Post Surgery Leg Strengthening Tips for Patients
What are some leg-strengthening exercises that will expedite recovery for athletes and physically active individuals who have undergone leg surgery?
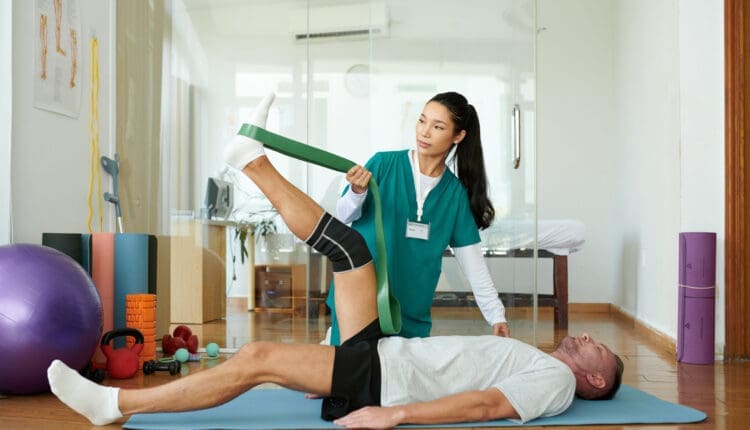

Post Surgery Leg Strengthening
Leg muscles may weaken after hip, knee, ankle, or foot surgery. This happens because those muscles are not used as much during recovery. Gaining back strength and muscle endurance after an injury or surgery is an important step in recovery. Leg exercises can help regain mobility and prevent complications like blood clots and pressure sores after surgery or an injury, which is why engaging in post-surgery leg strengthening is important once the doctor gives the ok.
Benefits
post-surgery leg strengthening exercises have several benefits, including
- Rebuilds strength and confidence
- Retraining for optimal mobility and flexibility
- Prevents pressure sores
- Prevents blood clots
When the leg muscles are contracted, they move blood like a pump, maintaining proper circulation. Moving in a bed after surgery also helps prevent pressure sores from forming and blood clots. A physical therapy team will determine the right leg exercises for each individual and their injury/condition. This is an important step when moving forward after surgery. (Hoogeboom T. J. et al., 2014)
Starting Out
The first exercises should target all the major muscles of the leg. (Madara K. C. et al., 2019)
Gluteal Sets
This isometric exercise means the muscles contract while no motion occurs at the hip joints. To perform:
- Lie on your back and tighten your buttock muscles.
- Hold the muscles tight for 5 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 10 or 15 times.
- Gluteal sets can be done several times per day.
Heel Slide
Heel slides can help regain strength in the major muscles of the leg. To perform:
- Lie on your back.
- Bend the knee of the surgical leg and slowly slide the heel toward your butt.
- Slide as far as possible and hold for 5 seconds.
- Slowly return to the starting position and repeat.
Short Arc Quad
The short arc quad, or SAQ, is a simple way to get the quadricep muscles working. To perform:
- Lie on your back with a towel roll, small ball, or something similar under the knee.
- Slowly straighten the knee.
- Tighten the quad muscle on the top of the thigh.
- Hold for 3 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Quad Set
This exercise helps get the quad muscles working. It also helps control the position of the kneecap. To perform:
- Lie on your back.
- Place a small towel roll under the knee.
- Try to press the back of the knee flat against the floor.
- Hold for 10 seconds and release.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Individuals can complete quad sets bilaterally or with both knees simultaneously. This makes the stronger leg help strengthen the weaker side.
Straight Leg Raise
To perform:
- Lie on your back.
- Lift your leg straight off the floor until it is at the height of the opposite bent knee.
- Hold for 10 seconds and slowly lower.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Be sure to keep the knee straight for the entire exercise. Keep the opposite knee bent for comfort. To ensure the knee is straight, individuals can complete a quad set first and then the straight leg raise. The exercise can be more challenging by increasing repetitions or adding a 2- to 3-pound ankle weight on the thigh. For even more challenge, add the ankle weight to the ankle.
Hamstring Strengthening
Working out the hamstrings after injury or surgery is important. The hamstring muscles bend the knee and extend the hip backward. To perform:
- Lie on your stomach.
- Bend one knee to raise the lower limb straight in the air.
- Hold for 5 seconds and lower slowly.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Once the exercise is easy to do, increase the repetitions to 30. Individuals can also try adding a 2- to 3-pound ankle weight.
Physical therapy can help individuals regain mobility after injury or surgery. A therapist may prescribe exercises as part of an at-home exercise program. Over time progress will go from simple exercises to more challenging ones to improve balance and mobility. (Madara K. C. et al., 2019)
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
Before starting this or any other exercise program, consult a doctor and a physical therapist to find the right exercises for your situation. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Are You Recovering From Ankle Sprains?
References
Hoogeboom, T. J., Dronkers, J. J., Hulzebos, E. H., & van Meeteren, N. L. (2014). Merits of exercise therapy before and after major surgery. Current opinion in anaesthesiology, 27(2), 161–166. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000062
Madara, K. C., Marmon, A., Aljehani, M., Hunter-Giordano, A., Zeni, J., Jr., & Raisis, L. (2019). PROGRESSIVE REHABILITATION AFTER TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: A PILOT AND FEASIBILITY STUDY. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 14(4), 564–581.