Perspective: As a chiropractor, he assesses how structural issues, like spinal misalignments, contribute to symptoms. This is critical for GI injuries, as nerve compression can mimic or worsen digestive issues (Jimenez, n.d.).
This dual-scope approach ensures no aspect of the injury is overlooked. For example, a patient with stomach pain might have both a bruised intestine (detected via CT scan) and a misaligned spine (identified through a chiropractic examination). Dr. Jimenez can treat both, addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms.
Handling Medical and Legal Aspects
MVA cases often involve insurance claims or lawsuits, requiring detailed medical documentation. Dr. Jimenez’s expertise as a nurse practitioner allows him to:
- Provide Accurate Reports: He creates thorough medical records that detail the injury, treatment plan, and prognosis, which are essential for legal cases.
- Testify as an Expert: His credentials make him a credible witness in court, helping patients secure fair compensation.
- Navigate Insurance: He ensures treatments are properly coded and documented to maximize insurance coverage (LinkedIn, n.d.).
This combination of medical and legal skills is rare and invaluable for MVA victims.
Improving Overall Health
Dr. Jimenez’s integrative approach goes beyond symptom relief. By addressing structural, neurological, and nutritional factors, he helps patients achieve long-term health and well-being. For example, a patient with GI issues might receive chiropractic adjustments to restore nerve function, acupuncture to reduce pain, and a diet plan to support gut healing. This holistic strategy not only treats the injury but also improves overall wellness, reducing the risk of chronic issues (Jimenez, n.d.).
References
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on MVA recovery. Retrieved from https://dralexjimenez.com/\
LinkedIn. (n.d.). Dr. Alexander Jimenez profile. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Long-Term Recovery and Prevention
Recovering from GI injuries after an MVA takes time and a proactive approach. While acute injuries may heal within weeks, chronic symptoms, such as digestive issues or pain, can persist. Integrative care, as practiced by Dr. Jimenez, focuses on long-term recovery by:
- Monitoring Progress: Regular check-ups ensure injuries are healing properly and catch any new symptoms early.
- Lifestyle Changes: Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy habits, such as regular exercise and stress management, to support their recovery.
- Preventive Care: Chiropractic adjustments and acupuncture can prevent future issues by maintaining spinal health and reducing stress (The Barnes Firm, n.d.).
Patients should also be aware of warning signs, such as persistent pain or changes in bowel habits, and seek prompt care if they occur. By combining medical treatment with holistic therapies, patients can achieve a full recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
References
The Barnes Firm. (n.d.). Delayed stomach pain after a car accident. Retrieved from https://www.thebarnesfirm.com/delayed-stomach-pain-after-a-car-accident/
Conclusion
Motor vehicle accidents can cause significant damage to the gastrointestinal system, from organ injuries to chronic digestive issues. These injuries, often caused by blunt force trauma or seatbelt pressure, require careful diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. Nurse practitioners, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and integrative medicine specialists offer a powerful combination of therapies to address both the injury and its broader effects on the body. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s dual expertise as a nurse practitioner and chiropractor exemplifies this approach, using advanced diagnostics, chiropractic care, and holistic treatments to help patients recover fully. By addressing the root causes of injuries and supporting overall health, integrative care provides a path to lasting recovery for MVA victims.
References
BMC Emergency Medicine. (2024). Epidemiology of blunt abdominal trauma. BMC Emergency Medicine, 24(1), Article 1002. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-024-01002-0
Bryant PSC. (n.d.). Stomach pain after car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.bryantpsc.com/stomach-pain-after-car-accident/
Fletcher Law USA. (n.d.). Stomach pain after a Texas car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.fletcherlawusa.com/blog/stomach-pain-after-a-texas-car-accident/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on MVA recovery. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://dralexjimenez.com/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Integrative care for auto accident injuries. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://chiromed.com/
LinkedIn. (n.d.). Dr. Alexander Jimenez profile. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Lorfing Law. (n.d.). Stomach rigid hard after car accident Texas. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://lorfinglaw.com/blog/stomach-rigid-hard-after-car-accident-texas/
Maguire Law Firm. (n.d.). Stomach pain after a car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://maguirelawfirm.com/stomach-pain-after-a-car-accident/
Michigan Auto Law. (n.d.). Stomach pain & diarrhea after car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.michiganautolaw.com/personal-injury-lawyer/stomach-pain-diarrhea-after-car-accident/
Patterson Personal Injury. (n.d.). Pelvic & abdominal injury. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://pattersonpersonalinjury.com/common-car-injuries/pelvic-abdominal-injury/
Plaxen & Adler. (2024, July 16). Abdominal injuries from vehicle crashes. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.plaxenadler.com/2024/07/16/abdominal-injuries-from-vehicle-crashes/
Smith & Hassler. (n.d.). Stomach pain after car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.smithandhassler.com/articles/stomach-pain-after-car-accident/
The Barnes Firm. (n.d.). Delayed stomach pain after a car accident. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.thebarnesfirm.com/delayed-stomach-pain-after-a-car-accident/
UpToDate. (n.d.). Blunt abdominal trauma in adults: Initial evaluation and management. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/blunt-abdominal-trauma-in-adults-initial-evaluation-and-management/print
Wozniak, M., & Trus, T. (2022). Abdominal injuries in road traffic accidents – autopsy study. Journal of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, 39(1), 15-20. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-0848.2022.00004.8
Zinzuwadia, A., & Brohi, K. (2011). Chiropractic and acupuncture in trauma care. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, 34(9), 615-622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2011.09.004
Zinzuwadia, A., & Brohi, K. (2012). Abdominal injuries in seatbelt wearers. Injury, 43(11), 1897-1902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2012.07.189