Rheumatoid Arthritis Explained Simply Using Functional Wellness
Learn about functional wellness and how to adapt your lifestyle for better management and vitality from rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Joint Pain Through Chiropractic Care and Functional Wellness
It may feel like a trip full of pain, stiffness, and uncertainty if you have rheumatoid arthritis. Millions of Americans who have this chronic autoimmune disease are very worried about how to best manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Traditional medical treatment is important, but a new approach that combines functional wellness techniques with chiropractic adjustments offers new hope for managing pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring mobility.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis and How Does It Affect Your Body?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease that affects approximately 1% of the population worldwide, with women being affected three times more often than men (Smolen et al., 2016). Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear-and-tear damage to joints, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to persistent inflammation and progressive joint destruction (Gibofsky, 2014).
The Autoimmune Process Behind Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding what happens inside your body when you have RA helps explain why symptoms can be so challenging. The disease process begins when white blood cells, whose normal job is to protect against infections, instead invade the synovial membrane—the delicate lining surrounding your joints (Wasserman, 2011). This invasion triggers an inflammatory cascade that fundamentally alters the joint environment. When the immune system attacks the synovium, it causes the tissue to swell and become inflamed, a condition called synovitis. The inflamed synovial tissue then undergoes abnormal growth, forming layers of new cells rapidly. This abnormal tissue, called pannus, invades the joint space and secretes destructive proteins that break down cartilage, ligaments, and bone (Wasserman, 2011). The process is particularly damaging because the pannus tissue also produces excess fluid, contributing to the characteristic swelling and stiffness that people with RA experience. Research has revealed that multiple immune cells work together in this destructive process. Macrophages, which are a type of white blood cell, serve as master orchestrators of the inflammatory damage in RA. These cells produce large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (Jang et al., 2022). These inflammatory molecules not only damage local joint tissues but also circulate through the bloodstream, causing systemic effects.
The synovial fibroblasts, another type of cell in the joint lining, also contribute to tissue destruction by secreting additional cytokines and destructive enzymes, such as proteases and collagenases. Meanwhile, neutrophils—immune cells that accumulate in large numbers in the synovial fluid—release oxygen-derived free radicals that further damage the joint structures. Even the cartilage cells themselves, called chondrocytes, become activated by inflammatory signals and begin secreting enzymes that break down their own cartilage matrix (Jang et al., 2022). One of the hallmark features of RA is the activation of osteoclasts, specialized cells that break down bone tissue. Inflammatory cytokines drive the expression of RANK ligand, which signals osteoclasts to become more active. This leads to bone erosions—areas where bone has been eaten away—which can be seen on X-rays and are considered a defining characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (Jang et al., 2022).
embrace-your-balance-a-woman-s-guide-to-naturally-combatting-ra_6779b114.pdf
Common Symptoms and Risk Factors
RA symptoms typically develop gradually over weeks to months, though in some cases they can appear more suddenly. The most common early symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness that lasts for more than an hour in the morning. Unlike many other conditions, RA typically affects joints symmetrically, meaning that if your right wrist is affected, your left wrist is likely to be too (Smolen et al., 2016). Beyond joint symptoms, many people with RA experience systemic manifestations, including chronic fatigue, low-grade fever, weight loss, and general malaise. These whole-body symptoms reflect the fact that RA is not just a joint disease but rather a systemic condition affecting multiple organ systems. Some individuals develop firm bumps under the skin called rheumatoid nodules, particularly over pressure points like the elbows (Wasserman, 2011). The exact cause of RA remains unknown, but research has identified that both genetic and environmental factors contribute to disease development. Genetic susceptibility accounts for approximately 50-60% of the risk, with the strongest genetic risk factor being certain variants of the HLA-DRB1 gene, which contains a sequence called the shared epitope (Gibofsky, 2014). Environmental triggers also play a critical role in determining who develops RA. Smoking stands out as the strongest known environmental risk factor, with studies showing that tobacco use is specifically associated with an increased risk of developing antibody-positive RA. The risk increases with the amount and duration of cigarette use, and heavy smokers with more than 40 pack-years of smoking have approximately double the risk compared to never-smokers. Furthermore, the risk remains elevated even 20 years after smoking cessation (Environmental influences on risk for rheumatoid arthritis, 2005).
The interaction between smoking and genetic factors is particularly striking. Individuals who smoke and carry two copies of the shared epitope have a 21-fold higher risk of developing antibody-positive RA compared to nonsmokers without the shared epitope (Environmental influences on risk for rheumatoid arthritis, 2005). Research suggests that smoking may induce a process called citrullination in lung tissues, where proteins are chemically modified in ways that trigger the immune system to produce antibodies against them in genetically susceptible individuals. Other environmental factors associated with RA risk include birth weight, socioeconomic status, geographic location, occupation, and early-life exposures. Diet, hormonal factors, and the composition of the gut microbiome have also emerged as important modifiable factors that may influence disease development and progression (Environmental influences on risk for rheumatoid arthritis, 2005).
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Damages Joints in Upper and Lower Extremities
Understanding how RA affects different parts of the body helps patients and healthcare providers develop targeted treatment strategies. The disease has a particular affinity for certain joints, and the patterns of involvement can significantly impact function and quality of life.
Upper Extremity Joint Involvement
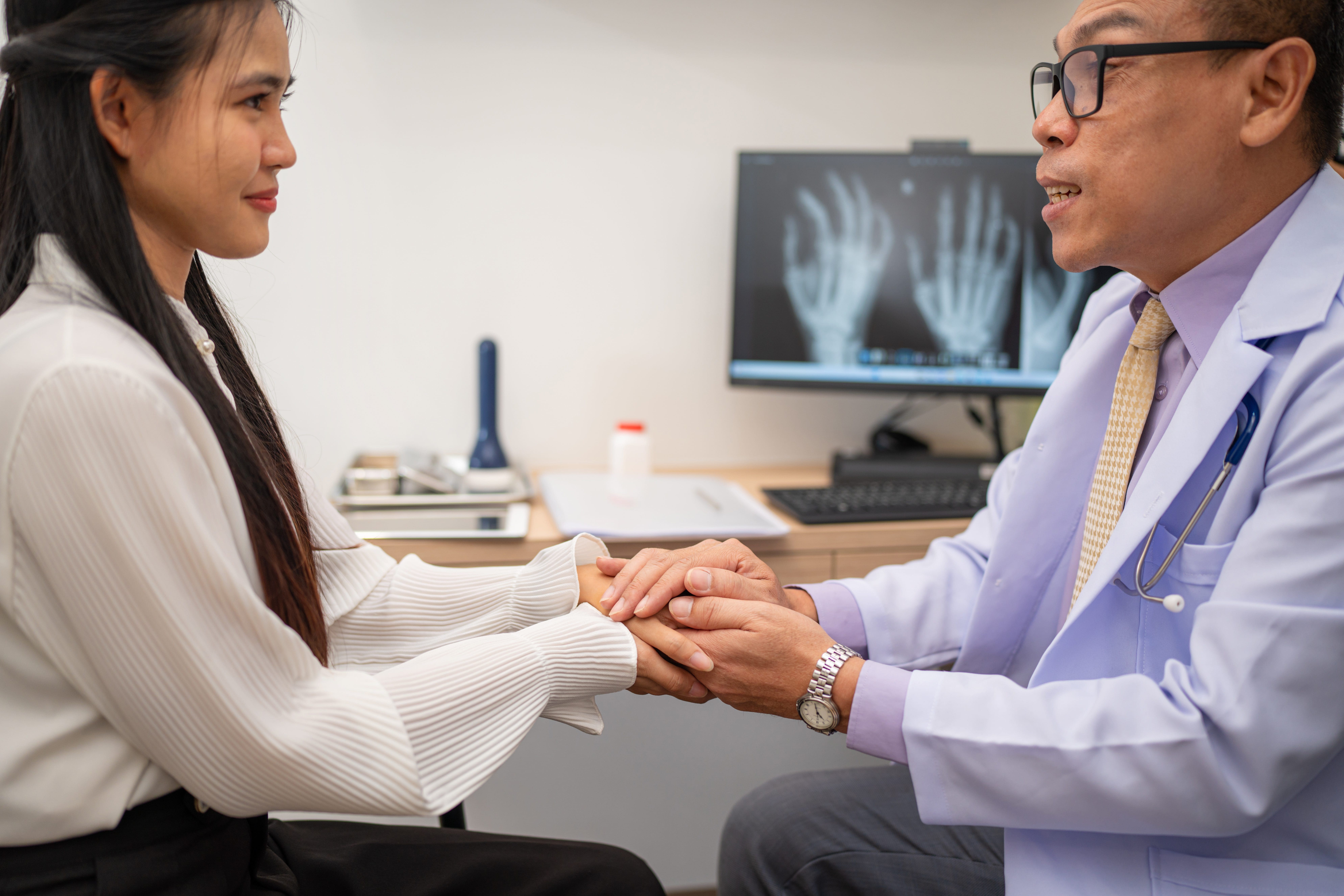
The hands and wrists are among the most commonly affected areas in RA, with approximately 90% of people with the condition experiencing symptoms in at least one hand joint over the course of their disease. For about 20% of patients, hand and wrist symptoms are actually the first signs of RA (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). The small joints of the hands are particularly vulnerable. The metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, located at the base of the fingers where they connect to the hand, and the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints in the middle of the fingers are frequently affected. The wrist joint, which is actually composed of multiple smaller joints working together, is also commonly involved early in the disease process (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). When RA affects the hands, the inflammatory process follows the same pattern described earlier, but with some unique consequences. The synovial tissue not only surrounds the joints but also encases the tendons that allow finger movement. When this tendon sheath becomes inflamed—a condition called tenosynovitis—it can damage or even rupture the tendons. One common manifestation is trigger finger, in which a finger becomes stuck in a bent position due to inflammation of the flexor tendon (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). As the disease progresses, the destruction of cartilage and bone, combined with weakened ligaments, leads to characteristic hand deformities. Swan neck deformity, where the finger bends backward at the PIP joint and forward at the tip, and boutonniere deformity, with the opposite pattern of bending, are classic findings in advanced RA. The MCP joints may also subluxate, meaning the bones partially slip out of proper alignment, often causing the fingers to drift toward the little finger side in a pattern called ulnar deviation (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
The wrist joint deserves special attention because inflammation here can compress the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel, causing carpal tunnel syndrome. This adds numbness, tingling, and weakness in the thumb and associated fingers to the already considerable burden of hand symptoms (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). Research has shown that hand dexterity, grip strength, and the ability to pinch objects between the thumb and fingers are likely to be affected by RA. Grip strength tends to be particularly weak when inflammation levels are high, and problems with hand function are largely the result of joint damage. This damage often occurs early in the disease process, which is why early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are so important (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
Lower Extremity Joint Involvement
More than 90% of people with RA develop foot and ankle symptoms over the course of their disease, and approximately 20% of patients have foot and ankle symptoms as their first manifestations of the condition. The feet and ankles contain numerous small joints that are particularly susceptible to the inflammatory process (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023). The ankle joint, which provides up-and-down motion of the foot, is commonly affected. Early signs of ankle involvement include difficulty walking on inclines, ramps, or stairs. As the disease progresses, even simple activities like walking on flat ground and standing can become painful. The ankle inflammation can be particularly debilitating because it affects weight-bearing activities that are essential for daily function (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023). The hindfoot, or heel region, performs the important function of allowing side-to-side motion of the foot. When RA affects this area, people initially notice difficulty walking on uneven surfaces, such as grass or gravel. Pain commonly develops just beneath the fibula bone on the outside of the ankle. As the disease advances, the alignment of the foot may shift as bones move out of their normal positions, often resulting in a flatfoot deformity. This misalignment causes pain along the posterior tibial tendon on the inside of the ankle, which is the main structure supporting the foot’s arch (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023).
The midfoot, or top of the foot, contains ligaments that normally support the arch. When these ligaments become weakened by inflammation, the arch collapses, and the front of the foot may point outward. RA also damages the cartilage in the midfoot, causing arthritic pain that occurs with or without shoes. Over time, structural changes can create large bony prominences on the arch, making it very difficult to find comfortable footwear (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023). The forefoot, which includes the toes and ball of the foot, commonly develops bunions, claw toes, and pain under the ball of the foot. In RA, these problems often occur together and tend to be more severe than when they occur in isolation. The big toe may cross over the second toe, and painful bumps can develop on the ball of the foot where bones in the midfoot are pushed down from joint dislocations in the toes. The toes may become fixed in a claw-like position and appear prominent on the top of the foot. In severe cases, ulcers can form from the abnormal pressure distribution (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023). The knees are also frequently affected by RA. Insufficiency fractures—fractures that occur in bones weakened by inflammation and osteoporosis—are a significant cause of new-onset knee pain in RA patients. Research shows that many of these fractures are only visible on MRI scans and often experience significant delays in diagnosis, resulting in long-term pain and disability. Studies indicate that more than 60% of patients with one insufficiency fracture will experience additional fracture episodes over subsequent years (Insufficiency fractures of the knee, ankle, and foot in rheumatoid arthritis, 2020).
The Broader Impact of Joint Damage
The cumulative effect of joint damage in both upper and lower extremities can be profound. Hand involvement affects the ability to perform self-care activities like dressing, grooming, and eating. It can impact professional activities, particularly for people whose jobs require fine motor skills or manual dexterity. The psychological impact of visible hand deformities should not be underestimated, as many patients report feelings of self-consciousness and social withdrawal (Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). Foot and ankle involvement directly affects mobility and independence. The ability to walk, stand for extended periods, and participate in physical activities may be severely compromised. This can lead to reduced physical activity, which, in turn, contributes to cardiovascular deconditioning, weight gain, and an increased risk of other health problems (Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle, 2023). The combination of upper and lower extremity involvement creates unique challenges. Simple activities that most people take for granted—like walking to the mailbox and opening the mail, preparing a meal, or getting dressed—may require significant effort and cause considerable pain. This functional limitation contributes to the high rates of disability observed in people with RA and underscores the importance of comprehensive treatment approaches that address both disease activity and functional capacity.
From Inflammation to Healing- Video
Environmental Factors and Overlapping Risk Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis Development
Understanding the environmental factors that contribute to RA is crucial for both prevention and management. While we cannot change our genetic makeup, many environmental exposures can be modified to reduce disease risk or improve outcomes.
The Gut-Joint Axis: How Gut Health Influences RA
One of the most exciting areas of recent RA research involves the gut microbiome—the trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms living in our digestive tract. Growing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbial community, plays a significant role in RA development and progression. Research in animal models has consistently demonstrated that gut dysbiosis is associated with the development of inflammatory arthritis. Germ-free mice, lacking gut bacteria, exhibit reduced arthritis symptoms in several spontaneous RA models. However, introducing certain bacteria into these germ-free mice can trigger the production of autoantibodies and the development of arthritis. Furthermore, changes in the intestinal microbial community occur in the pre-clinical phase before arthritis symptoms appear, suggesting that gut dysbiosis may actually help trigger the disease process (Gut-joint axis, 2023). Studies comparing the gut microbiota of RA patients with that of healthy individuals have found consistent differences. People with RA tend to have fewer beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which are important for gut health, while having higher levels of potentially harmful bacteria, such as Prevotella copri. A meta-analysis of multiple studies found that RA patients exhibit a depletion of anti-inflammatory butyrate-producing bacteria and an enrichment of pro-inflammatory bacteria (Gut-joint axis, 2023). The mechanisms by which gut dysbiosis contributes to RA are complex and multifaceted. Gut bacteria can influence the activation and differentiation of both innate and adaptive immune cells. Dysbiosis can also alter intestinal barrier function, leading to what is sometimes called “leaky gut,” where the protective intestinal lining becomes more permeable. This allows bacterial components and food proteins to enter the bloodstream, potentially triggering immune responses that contribute to autoimmunity (Your Gut Health and Its Connection to Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025). Some gut bacteria can produce metabolites that have immunomodulatory effects. For example, butyrate, which is produced by certain beneficial bacteria when they digest dietary fiber, has anti-inflammatory properties and helps maintain intestinal barrier function. The depletion of butyrate-producing bacteria in RA patients may therefore contribute to increased intestinal permeability and systemic inflammation (Gut-joint axis, 2023). Interestingly, intra-articular bleeding can trigger inflammatory responses similar to those seen in RA, with iron deposition in the synovium leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines. This suggests that mechanical trauma combined with the right immunological predisposition can contribute to chronic joint inflammation (Inflammatory diseases causing joint and bone destruction, 2024).
Other Environmental Triggers and Modifiable Risk Factors
Beyond the gut microbiome, numerous other environmental factors have been associated with RA risk and disease severity. Air pollution and exposure to particulate matter, tobacco smoke, and heavy metals have all been linked to increased risk of developing rheumatoid and other autoimmune diseases (Environmental factors and rheumatic diseases, 2025). Occupational exposures also matter. Jobs involving dust inhalation or exposure to certain chemicals may increase the risk of RA. Socioeconomic status and geographic location have been associated with disease development, though the mechanisms behind these associations are likely complex and multifactorial (What is the cause of rheumatoid arthritis?, 2019). Hormonal factors play a role, as evidenced by the higher prevalence of RA in women and the relationship between disease activity and reproductive events like pregnancy and menopause. Some research suggests that estrogen exposure may influence RA development and progression, though the relationship is complex and not yet fully understood (Osteoarthritis: The importance of hormonal status in midlife women, 2022). Body mass index (BMI) has emerged as another modifiable risk factor. Higher BMI is associated with increased RA risk and may influence disease severity and treatment response. The mechanisms likely involve both mechanical stress on joints and the pro-inflammatory effects of adipose tissue (Rheumatoid arthritis and the intestinal microbiome, 2024). Early life factors also appear to matter. Birthweight has been associated with RA risk, suggesting that developmental programming may influence later susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Breastfeeding duration and early childhood infections have also been studied as potential factors that may shape immune system development and influence later disease risk (Environmental influences on risk for rheumatoid arthritis, 2005). The concept of “overlapping risk profiles” refers to the clustering of multiple risk factors. For example, an individual might have genetic susceptibility, a history of smoking, gut dysbiosis, and vitamin D deficiency. Each of these factors independently increases RA risk, but their combined effect may exceed the sum of their individual effects. This is why a comprehensive, multifactorial approach to prevention and treatment is so important.
The Clinical Rationale for Chiropractic Care in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
For many years, chiropractic care was primarily associated with back and neck pain. However, mounting evidence suggests that chiropractic approaches can be valuable as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for people with RA. The clinical rationale for incorporating chiropractic care into RA management is based on several interconnected mechanisms.
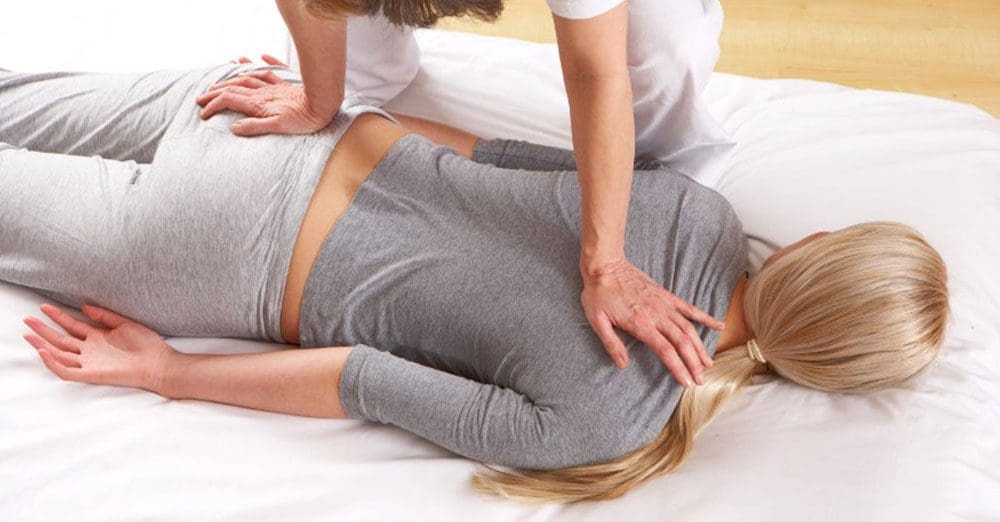
Restoring Joint Mobility and Reducing Mechanical Stress
One of the hallmark symptoms of RA is joint stiffness, which can make everyday activities incredibly challenging. Chiropractic adjustments and manual therapy techniques aim to restore proper joint alignment and improve mobility through gentle, targeted interventions. Manual therapy encompasses a variety of techniques, including joint mobilization, soft tissue manipulation, and specific adjustment procedures. When applied appropriately, these techniques can help reduce joint restrictions, improve range of motion, and alleviate stiffness (Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis And How Chiropractic Care May Help, 2025). A randomized clinical pilot study examined the effects of manual therapy—specifically postisometric relaxation and joint mobilization—on knee pain and function in patients with RA. The study found that patients receiving manual therapy experienced significant decreases in pain intensity compared to those receiving standard exercise alone. The techniques appeared safe when performed by trained practitioners who adapted their approach to each patient’s individual needs (Manual Therapy in Knee Pain and Function, 2020). Another study on hand joints found that low-grade mobilization of metacarpophalangeal joints appeared feasible, safe, and effective for RA patients. Despite most participants having minimal inflammatory activity at baseline, there were significant reductions in pain and increases in joint space over four weeks of treatment, with benefits persisting at one-month follow-up (Manual Therapy in Knee Pain and Function, 2020). The mechanisms by which manual therapy reduces pain and improves function are multifaceted. Gentle mobilization techniques can stimulate mechanoreceptors in joint tissues, potentially modulating pain signals traveling to the brain. Joint mobilization also appears to affect synovial fluid production, potentially improving joint lubrication and nutrition. Additionally, manual therapy can reduce muscle tension around affected joints, decreasing secondary pain and improving overall comfort (Understanding the Benefits of Manual Therapy for Arthritis, 2024). It is important to emphasize that chiropractors working with RA patients use techniques specifically tailored to the condition. High-velocity thrust adjustments that might be appropriate for mechanical back pain would generally not be suitable for actively inflamed or structurally compromised rheumatoid joints. Instead, practitioners employ low-force techniques, gentle mobilizations, and soft tissue approaches that respect the delicate nature of affected joints (Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis And How Chiropractic Care May Help, 2025).
Supporting Nervous System Function and Immune Regulation
The nervous system and immune system are intimately connected, and this relationship provides another rationale for chiropractic care in RA management. The spine houses the central nervous system, and proper spinal alignment is believed to support optimal neural communication throughout the body. Misalignments in the spine, called subluxations in chiropractic terminology, may disrupt nerve communication and potentially affect immune system function. By correcting these misalignments through targeted adjustments, chiropractors aim to optimize nervous system function, which may, in turn, support better immune regulation (Chiropractic Care for Autoimmune Disease Management, 2025). The vagus nerve, a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system, deserves special attention in this context. This nerve originates in the brainstem, travels through the upper cervical spine, and innervates numerous organs throughout the body. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation via the “cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.” When the vagus nerve is activated, it can dampen inflammatory responses throughout the body (Vagus nerve stimulation in musculoskeletal diseases, 2021). Research has shown that vagus nerve stimulation can reduce disease activity in RA patients. Several small pilot studies have demonstrated that both invasive and transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation are associated with significant decreases in RA disease activity. The treatment appears to work by dampening the inflammatory response of circulating immune cells and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Vagus nerve stimulation in musculoskeletal diseases, 2021). While chiropractic adjustments are different from electrical vagus nerve stimulation, some practitioners and researchers theorize that certain adjustments—particularly those involving the upper cervical spine—may influence vagus nerve function through mechanical and neurological mechanisms. Though this hypothesis requires more research, it provides a plausible explanation for some of the systemic benefits that RA patients report from chiropractic care. Chiropractic care may also help activate the parasympathetic nervous system more broadly, promoting a state of relaxation and “rest and digest” that counteracts the “fight or flight” stress response. Chronic activation of the stress response contributes to inflammation and can exacerbate RA symptoms. By helping patients achieve a more balanced autonomic state, chiropractic care may indirectly support better disease management (5 Ways Chiropractic Care Can Support Autoimmune Disease Management, 2025).
Comprehensive Approach: Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s Clinical Perspective
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, brings a unique dual perspective to RA management as both a board-certified chiropractor and a Family Practice Nurse Practitioner. His integrated approach at El Paso’s Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic combines advanced medical expertise with chiropractic care to address the complex needs of patients with chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Dr. Jimenez’s clinical approach emphasizes the importance of thorough diagnostic evaluation. He uses advanced imaging techniques and diagnostic assessments to fully understand each patient’s condition. This comprehensive evaluation enables him to create personalized treatment plans that address not only symptoms but also the underlying factors contributing to inflammation and dysfunction (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025). As a Certified Functional Medicine Practitioner (CFMP) and Institute for Functional Medicine Certified Practitioner (IFMCP), Dr. Jimenez employs detailed functional health assessments that evaluate personal history, current nutrition, activity behaviors, environmental exposures to toxic elements, psychological and emotional factors, and genetics. This holistic evaluation, inspired by the Living Matrix Functional Medicine Assessment, helps identify root causes of chronic disorders and enables truly personalized treatment (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025). His dual-scope practice allows him to integrate multiple therapeutic modalities. For RA patients, this might include chiropractic adjustments to improve joint mobility and relieve pain, functional medicine interventions to address gut health and nutritional status, acupuncture or electro-acupuncture to modulate pain and inflammation, and personalized wellness programs incorporating nutrition, exercise, and stress management strategies (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025). Dr. Jimenez emphasizes that his approach is collaborative and patient-centered. He works closely with rheumatologists, orthopedic specialists, and other medical providers to ensure coordinated care. If he believes another specialist would better serve a patient’s needs, he provides appropriate referrals, ensuring patients receive the highest standard of care (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025). His practice philosophy aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols and focuses on restoring health naturally whenever possible. For RA patients, this means using non-invasive protocols as a priority while recognizing that pharmaceutical interventions may be necessary. The goal is to help patients achieve optimal health through a combination of approaches tailored to their individual needs and circumstances (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025).
Functional Wellness Strategies to Combat Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
While chiropractic care addresses mechanical and neurological aspects of RA, functional wellness strategies target the underlying biochemical and lifestyle factors that influence disease activity. A truly comprehensive approach combines both elements.
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition: The Foundation of Functional Wellness
Diet plays a powerful role in modulating inflammation, and emerging evidence suggests that nutritional interventions can significantly improve outcomes for people with RA. The functional medicine approach to nutrition for RA is highly individualized, recognizing that different people may have different trigger foods and nutritional needs. The Mediterranean diet has received particular attention in RA research. This dietary pattern emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, olive oil, nuts, seeds, beans, and peas while limiting processed foods and red meat. Research shows that the Mediterranean diet can lower inflammation and improve RA symptoms. In one study, women with RA who followed a Mediterranean-type diet for 6 weeks experienced less joint pain and morning stiffness, as well as better overall health, compared to a control group (The Best and Worst Foods for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024). Omega-3 fatty acids, which are abundant in the Mediterranean diet, deserve special attention. These healthy fats, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts, have well-documented anti-inflammatory properties. They work by modifying the synthesis of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids, cytokines, and reactive oxygen species. Clinical studies have shown that omega-3 supplementation can decrease morning stiffness, reduce the number of tender joints, and lower the need for NSAIDs in RA patients (Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin D Improves Inflammatory Biomarkers, 2025). A meta-analysis found that consuming 2.7 grams of EPA/DHA daily for 3 months significantly decreased inflammatory markers, such as interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein, as well as overall disease activity. Higher dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids during the year preceding DMARD initiation has been associated with better treatment results in patients with early RA (Are dietary vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and folate associated with treatment response?, 2017). The autoimmune protocol (AIP) diet is a more restrictive anti-inflammatory approach that may be helpful for some RA patients. This diet eliminates potential inflammatory triggers, including grains, dairy, eggs, legumes, nightshade vegetables, coffee, alcohol, nuts, seeds, refined sugars, and processed oils. Instead, it focuses on freshly prepared, nutrient-dense foods, fermented foods, and bone broth to support gut health. After a period of strict elimination, foods are gradually reintroduced to identify individual dietary triggers (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
Specific foods and nutrients have been identified as particularly beneficial for RA:
- Colorful fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants and phytonutrients that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Berries, leafy greens like spinach and kale, and colorful vegetables like broccoli, beets, and carrots are particularly beneficial. These foods provide vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds that support immune function and reduce inflammation (Embracing an Anti-inflammatory Diet for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2009).
- Beans and legumes are rich in fiber, which can help lower C-reactive protein levels and support a healthy gut microbiome. They also provide plant-based protein to maintain muscle mass around joints. Red beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent choices (The Best and Worst Foods for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
- Herbs and spices offer concentrated anti-inflammatory compounds. Turmeric contains curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory properties when combined with black pepper (which contains piperine to enhance absorption). Ginger, which is related to turmeric, may have similar effects. Other beneficial spices include clove, coriander, garlic, and capsaicin from chili peppers (Rheumatoid Arthritis Diet, 2013).
- Healthy fats from sources like olive oil and avocados provide monounsaturated fats that can help reduce inflammation. Extra virgin olive oil also contains oleocanthal, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen (Embracing an Anti-inflammatory Diet for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2009).
On the flip side, certain foods may worsen inflammation and should be limited or avoided:
- Processed foods and refined sugars can spike blood sugar levels and trigger inflammatory responses. They also provide empty calories without the nutrients needed to support immune function (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Refined vegetable oils high in omega-6 linoleic acid, such as corn, safflower, sunflower, and cottonseed oils, can promote inflammation when consumed in excess relative to omega-3 fats (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Conventionally-raised red meat may contribute to inflammation, particularly when consumed in large amounts. Grass-fed options are preferable if red meat is consumed (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Potential food sensitivities vary by individual but commonly include gluten, dairy, eggs, and nightshade vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, white potatoes) for some people with RA. An elimination and reintroduction protocol can help identify personal trigger foods.
A functional medicine study examined the impact of a 12-week nutritional program on RA patients. The program focused on improving nutrition and digestive function, removing inflammatory triggers, and supporting gut health through diet modifications and targeted supplementation. Patients in the functional medicine group showed statistically significant improvements in pain, physical, and mental health scores compared with those receiving standard care alone (The impact of functional medicine on patient-reported outcomes, 2020).
Supporting Gut Health and the Microbiome
Given the strong evidence linking gut dysbiosis to RA, supporting gut health is a crucial component of functional wellness strategies. Several approaches can help restore a more balanced microbiome:
- Probiotic supplementation may help increase beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Some research suggests that specific probiotic strains can modulate immune responses and reduce systemic inflammation. However, the optimal strains, doses, and treatment duration are still being investigated (Rheumatoid arthritis and the intestinal microbiome, 2024).
- Prebiotic fiber feeds beneficial gut bacteria and supports their growth. High-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes provide the substrate that good bacteria need to produce beneficial metabolites, such as butyrate. Supplemental prebiotic fibers such as inulin, fructooligosaccharides, or partially hydrolyzed guar gum may also be helpful (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha contain live beneficial bacteria and may help diversify the gut microbiome. These traditional foods have been consumed for centuries in various cultures and are increasingly recognized for their health benefits (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Bone broth is rich in gelatin, collagen, and amino acids, such as glutamine, that support intestinal barrier function. While more research is needed, many functional medicine practitioners recommend bone broth as part of a gut-healing protocol (Integrative Approaches to the Testing and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2025).
- Reducing factors that harm the microbiome is equally important. This includes minimizing unnecessary antibiotic use, avoiding artificial sweeteners and emulsifiers that may negatively affect gut bacteria, managing stress, and limiting alcohol consumption.
The Critical Role of Vitamin D and Other Nutrients
Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in RA patients and has been linked to chronic pain and lower quality of life scores. Multiple studies have found associations between vitamin D status and RA disease activity, suggesting that optimizing vitamin D levels may be an important therapeutic strategy (Can Vitamin D Help Relieve Your Rheumatoid Arthritis?, 2018). Research has shown that vitamin D supplementation can improve disease activity scores and reduce inflammatory markers in RA patients. One randomized controlled trial found that 60,000 IU per week of vitamin D3 for eight weeks significantly improved Disease Activity Score-28 (DAS-28) scores and reduced levels of IL-17 and TNF-α compared to placebo. Higher dietary vitamin D intake during the year before starting DMARD treatment has been associated with better treatment outcomes (Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin D Improves Inflammatory Biomarkers, 2025). Vitamin D helps regulate immune function through multiple mechanisms. T cells and B cells have vitamin D receptors, indicating direct immunomodulatory effects. Vitamin D appears to help balance Th1 and Th17 immune responses, which are often overactive in RA, while supporting regulatory T cells that help maintain immune tolerance (Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin D Improves Inflammatory Biomarkers, 2025). For most adults, 1,000-2,000 IU daily of vitamin D3 is recommended for maintenance, though higher doses may be needed initially to correct deficiency. Blood testing of 25(OH)D levels can help guide appropriate dosing. Functional medicine practitioners typically aim for levels between 40 and 60 ng/mL, though optimal targets may vary by individual (Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin D Improves Inflammatory Biomarkers, 2025).
Other important nutrients for RA management include:
- Magnesium plays a role in numerous enzymatic reactions and may help with sleep quality and muscle relaxation. Many people with RA are deficient in magnesium, and supplementation may improve sleep quality (Improving Sleep Quality with Autoimmune Disease, 2025).
- Selenium is an antioxidant mineral that supports immune function and may help reduce oxidative stress in RA.
- Zinc is crucial for immune system function and wound healing. However, supplementation should be monitored as excessive zinc can interfere with copper absorption.
- B vitamins, particularly folate and B12, are important for patients taking methotrexate, as this medication can interfere with folate metabolism. Adequate folate intake may help reduce methotrexate side effects without compromising its effectiveness (Are dietary vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and folate associated with treatment response?, 2017).
Exercise and Physical Activity: Moving Despite the Pain
Regular physical activity is one of the most beneficial interventions for people with RA, yet pain and fatigue often create barriers to exercise. Research consistently shows that appropriate exercise helps relieve RA symptoms and improve day-to-day functioning without exacerbating disease activity (Best Exercises for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2023).
The benefits of exercise for RA patients are multifaceted. Physical activity helps reduce pain and stiffness, improve joint mobility and function, maintain or increase muscle strength, enhance cardiovascular fitness, support weight management, reduce fatigue, improve sleep quality, and boost mood and overall well-being (Role of physical activity in the management, 2017).
A comprehensive exercise program for RA should incorporate several components:
- Range-of-motion and flexibility exercises help maintain or improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. These should be performed daily and include gentle stretching of all major joints. During acute flares, when joints are actively inflamed, range-of-motion exercises should be gentle and pain-free. As inflammation subsides, more active stretching can be incorporated (Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2004).
- Strengthening exercises help maintain muscle mass and joint stability. Isometric exercises, where muscles contract without moving the joint, are particularly valuable during periods of active inflammation. These exercises can be performed at relatively low intensity (40% of maximum voluntary contraction) and held for 6 seconds, repeated 5-10 times daily. As disease activity improves, progressive resistance training with light weights or resistance bands can be added (Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2004).
- Aerobic conditioning improves cardiovascular health, increases muscle endurance, and helps manage fatigue. Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, cycling, water aerobics, and tai chi are excellent options. Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 30 minutes, five times per week, or intensive exercise for 20 minutes, three times per week, can provide significant benefits (Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
- Balance and coordination exercises help prevent falls and improve functional capacity. Activities like tai chi, gentle yoga, and standing on balance boards stimulate the sensorimotor system and enhance joint stability (Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
Important principles for exercising with RA include:
- Start slowly and progress gradually
- Listen to your body and respect pain signals
- Avoid exercise during acute flares of highly inflamed joints
- Include adequate rest periods
- Stop if pain persists for more than two hours after exercise or if you experience increased swelling, loss of strength, or excessive fatigue
- Work with a physical therapist to develop an individualized program
- Choose activities you enjoy to enhance long-term adherence
Recent research has shown an interesting bidirectional relationship between physical activity and disease activity. Changes in RA disease activity inversely correlate with variations in physical activity—when disease activity increases, physical activity tends to decrease, and vice versa. This suggests that monitoring physical activity levels may provide valuable information about disease status (Role of physical activity in the management, 2017).
Sleep Optimization: The Underestimated Healing Tool
Up to 70% of people with RA experience sleep problems, and poor sleep quality can significantly worsen disease symptoms. Sleep disturbances and RA create a vicious cycle: pain and inflammation disrupt sleep, and poor sleep increases pain sensitivity and inflammatory markers, which further exacerbate RA symptoms (Understanding the Relationship Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sleep, 2023). The relationship between sleep and inflammation is complex and bidirectional. During sleep, the body engages in critical repair and restoration processes. The immune system uses this time to produce and distribute certain immune cells and anti-inflammatory molecules. Sleep deprivation disrupts these processes, leading to increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreased production of anti-inflammatory mediators (The Importance of Sleep Hygiene, 2024). Research shows that acute sleep deprivation correlates with increased pain and arthritis symptoms the following day. Conversely, improved sleep quality is associated with reduced pain sensitivity, better pain management, lower inflammatory markers, improved immune regulation, enhanced mood and cognitive function, and increased energy levels (10 Tips to Improve Sleep with Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2023). Strategies to improve sleep quality in RA include:
- Pain management is fundamental. Working with your healthcare team to optimize pain control helps you sleep more restfully. Taking medications at appropriate times, using heat or cold therapy before bed, ensuring comfortable sleeping positions with supportive pillows, and practicing gentle stretching before bed may all help (Understanding the Relationship Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sleep, 2023).
- Establishing a consistent sleep routine helps regulate your body’s internal clock. Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. Create a relaxing pre-bedtime routine that might include reading, meditation, gentle stretching, or taking a warm bath (The Importance of Sleep Hygiene, 2024).
- Optimizing your sleep environment can make a significant difference. Keep your bedroom cool (around 65-68°F), dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains or an eye mask if needed. Consider a white noise machine if you’re sensitive to sounds. Invest in a supportive mattress and pillows that accommodate your specific needs (Improving Sleep Quality with Autoimmune Disease, 2025).
- Practicing good sleep hygiene means avoiding caffeine and alcohol in the evening, limiting screen time before bed (blue light from devices can suppress melatonin production), avoiding large meals close to bedtime, getting regular exercise but not too close to bedtime, and keeping the bedroom for sleep and intimacy only (The Importance of Sleep Hygiene, 2024).
- Managing stress and mental health is crucial, as anxiety and depression commonly accompany RA and can significantly disrupt sleep. Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, mindfulness meditation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can be very effective. Seeking support from a therapist or support group may also help (Understanding the Relationship Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sleep, 2023).
- Sleep aids and supplements may be appropriate for some individuals. Melatonin can help regulate sleep-wake cycles and may have additional anti-inflammatory properties. Magnesium supports muscle relaxation and sleep quality. Herbal teas like chamomile may promote relaxation. However, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, as some may interact with RA medications (Improving Sleep Quality with Autoimmune Disease, 2025).
Stress Management and Mind-Body Techniques
Chronic stress is both a contributing factor to RA development and a consequence of living with the disease. Stress triggers the release of cortisol and other hormones that can promote inflammation and suppress immune function. Additionally, stress can worsen pain perception, disrupt sleep, and negatively impact overall quality of life (5 Ways Chiropractic Care Can Support Autoimmune Disease Management, 2025).
Mind-body techniques offer powerful tools for managing stress and improving well-being:
- Mindfulness meditation involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. Research has shown that mindfulness practices can reduce pain, decrease stress and anxiety, improve sleep quality, enhance emotional regulation, and reduce inflammatory markers. Even brief daily sessions of 10-20 minutes can provide benefits (incorporating wellness practices, 2021).
- Deep breathing exercises activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and countering the stress response. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing (inhaling for 4 counts, holding for 4, exhaling for 4, holding for 4), or extended exhalation (inhaling for 4 counts, exhaling for 6-8 counts) can be practiced anywhere and provide immediate calming effects.
- Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups throughout the body. This technique helps increase body awareness, reduce muscle tension, and promote overall relaxation.
- Tai chi is a gentle movement practice combining flowing movements, deep breathing, and meditation. Multiple studies have found that tai chi can improve mood, quality of life, pain, and physical function in people with RA. When taught by a qualified instructor, tai chi is safe for most people with RA, though movements should be modified to avoid positions that cause pain (Rheumatoid arthritis – Diagnosis and treatment, 2025).
- Yoga offers another mind-body approach that may benefit people with RA. Gentle or restorative yoga practices can improve flexibility, strength, balance, and stress management. As with tai chi, it’s important to work with an instructor experienced in working with people who have chronic pain or arthritis.
- Biofeedback and neurofeedback are techniques that help people learn to control certain physiological processes through real-time feedback. These approaches can be helpful for pain management and stress reduction.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) addresses the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to pain and distress. CBT has been shown to help people with chronic pain develop better coping strategies, reduce pain-related disability, and improve quality of life.
Additional Non-Surgical Treatments and Practical Strategies for Symptom Relief
Beyond the foundational strategies of nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management, several additional approaches can help reduce RA symptoms and improve daily functioning.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to affected joints can provide significant relief:
- Heat therapy helps relax muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce stiffness. Warm baths, heating pads, warm paraffin wax treatments, and moist heat packs can all be beneficial. Heat is generally most helpful for chronic stiffness and before activity (Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2004).
- Cold therapy helps reduce inflammation, numb pain, and decrease swelling. Ice packs, cold compresses, or cool water immersion can be used for 15-20 minutes at a time. Cold is often most helpful during acute flares or after activity (Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2004).
Some people find contrast therapy—alternating between heat and cold—particularly helpful for reducing stiffness and improving circulation.
Assistive Devices and Joint Protection
Using appropriate assistive devices and practicing joint protection techniques can significantly reduce strain on affected joints and improve function:
- Ergonomic tools like jar openers, built-up handles on utensils, reachers, and button hooks make daily tasks easier without stressing joints.
- Braces and splints can provide support, reduce pain, and prevent deformity. Wrist splints, finger splints, knee braces, and ankle-foot orthoses may all be beneficial depending on which joints are affected.
- Proper footwear is crucial for people with foot involvement. Shoes should have good arch support, cushioning, and a wide toe box. Custom orthotics may be recommended by a podiatrist.
- Joint protection principles include using larger, stronger joints when possible, avoiding positions that push joints toward deformity, taking frequent breaks during activities, planning ahead to conserve energy, and using good body mechanics and posture.
Occupational and Physical Therapy
Working with occupational and physical therapists can provide tremendous benefits:
- Occupational therapists help with activities of daily living, recommend assistive devices, teach joint protection techniques, and provide hand therapy, including exercises and splinting.
- Physical therapists develop individualized exercise programs, provide manual therapy, teach proper body mechanics, and help with pain management strategies.
Both types of therapy have strong evidence supporting their use in RA management and should be considered part of comprehensive care (Rehabilitation Management for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, 2012).
Complementary Therapies
Several complementary therapies have shown promise for RA symptom management:
- Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body. Some studies suggest it can help reduce pain and improve joint function in RA, though more research is needed (Exploring Alternative Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
- Massage therapy can help alleviate pain, reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. Working with a licensed massage therapist experienced in treating people with RA is important (Exploring Alternative Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2024).
- Hydrotherapy or aquatic therapy takes advantage of the buoyancy and resistance of water. Warm water exercise can improve strength and range of motion while minimizing joint stress (Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2004).
Lifestyle Modifications
Small changes to daily habits can add up to significant improvements:
- Energy conservation involves pacing activities, planning ahead, prioritizing tasks, and taking regular rest breaks to manage fatigue.
- Stress reduction techniques should be incorporated into daily life, not just practiced during dedicated sessions. This might include brief breathing exercises throughout the day, listening to calming music, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies.
- Social connection is important for both emotional and physical health. Maintaining relationships, participating in support groups, and staying engaged with community can all support better outcomes.
- Avoiding smoking is crucial, as smoking not only increases RA risk but also reduces the effectiveness of treatments and increases disease severity. If you smoke, quitting is one of the most important steps you can take.
- Limiting alcohol is also advisable, as alcohol can interfere with RA medications and may exacerbate inflammation and gut dysbiosis.
Integrating Chiropractic Care with Functional Wellness: A Holistic Framework
The most effective approach to managing RA combines multiple strategies tailored to each individual’s unique needs, circumstances, and preferences. Dr. Jimenez’s integrated model exemplifies how chiropractic care and functional wellness can work together synergistically. In this model, chiropractic adjustments and manual therapy address the mechanical and neurological aspects of the condition—improving joint mobility, reducing mechanical stress, supporting nervous system function, and providing pain relief. Meanwhile, functional medicine interventions target the underlying biochemical and lifestyle factors—optimizing nutrition and gut health, correcting nutrient deficiencies, supporting detoxification pathways, and addressing environmental triggers (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025). This comprehensive approach recognizes that RA is a multifactorial disease requiring multifactorial solutions. No single intervention is likely to be sufficient on its own, but combining evidence-based therapies can yield meaningful improvements in symptoms, function, and quality of life. The functional medicine assessment process begins with an extensive evaluation. Practitioners take a detailed medical history from birth, explore dietary and lifestyle patterns, assess environmental exposures at home, work, and leisure, evaluate digestive health and gut symptoms, review stress levels and mental health, examine hormonal function, and analyze genetic predispositions when relevant (Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment – Melbourne Functional Medicine, 2025). With this comprehensive picture, a personalized treatment plan is developed that might include dietary modifications to remove triggers and emphasize anti-inflammatory foods, targeted nutritional supplements to address deficiencies and support immune function, gut health interventions including probiotics, prebiotics, and gut-healing nutrients, stress management and mind-body techniques, sleep optimization strategies, appropriate exercise programming, and environmental modifications to reduce toxic exposures (Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment – Melbourne Functional Medicine, 2025). Regular monitoring and adjustment of the treatment plan ensure that it continues to meet the patient’s evolving needs. This might involve periodic laboratory testing to assess inflammatory markers, nutrient status, and other relevant biomarkers, reassessment of symptoms and functional capacity, and modification of interventions based on response (Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment – Melbourne Functional Medicine, 2025). Throughout this process, communication and coordination with the patient’s rheumatologist and other healthcare providers are essential. The goal is not to replace conventional medical treatment but to complement it, potentially enhancing its effectiveness while addressing aspects of health that may not be the primary focus of standard rheumatology care.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Journey with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis is hard all the time, but knowing more about the disease and having access to a wide range of treatment options can make a big difference. Chiropractic care and functional wellness strategies together can help you better manage your symptoms, improve your function, and enhance your quality of life. The evidence examined in this article indicates that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not merely a joint disorder but a multifaceted systemic condition affected by genetic predispositions, environmental exposures, gastrointestinal health, nutritional status, stress levels, and lifestyle decisions. This comprehension facilitates a multitude of intervention opportunities beyond traditional pharmaceutical methods. Chiropractic care can safely improve joint mobility, reduce pain, support nervous system function, and help manage the mechanical aspects of RA when provided by practitioners who have experience with autoimmune conditions. Clinical studies have shown that manual therapy techniques that are specifically designed for people with RA can be helpful and should be a part of comprehensive care. Functional wellness strategies, such as anti-inflammatory nutrition, gut health support, targeted supplementation, appropriate exercise, sleep optimization, and stress management, address the fundamental factors that influence disease activity and symptoms. The new studies on the gut-joint axis, the roles of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, and the microbiome in autoimmune disease provide these treatments with a scientific basis. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s integrated approach shows how these different parts can work together to make a complete treatment plan. He is a chiropractor and a nurse practitioner, and he is also certified in functional medicine. This means he can provide care that covers both the structural and biochemical aspects of chronic inflammatory conditions. The message for patients is one of hope and strength. You have more control over your health than you might think, even though RA is a serious condition that needs ongoing medical care. The decisions you make about what you eat, how you move, how you handle stress, and how you support your body’s healing can have a big impact on how your disease progresses and how good your life is. To manage RA well, you need a full range of support from a healthcare team that includes your rheumatologist, a chiropractor who understands inflammatory conditions, and functional medicine practitioners. This team-based approach, along with your active participation in self-care strategies, gives you the best chance of getting the best results. It’s important to remember that dealing with RA is a journey, not a destination. It may take time to make progress, and there will probably be setbacks along the way. But many people with RA can lessen their symptoms, get better at doing things, and live full, meaningful lives with the right support, patience, and determination.
References
- Environmental influences on risk for rheumatoid arthritis. (2005). PMC – National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2898190/
- Gibofsky, A. (2014). Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A synopsis. American Journal of Managed Care, 20(7 Suppl), S128-S135.
- Gut-joint axis: Gut dysbiosis can contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis via multiple pathways. (2023). Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 13, 1092118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1092118
- Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis. (2024). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Hand_Rheumatoid_Arthritis
- Inflammatory diseases cause joint and bone destruction. (2024). PMC – National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11415468/
- Insufficiency fractures of the knee, ankle, and foot in rheumatoid arthritis. (2020). PMC – National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7431358/
- Jang, S., Kwon, E.-J., & Lee, J. J. (2022). Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathogenic roles of diverse immune cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020905
- Manual Therapy (Postisometric Relaxation and Joint Mobilization) in Knee Pain and Function Experienced by Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Clinical Pilot Study. (2020). PMC – National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7453239/
- Radu, A.-F., & Bungau, S. G. (2021). Management of rheumatoid arthritis: An overview. Cells, 10(11), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112857
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle. (2023). OrthoInfo – American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis-of-the-foot-and-ankle/
- Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., & McInnes, I. B. (2016). Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet, 388(10055), 2023-2038. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
- The impact of functional medicine on patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis. (2020). PMC – National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7544031/
- Vagus nerve stimulation in musculoskeletal diseases. (2021). Joint Bone Spine, 88(3), 105149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2021.105149
- Wasserman, A. M. (2011). Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. American Family Physician, 84(11), 1245-1252.
Important Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. The information presented here is based on current research and clinical perspectives, but rheumatoid arthritis is a serious medical condition that requires professional diagnosis and treatment.
Please note the following:
- Do not use this information to diagnose or treat any health condition. If you suspect you have rheumatoid arthritis or are experiencing joint pain, swelling, or other concerning symptoms, consult with a qualified healthcare provider, preferably a rheumatologist, for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
- Do not stop or modify prescribed medications without consulting your physician. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and other medications prescribed for RA are essential for controlling disease activity and preventing joint damage. The approaches discussed in this article are intended to complement, not replace, conventional medical treatment.
- Always inform your healthcare team about all treatments you are using, including chiropractic care, supplements, dietary changes, and other complementary therapies. This ensures coordinated care and helps prevent potential interactions or complications.
- Individual results may vary. The research and clinical experiences described in this article represent general findings that may not apply to every individual. Your response to any treatment approach will depend on numerous factors, including disease severity, presence of other medical conditions, medications, and individual characteristics.
- Chiropractic care and manual therapy should be performed only by licensed, trained professionals with experience treating patients with inflammatory arthritis. Not all techniques are appropriate for all patients, and adjustments must be carefully tailored to each individual’s condition.
- Some supplements and dietary approaches may interact with RA medications or may not be appropriate for individuals with certain medical conditions. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
This article was prepared with care based on available research and clinical expertise, but medical knowledge continues to evolve. The information provided should be considered in the context of your individual situation and in consultation with qualified healthcare professionals who can evaluate your specific needs and circumstances.
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911 or seek immediate medical attention. Do not rely on information from this or any online article in emergency situations.
Written with clinical insights from Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP, who specializes in integrative approaches to chronic pain and inflammatory conditions through chiropractic care and functional medicine at El Paso’s Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic.
For more information about Dr. Jimenez’s comprehensive approach to patient care, visit https://dralexjimenez.com/ or connect on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/