Bunions Management: Relief and Care Strategies
What is the most effective method for managing the initial symptoms of bunions?
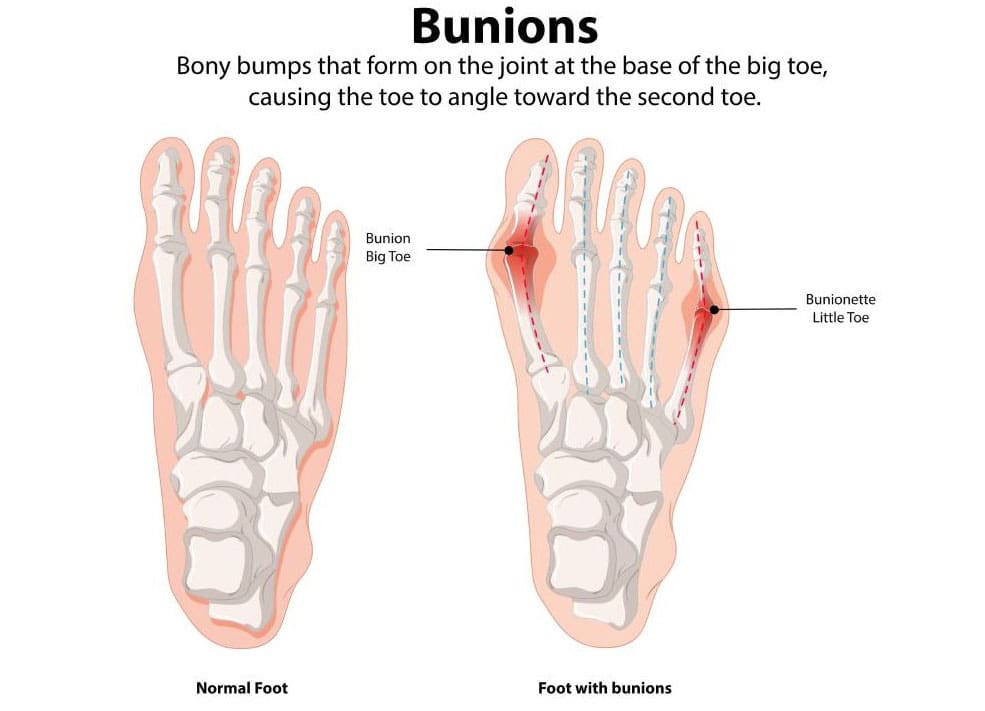
Bunions
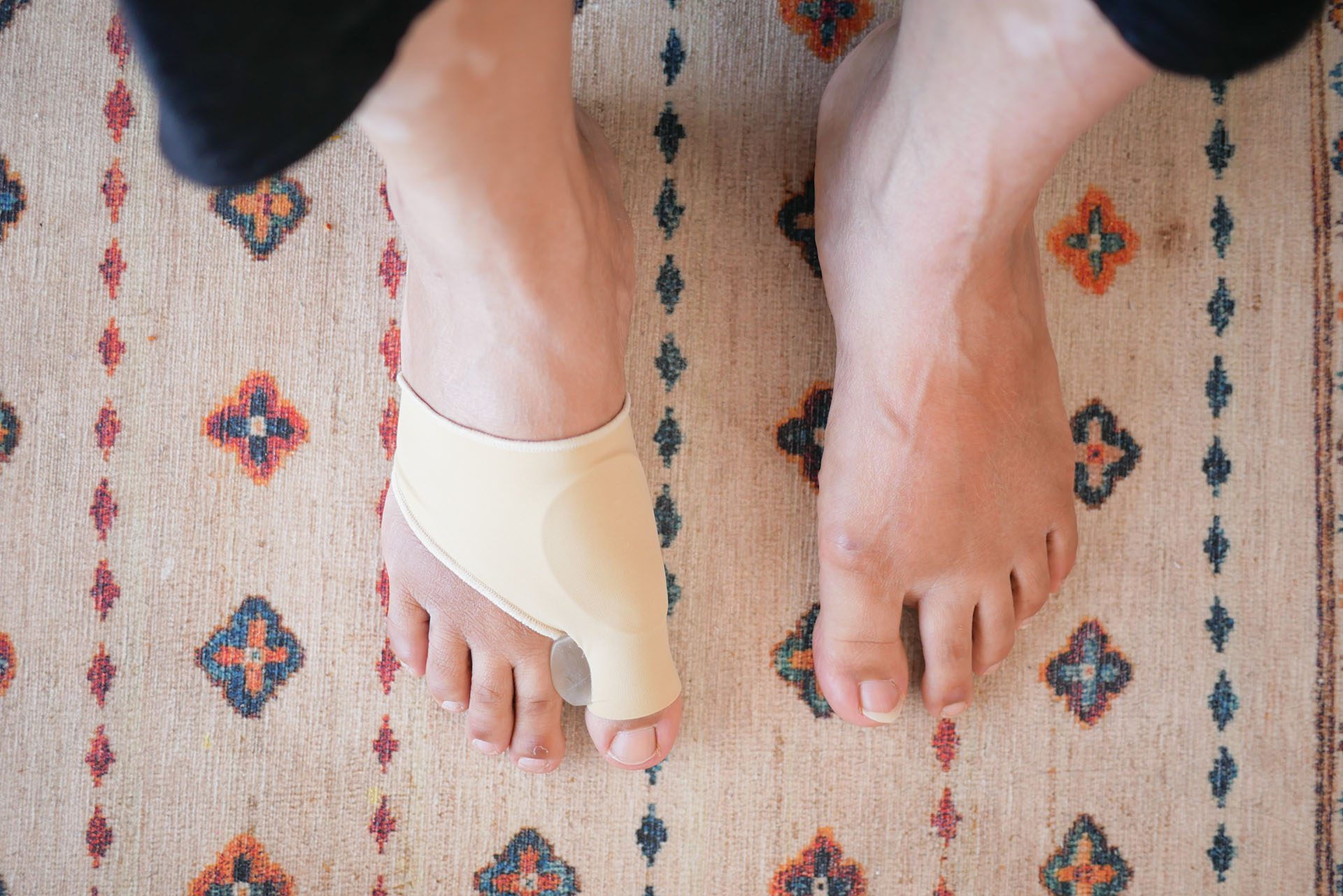
A bunion, which is also known as hallux valgus, is a bony bump that is frequently excruciating and located on the side of the big toe. A misalignment of the big toe is the most prevalent cause of bunions. Redness, edema, tenderness, and thickened skin around the big toe joint are early indications of bunions. Although it is impossible to halt the progression of a bunion, it is possible to alleviate its symptoms as it progresses. Pain management strategies and various treatment options are among the early indications of bunions. (MedlinePlus, 2024)
Visual Signs of Early Symptoms
Bunions initially develop slowly and do not cause significant discomfort right away. When a bunion first begins to form, you can notice the following symptoms around your metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, which joins the base of your big toe to the remainder of your foot. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
- Erythema
- Edema Hyperpigmentation
- Hyperkeratotic skin
- A bony protrusion exists
- Prominence where the hallux deviates towards the second digit or even beneath it
- Calluses and corns
Initial Somatic Indicators
Although bunions may not be immediately apparent, they can still cause discomfort in the early stages. The following are some of the initial physical indicators of a developing bunion: (MedlinePlus, 2024)
- Pain in the foot and big toe
- This discomfort is especially evident during ambulation or when donning constrictive, pointed footwear.
- Decreased movement of the big toe
- Tenderness
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Heat
Stages
Bunions are typically progressive, meaning they tend to deteriorate over time. Failure to implement preventive measures for your bunions may result in consequences. Subsequent symptoms often accompany advanced-stage bunions. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
- Persistent, intense pain in and around the metatarsophalangeal joint and the lateral and plantar aspects of the foot
- Bursitis results in the formation of a fluid-filled cyst near the base of the big toe.
- Hallux adducting and maybe overlapping the second toe
- Excessive osseous proliferation along the lateral aspect of the hallux
- Inability to accommodate your standard footwear
- Impediment in ambulation
- Hammertoe abnormalities occur when the second, third, or fourth toes exhibit an upward bend at the middle joint, like a hammer or claw.
- Hallux rigidus, a kind of arthritis affecting the big toe
Halt the Advancement
Once bunions have begun to form, they will become irreversible. Nevertheless, some methods exist to prevent their exacerbation or the onset of additional issues. These encompass (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022)
- Refraining from wearing improperly fitting footwear and elevated heels
- Utilizing orthopedic footwear and/or broad, comfy, soft-soled, and low-heeled shoes
- Inserting spacers between the toes to avert friction and irritation
- Applying over-the-counter (OTC) pads composed of felt, silicone, or foam to the bunion
- Extending your calf muscles to enhance joint alignment
Analgesic Administration
Ice packs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as Advil or Motrin (ibuprofen), may alleviate bunion discomfort. Research indicates that Botox injections into the forefoot muscles may offer analgesic benefits. (Hurn, S. E., et al., 2022)
Non-invasive Therapy in Initial Phases
If your bunions continue to deteriorate despite using the aforementioned self-care measures, you may need to seek intervention from a podiatrist or another healthcare professional. A healthcare professional may advise
Foot orthoses, commonly referred to as orthotics
- Orthoses, also known as foot orthoses, are specially designed implants that alleviate bunion-associated pain and prevent chafing.
Splints
- Bunion splints, commonly used at night, are orthotic devices designed to help realign the toes. (Aebischer, A. S., & Duff, S. 2020)
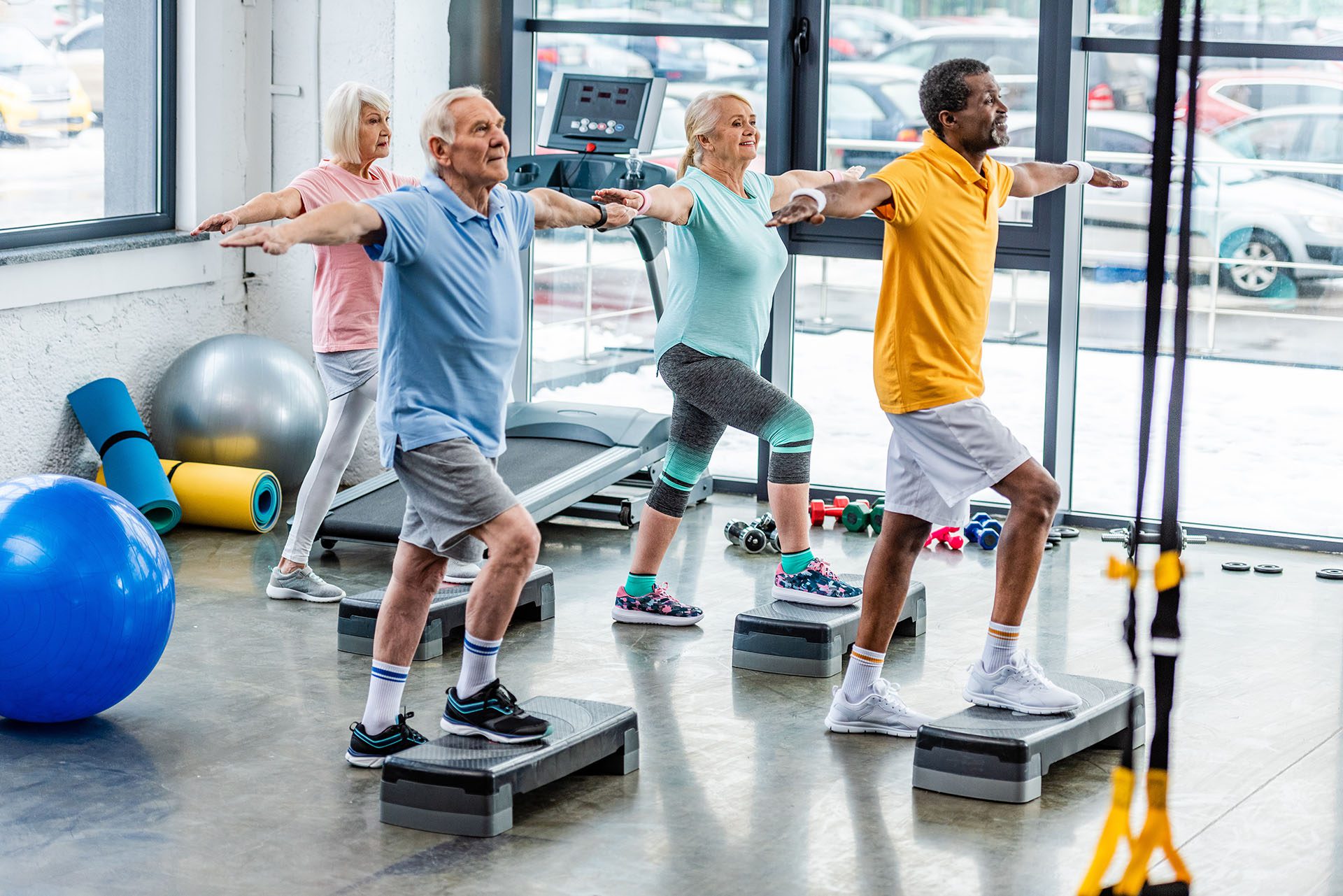
Physical Therapy
- A physical therapist can assist you by offering exercises to enhance the alignment of your feet and joints. They may further administer manual treatment to alleviate pain. (Hurn, S. E., et al., 2022)
Podiatrist
A podiatrist is a medical doctor (M.D.) specializing in the treatment of health issues affecting the foot, ankles, and lower legs. Request a referral to a podiatrist from your healthcare physician if you seek assistance in managing your bunion problems. (American Podiatric Medical Association, 2025)
Chiropractic Perspective
Chiropractors focus on biomechanical alignment and musculoskeletal health, viewing bunions as part of a broader kinetic chain dysfunction. Their approach emphasizes manual therapies and functional restoration.
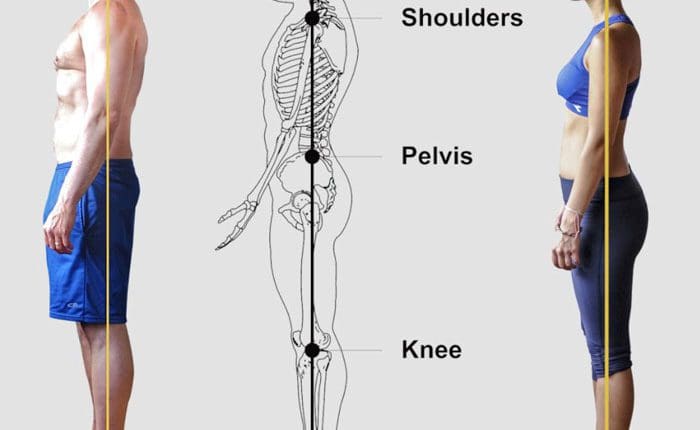
- Biomechanical Assessment:
- Evaluate foot, ankle, knee, hip, and spinal alignment to identify compensatory patterns contributing to bunion formation (e.g., overpronation, pelvic misalignment).
- Assess gait and foot mechanics to identify areas of abnormal stress on the big toe joint.
- Chiropractic Interventions:
- Adjustments: Perform gentle manipulations to the foot and ankle (e.g., metatarsal or tarsal adjustments) to improve joint mobility and reduce stress on the bunion. Spinal or pelvic adjustments may address upstream biomechanical issues.
- Soft Tissue Therapy: Utilize techniques such as myofascial release or instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization to reduce tension in the foot’s muscles and fascia, thereby improving circulation and flexibility.
- Taping: Apply kinesiology tape to support the big toe and reduce strain during movement.
- Corrective Exercises:
- Prescribe exercises to strengthen intrinsic foot muscles and improve toe alignment, such as:
- Toe spreading: Actively spread toes apart to strengthen the abductor hallucis.
- Arch strengthening: Perform short foot exercises to support the medial longitudinal arch.
- Calf stretches: Address tight Achilles tendons that contribute to foot strain.
- Recommend balance and proprioception exercises (e.g., standing on one leg) to improve overall foot stability.
- Prescribe exercises to strengthen intrinsic foot muscles and improve toe alignment, such as:
- Orthotic and Footwear Guidance:
- Fit patients with custom orthotics to correct overpronation or supination, which can exacerbate bunions.
- Advise on minimalist or wide-toe-box shoes to promote natural foot mechanics, aligning with chiropractic principles of functional movement.
- Holistic Approach:
- Address lifestyle factors, such as posture and ergonomics, that affect lower extremity alignment.
- Educate on anti-inflammatory diets (e.g., rich in omega-3 fatty acids, low in processed sugars) to help reduce joint inflammation.
Nurse Practitioner Perspective
NPs focus on holistic patient care, symptom management, and coordinating multidisciplinary treatment. Their approach to bunions focuses on pain relief, slowing the progression, and providing patient education.
- Assessment and Diagnosis:
- Conduct a thorough history and physical exam to evaluate bunion severity, pain level, and contributing factors (e.g., footwear, family history, arthritis).
- Order imaging (X-rays) if needed to assess joint alignment and rule out complications like osteoarthritis or bone spurs.
- Screen for systemic conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, gout) that may worsen bunions.
- Conservative Management:
- Footwear Education: Recommend wide-toe-box shoes with low heels to reduce pressure on the bunion. Avoid high heels and narrow shoes.
- Orthotics: Prescribe custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts to support the arch, redistribute pressure, and correct foot mechanics.
- Padding and Splinting: Suggest bunion pads or spacers to cushion the area and reduce friction. Night splints may help align the toe, though evidence for their effectiveness is mixed.
- Pain Relief: Advise over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) for pain and inflammation, ensuring proper dosing and monitoring for side effects. For severe cases, refer to a specialist for corticosteroid injections.
- Physical Therapy: Refer to a physical therapist for exercises to strengthen foot muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance gait. Examples include toe stretches, towel curls, and marble pickups.
- Patient Education:
- Educate on weight management to reduce stress on the feet.
- Discuss lifestyle changes, such as avoiding prolonged standing or high-impact activities that worsen symptoms.
- Highlight the progressive nature of bunions and the importance of early intervention.
- Referral and Coordination:
- Refer to a podiatrist or orthopedic surgeon if conservative measures fail or if the bunion causes significant pain, deformity, or functional impairment.
- Collaborate with chiropractors, physical therapists, or other specialists for a comprehensive care plan.
Both NPs and chiropractors emphasize:
- Early Intervention: Addressing bunions early can prevent the worsening of deformity.
- Footwear Modification: Wearing wide, supportive shoes is critical to reducing pressure.
- Exercise and Mobility: Strengthening and stretching exercises improve foot function.
- Pain Management: Non-invasive methods, such as padding, icing, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are the first-line approach.
- Referral for Surgery: If conservative measures prove ineffective, a specialist may be consulted for surgical options, such as bunionectomy, although this is typically considered a last resort.
Limitations and Considerations
- Evidence Gaps: While orthotics and exercises are widely recommended, studies on their efficacy for bunions are limited. Splints may not correct severe deformities.
- Individual Variation: Treatment must be tailored to the patient’s bunion severity, lifestyle, and comorbidities.
- Surgical Indications: Severe pain, joint damage, or inability to walk may necessitate surgical consultation, which neither NPs nor chiropractors are qualified to perform.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Dr. Jimenez, a nurse practitioner, integrates medical expertise with chiropractic care to address a wide range of conditions. The clinic provides individualized care programs that incorporate functional medicine, acupuncture, electroacupuncture, and sports medicine. The clinic addresses chronic pain syndromes and injuries by prioritizing strength, agility, and flexibility. Comprehensive care programs, combined with in-person and virtual health coaching, ensure personalized treatment and wellness outcomes for patients of all ages and abilities.
Enhance Your Performance with Functional Foot Orthotics
References
MedlinePlus (2024). Bunions. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). “Bunions.” OrthoInfo. from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/bunions/.
Hurn, S. E., Matthews, B. G., Munteanu, S. E., & Menz, H. B. (2022). Effectiveness of Nonsurgical Interventions for Hallux Valgus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis care & research, 74(10), 1676–1688. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24603
Aebischer, A. S., & Duff, S. (2020). Bunions: A review of management. Australian Journal of General Practice, 49(11), 720–723. https://doi.org/10.31128/AJGP-07-20-5541
American Podiatric Medical Association. (2025). “What is a podiatrist?” Advancing foot and ankle medicine and surgery. from https://www.apma.org/patients-and-the-public/what-is-a-podiatrist/.