Finger Pulley Anatomy: Understanding Your Fingers’ Structure
Finger pulley injuries are unique digital injuries distinct from sprains or dislocations. They occur specifically in rock climbers and occasionally in baseball pitchers. What are the symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments available?
Finger Pulley Injury
A finger pulley injury, common in activities like climbing, involves damage to the fibrous bands (pulleys) that hold tendons against bones. This causes pain, swelling, and potentially bowstringing of the tendons.
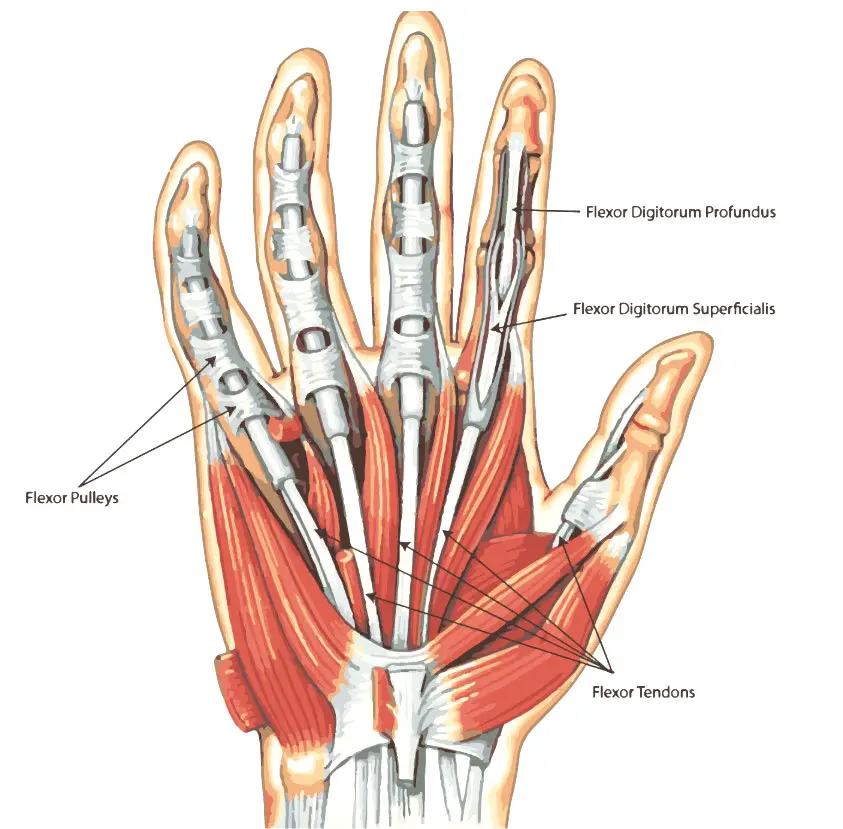
- Finger pulleys are structures that hold tendons against the bones of the fingers.
- Injury symptoms include pain, swelling, and a popping sound heard at the time of the injury.
- Finger pulley injuries, or ruptures of the digital pulley, are seen almost exclusively in rock climbers. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021)
This activity stresses the digits when maneuvering along uneven surfaces while supporting the entire body’s weight. The injuries result from the mechanics of the finger tendons and joints and the position the fingers hold while rock climbing. Rock climbing has grown in popularity. The only other sport in which this injury has been described is baseball, in pitchers. The forces acting on the finger are very different in these activities, but both place high stress on the finger pulleys.
 Digital Pulleys
Digital Pulleys
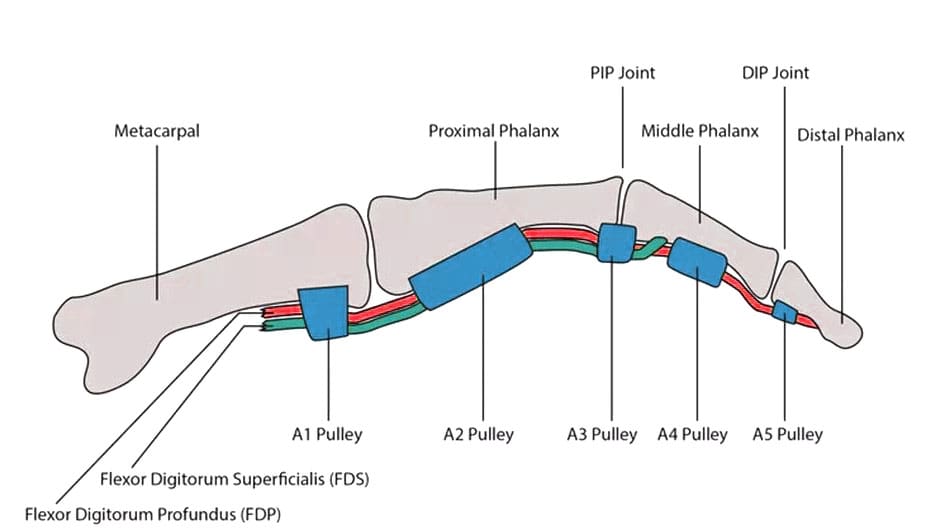
Everyone has structures in their fingers called digital pulleys. These pulleys hold the tendons against the bones of the fingers. Each finger has eight pulleys, but only two are considered critical to prevent the finger tendons’ bowstringing (when one pulley gives out or ruptures). This can result in various injury outcomes, from a simple strain of the pulley to ruptures of multiple pulleys in a single digit. Pain, stiffness, and an inability to fully flex the finger can occur. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) In severe situations, when the tendons are bowstringing, the tendon may lift away from the finger when making a fist.
Symptoms
Pain and Tenderness
- Localized pain and tenderness at the finger’s base, particularly when gripping or bending. Pain on the palm side of finger and tenderness with pressure
Swelling
- Swelling and bruising around the affected finger joint, especially on the palm side.
Popping Sound
- Some climbers report hearing a “pop” at the time of injury. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016)
Stiffness and Difficulty Bending
- Stiffness and pain when bending the fingers or difficulty gripping. Difficulty forming a fist
Bowstringing
- Visible displacement of the tendon from its normal position, causing a bulge at the finger’s base.
Most commonly, the middle or index digit is the injured finger. The two critical pulleys in the finger are designated the A2 and A4. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) Individuals may see swelling, redness, and inflammation at the base of the finger (A2) and/or in the space between the two finger joints closest to the tip of the finger (A4). In rock climbers, either or both of those pulleys may be injured. In baseball pitchers, the injury is typically isolated to the A4 pulley.
Causes
- Overuse and Repetitive Strain: Frequent or intense gripping or crimping, common in rock climbing and other activities, can cause pulley injuries.
- Dynamic or Sudden Movements: Desperate or dynamic moves or poor technique can lead to injury.
- Excessive Force: Pulleys can rupture when the force exerted on them is too great.
- Mechanism of injury: The A2 pulley is the most commonly injured, followed by the A4 pulley.
Diagnosis
Emergency treatment is generally unnecessary. However, it is important to have suspected digital pulley injuries examined by a specialist within several days to a week after the injury. The most important aspect of an evaluation is determining whether the injury has caused the bowstringing of the tendons. Imaging tests may be performed to help with the diagnosis and plan treatment. An ultrasound is recommended as the initial imaging technique. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021)
If an ultrasound is inconclusive, an MRI may be advised. Sometimes, an MRI is performed with the finger held straight and then bent to see if the tendons are bowstringing. An X-ray can also help exclude other causes of finger pain, including sprains and fractures.
Treatment
Conservative Care
- Immobilization, physical therapy, and pulley-protective measures, such as splints or taped fingers, are often used.
Surgery
- Surgery may be necessary for severe grade IV injuries where conservative care fails.
- Only in situations where there are multiple pulley ruptures or if there is delayed treatment should surgery be necessary.
Rehabilitation
- Focuses on regaining flexibility, strength, and grip function through exercises and physical therapy.
If the tendons do not bowstring, treatment usually protects the injured finger until swelling and pain subside. If there is bowstringing of the tendons, more careful management of the injury is needed. Individuals who suspect a pulley injury rest or splint the finger and use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as necessary for pain until they can get a medical evaluation. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) Physical therapy is recommended for most injuries, along with immobilization, the H-tape method, and a protective pulley splint. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021) Specialized splints and therapy techniques can allow the pulleys to heal properly.
Returning to activity varies significantly with the severity of the injury. With mild pulley strains, full activity can be resumed as soon as swelling and pain have subsided. Treatment for full ruptures being treated non-surgically is typically between one and three months. For individuals requiring surgical reconstruction of a pulley injury, restrictions may apply up to a year after the surgery.
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
To prevent complications, a healthcare provider should evaluate pulley injuries as soon as possible. Treatment most often consists of physical therapy, but surgery may be necessary. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Sports Injury Treatments
References
Miro, P. H., vanSonnenberg, E., Sabb, D. M., & Schöffl, V. (2021). Finger Flexor Pulley Injuries in Rock Climbers. Wilderness & environmental medicine, 32(2), 247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wem.2021.01.011
Carruthers, K. H., Skie, M., & Jain, M. (2016). Jam Injuries of the Finger: Diagnosis and Management of Injuries to the Interphalangeal Joints Across Multiple Sports and Levels of Experience. Sports Health, 8(5), 469–478. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738116658643


 Digital Pulleys
Digital Pulleys