Bone Density Test and Its Importance for Health
What is a bone density test, how is it performed, and what do the results mean?
Bone Density Test
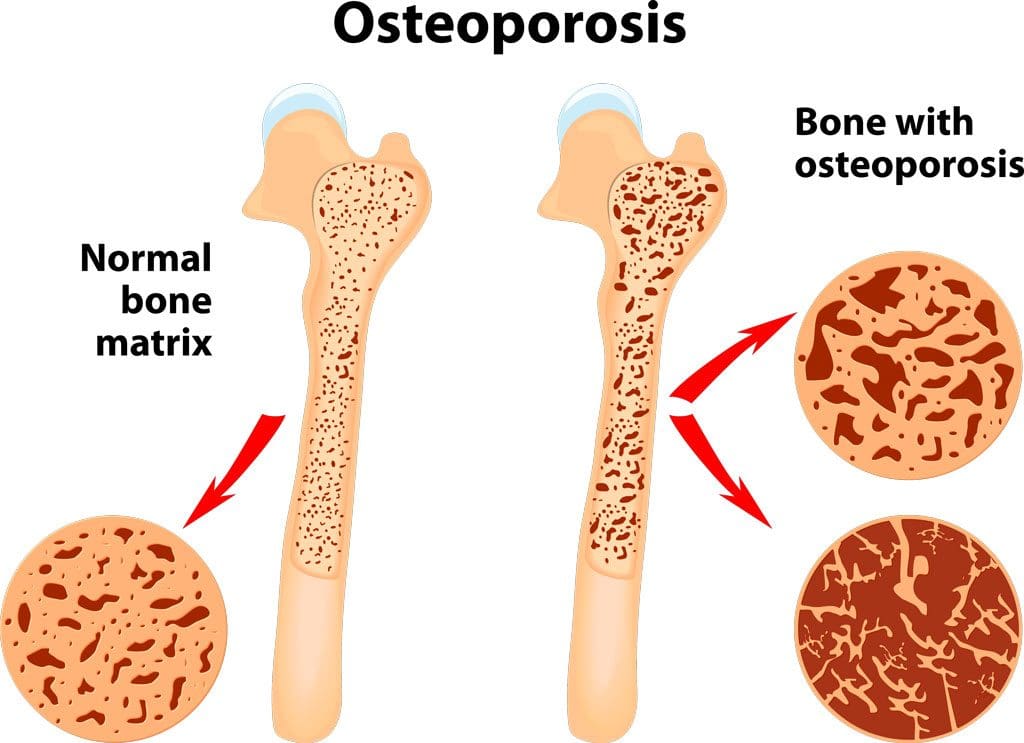
A bone density test examines bone mass, which indicates overall bone strength. Assessing bone density or mass is necessary for diagnosing osteopenia or osteoporosis, conditions that increase the risk of broken bones. The scan is performed through dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), which examines the thickness of the bones. Results from DEXA scans are compared to standardized values to determine whether bone density is lower than normal and whether osteopenia or osteoporosis is present.
Examination
The procedure examines bone density, or bone mass. The bones’ density, or mass, is an overall indicator of bone strength. The greater the bone density, the thicker and stronger the bones are. The test is used to diagnose osteoporosis, a condition characterized by brittle bones at risk of breaking due to significantly low bone density. A bone density test can also diagnose osteopenia, a condition characterized by lower than normal bone mass that can lead to osteoporosis. (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, 2025) It is recommended that all women aged 65 and older and all men aged 70 and older have a bone density scan to screen for bone loss to help prevent fractures. (Kling J. M., Clarke B. L., & Sandhu N. P. 2014)
- Bone density scans can establish a baseline level of bone density and track changes over time.
- For individuals with osteoporosis or osteopenia, a bone density scan can help track how well their bones respond to treatment.
Procedure
The most common bone density test is a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, or DEXA, scan. A DEXA scan is similar to getting an X-ray taken, but it uses two beams to produce a more detailed and sensitive reading. (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, 2025)
- During a DEXA scan, the patient will lie on their back on a table with their legs elevated on a padded platform.
- An X-ray scanner will pass over the spine and hips while another scans beneath.
- While the scan takes place, the patient will be asked to hold very still to obtain an accurate image.
- The scan will obtain bone density readings from the spine and hip, the two most commonly fractured bones, and generally takes less than 30 minutes.
Results
A DEXA scan measures bone density in grams per centimeter squared (g/cm²). This number indicates how densely bone cells are packed together in a specific area of bone. This bone density reading is then compared to a standardized value to determine if bone density is within a normal range or lower than average.
For postmenopausal women and men aged 50 and older, bone density values are given a T score. The T-scores are then compared to a standardized bone density level of a healthy 30-year-old adult with peak bone density levels. (Kling J. M., Clarke B. L., & Sandhu N. P. 2014) Scores indicate the following: (Kling J. M., Clarke B. L., & Sandhu N. P., 2014)
- Equal to minus 1.0 or above: Normal bone density
- Between minus 1.0 and minus 2.5: Low bone density (osteopenia)
- Equal to minus 2.5 or below: Osteoporosis
- Bone density values are reported as a Z score for women who have not undergone menopause and men under 50 years old.
- Z scores are compared to bone density levels of individuals of the same age and sex.
- A Z score of minus 2.0 or lower indicates low bone density, which can be caused by factors other than aging, such as medication side effects, nutritional deficiencies, or thyroid problems.
Arthritis Diagnosis
Because a DEXA scan only measures the thickness of bones, it doesn’t work to diagnose arthritis. An X-ray of the affected joint is currently the most accurate way to diagnose arthritis. The Kellgren-Lawrence classification system categorizes the extent of arthritis based on the severity of joint damage seen on an X-ray. According to this system, arthritis can be classified as: (Kohn M. D., Sassoon A. A., & Fernando N. D. 2016)
Grade 1 (minor)
- Minimal or no joint space narrowing, with possible bone spur formation.
Grade 2 (mild)
- Possible joint space narrowing, with definite bone spur formation.
Grade 3 (moderate)
- Definite joint space narrowing, moderate bone spur formation, mild sclerosis (abnormal thickening of bone), and possible deformation of bone ends.
Grade 4 (severe)
- Severe joint space narrowing, large bone spur formation, marked sclerosis, and definite deformation of bone ends.
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
Exercise can be incredibly beneficial for improving bone density, joint mobility, and the strength of surrounding muscles, which support and protect joints and bones. Talk to a healthcare provider to learn what interventions and available treatment options would be the most effective. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Osteoporosis
References
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (2025). Bone mineral density tests: what the numbers mean. Retrieved from https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/bone-mineral-density-tests-what-numbers-mean
Kling, J. M., Clarke, B. L., & Sandhu, N. P. (2014). Osteoporosis prevention, screening, and treatment: a review. Journal of women’s health (2002), 23(7), 563–572. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2013.4611
Kohn, M. D., Sassoon, A. A., & Fernando, N. D. (2016). Classifications in Brief: Kellgren-Lawrence Classification of Osteoarthritis. Clinical orthopaedics and related research, 474(8), 1886–1893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-4732-4

