Cupping as Alternative Medicine for Pain Relief
For individuals experiencing musculoskeletal pain symptoms like lower back pain and shoulder pain, can incorporating cupping therapy help bring relief and manage pain?
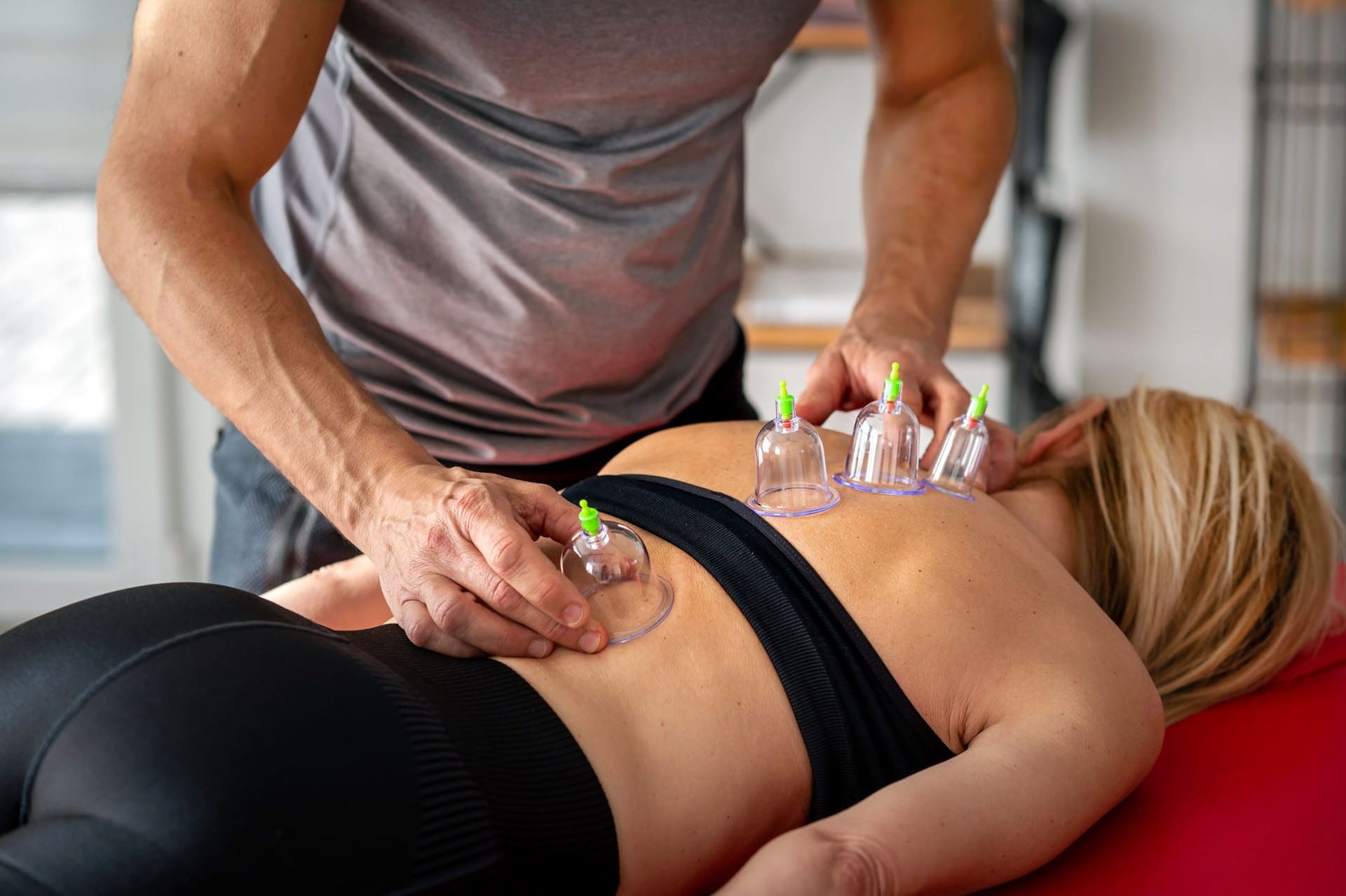
Cupping Therapy
This ancient treatment is gaining public acceptance, and awareness has heightened, with various individuals and athletes being seen with round marks on their shoulders and backs. It is a pain treatment that, like acupuncture, comes from traditional Chinese medicine, or TCM. The therapy involves placing glass, silicone, or bamboo cups on the skin to create suction. The treatment is an alternative medicine technique used to relieve musculoskeletal pain. The suction is believed to promote healing (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
Increasing Blood Circulation
- The suction draws blood to the area, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Releasing Muscle Tension
- The suction can stretch and pull on muscles, which can help relieve pain and tightness.
Breaking Up Adhesions
- The suction can help break up scar tissue and adhesions that can cause pain and restricted movement.
Detoxifying the Body
- Some practitioners believe that cupping can help remove toxins from the body.
It is typically performed by a trained practitioner who places the cups on the skin and leaves them in place for several minutes. The cups can be placed on various body areas, including the back, neck, shoulders, and legs. (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
Benefits
- Pain relief, especially for muscle and joint pain
- Reduced inflammation
- Improved circulation
- Increased range of motion
- Detoxification
Procedure
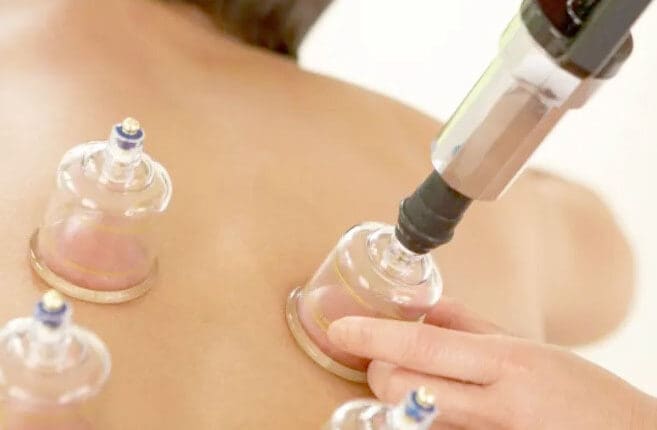
The medical practice involves creating skin suction using glass, ceramic, or plastic cups. How it’s done:
Preparation
- The practitioner cleans the area where the cups will be placed.
- They may apply oil or massage cream to the skin for easier movement of the cups.
Techniques
Dry
- The practitioner heats the inside of the cup with a flame or pump, creating a vacuum.
- The cup is then placed on the skin, which adheres due to the negative pressure.
- The cup remains on the skin for several minutes, allowing the suction to draw blood and tissue into the cup.
Wet
- Like the dry technique, the practitioner makes small incisions in the skin before applying the cup.
- This allows blood to flow into the cup, creating a more intense suction.
Aftercare
- The cups are removed, and the practitioner may apply pressure to the area to stop bleeding.
- The patient is advised to avoid strenuous activity and hot showers for a few hours after the treatment.
The benefits of therapy include opening pores, stimulating blood flow, filtration, and balancing energy flow through the body. It’s often combined with massage and acupuncture. (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
It also aims to alleviate symptoms of systematic diseases like diabetes and hypertension. However, more research is needed to see and fully analyze the effects of the treatment. (Aboushanab T. S., & AlSanad S. 2018)
Risks
The therapy is generally safe when done correctly and by a licensed professional. However, there is some risk of side effects like skin discoloration and scarring. Reports of rare side effects include bleeding inside the skull from cupping on the scalp and anemia from repeated wet techniques. (National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, 2018) Other side effects can include:
Bruising
- It can cause temporary bruising at the site of the cups.
Skin Irritation
- Some people may experience skin irritation or burns from the suction.
Infection
- There is a small risk of infection if the cups are not properly sterilized.
Who should avoid the therapy?
Those with skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis should avoid cupping, as it may worsen them. (National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, 2018)
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Beyond Medicine: The Power of Chiropractic Care
References
Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Cupping Therapy. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/16554-cupping
Aboushanab, T. S., & AlSanad, S. (2018). Cupping Therapy: An Overview from a Modern Medicine Perspective. Journal of acupuncture and meridian studies, 11(3), 83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jams.2018.02.001
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2018). Cupping. Retrieved from https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cupping