Key Prevention Strategies for Spinal Auto Injuries
Explore effective methods for spinal prevention, auto injuries and stay safe while navigating through traffic.
Buckle Up for Safety: Reducing Auto Injuries with Seatbelts and Expert Care in El Paso
Introduction
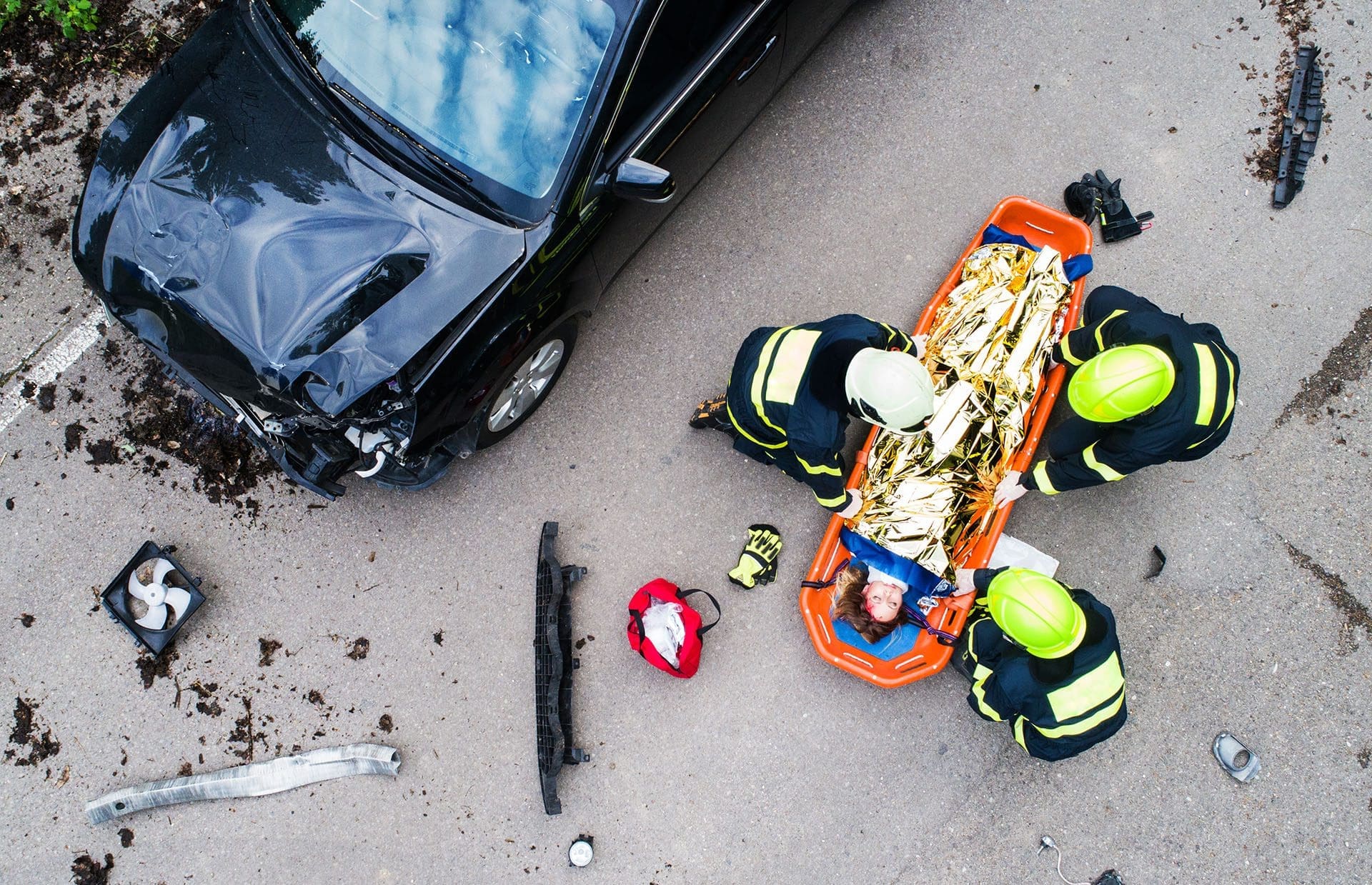
Motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) are a major cause of injuries worldwide, affecting millions each year. From minor bruises to severe neck pain, these crashes can change lives in an instant. One of the easiest ways to stay safe is by wearing a seatbelt, which research shows can cut the risk of serious injury or death by about half (CDC, 2025). In El Paso, Texas, where over 16,000 MVAs happened in 2022, seatbelts and expert medical care are key to recovery and prevention.
This blog post explores how seatbelts reduce auto injuries, especially those causing cervical (neck) pain, and why seeking care from professionals like Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a chiropractor with over 30 years of experience, is crucial. Dr. Jimenez not only treats injuries but also helps with personal injury claims, making him a trusted figure in El Paso. With a touch of humor inspired by Herman Munster, we’ll keep things engaging while diving into serious safety tips.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2025, January 30). Facts about seat belt use. https://www.cdc.gov/seat-belts/facts/index.html
Understanding Auto Injuries
Auto injuries from MVAs range from cuts and bruises to severe conditions like spinal fractures. Among the most common are neck injuries, especially whiplash, which happens when the head snaps back and forth during a crash, often in rear-end collisions (Mayo Clinic, 2024). Other neck injuries include:
- Strains and Sprains: Stretched or torn muscles and ligaments.
- Herniated Discs: Damaged cushions between spinal bones.
- Fractures: Broken neck bones, which are rare but serious.
Symptoms like pain, stiffness, headaches, or dizziness may not show up right away, sometimes taking days or weeks to appear (Alexander Orthopaedics, 2024). Without treatment, these injuries can lead to chronic pain or reduced mobility.
Why It Matters: Even minor crashes can cause hidden injuries. Seeking medical care immediately helps catch problems early and supports legal claims if someone else caused the accident.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2024, February 16). Whiplash – Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/whiplash/symptoms-causes/syc-20378921
- Alexander Orthopaedics. (2024, December 6). Common neck injuries from a car accident. https://alexanderorthopaedics.com/blog/common-neck-injuries-from-a-car-accident/
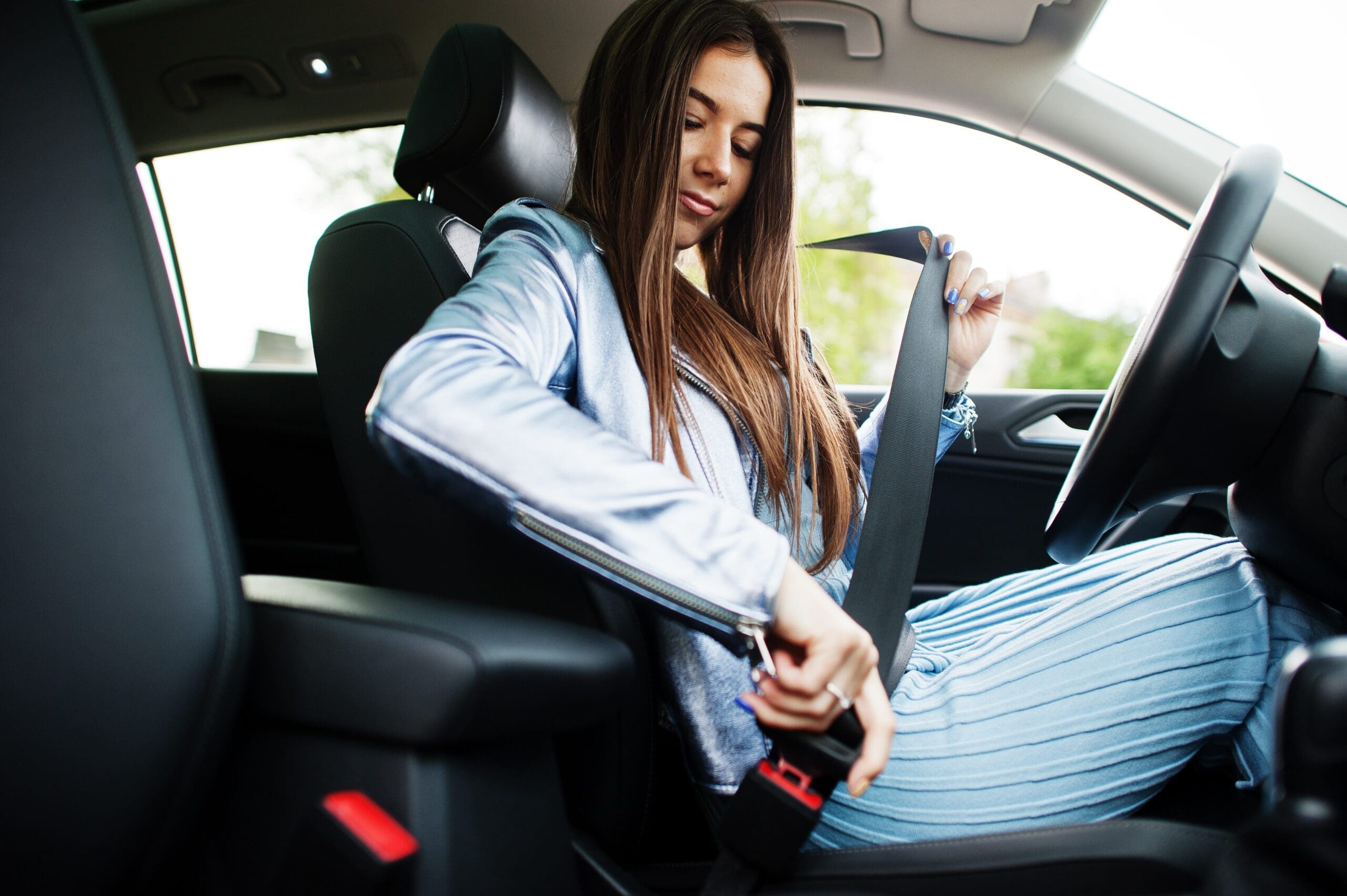
The Role of Seatbelts
Seatbelts are your car’s best safety feature, keeping you secure during a crash. They work by:
- Preventing Ejection: Only 1% of belted passengers are thrown from a car in a crash, compared to 75% of unbelted ones who die (The Zebra, 2023).
- Spreading Force: The belt distributes crash forces across strong body parts like the pelvis and chest.
- Slowing You Down: Seatbelts give you an extra second to stop, reducing impact with the dashboard or windshield (For the People, 2025).
The NHTSA estimates seatbelts saved 20,443 lives in 2019 and over 457,000 since 1968. In Texas, where seatbelt use is 91%, the “Click It or Ticket” campaign has saved over 6,000 lives since 2002 (TxDOT, 2021).
Herman Munster Moment: Imagine Herman Munster, the big guy from The Munsters, forgetting his seatbelt. Even he’d go flying without one! For us, buckling up is like having a superhero shield.
Myths Busted:
- Myth: Seatbelts trap you in a fire or water crash. Fact: These crashes are rare (0.5% of all crashes), and seatbelts keep you conscious to escape (NHTSA).
- Myth: Short trips don’t need seatbelts. Fact: Most fatal crashes happen within 25 miles of home at low speeds.
References
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. (n.d.). Seat belt safety: Buckle up America. https://www.nhtsa.gov/vehicle-safety/seat-belts
- The Zebra. (2023, January 30). Seat belt statistics in 2025. https://www.thezebra.com/resources/research/seat-belt-statistics/
- For the People. (2025, January 22). The role of seat belts in preventing serious injuries: Expert insights. https://www.forthepeople.com/blog/role-seat-belts-preventing-serious-injuries-expert-insights/
- Thompson Law. (2021, May 24). Texas seat belt law. https://1800lionlaw.com/texas-seat-belt-law/
Clinical Rationale for Seatbelt Use
Seatbelts protect you by managing the physics of a crash. When a car stops suddenly, your body keeps moving forward. Without a seatbelt, you could hit the steering wheel or be ejected, causing severe injuries. Seatbelts slow this motion, spreading the force across your body’s stronger parts (Cooney & Conway, 2021).
A 2018 study found seatbelts reduce the risk of major injuries by 53%, especially facial, abdominal, and spinal injuries (BMC Public Health, 2018). However, they may not significantly reduce neck injuries like whiplash, as the head can still move freely while the body is restrained (Kaizo Health, 2022).
Injury Types Reduced by Seatbelts:
| Injury Type | Risk Reduction | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Facial | 44% | Prevents hitting windshield |
| Abdominal | 13% | Protects internal organs |
| Spinal | 44% | Reduces fractures in some areas |
Limitations: Seatbelts can cause minor injuries like bruised ribs or, in rare cases, contribute to whiplash by holding the torso while the head moves. Proper headrests help reduce this risk (Consumer Reports, 2021).
References
- Cooney & Conway. (2021, August 9). How seat belts may help prevent fatalities. https://www.cooneyconway.com/blog/how-seat-belts-prevent-fatalities/
- BMC Public Health. (2018, December 28). Seatbelt use and risk of major injuries sustained by vehicle occupants during motor-vehicle crashes. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-018-6280-1
- Kaizo Health. (2022, January 17). What is whiplash? How seat belt injuries can affect the neck and spine. https://www.kaizo-health.com/what-is-whiplash-how-seat-belt-injuries-can-affect-the-neck-and-spine/
- Consumer Reports. (2021, September 20). Protection against whiplash injuries. https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/2012/12/how-to-save-your-neck-in-a-rear-end-crash/index.htm
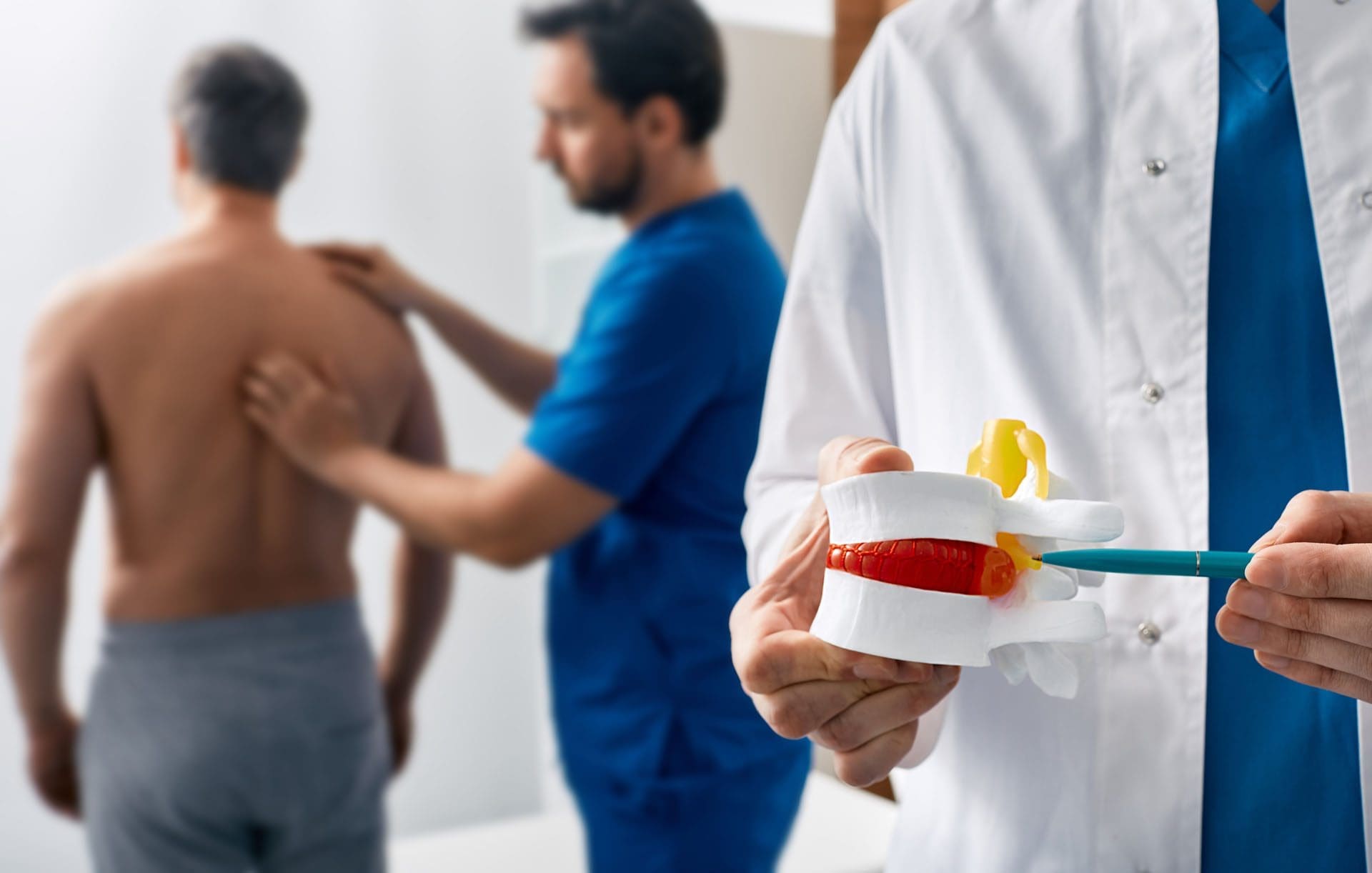
Cervical Pain from Auto Injuries
Cervical pain, or neck pain, is a hallmark of MVA injuries, often from whiplash. The cervical spine, made of seven vertebrae, supports your head and is vulnerable during crashes. Rapid neck movement can strain muscles, ligaments, or discs, causing pain (Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2024).
Symptoms:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Headaches, often at the base of the skull
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Numbness or tingling in arms
Complications: Untreated whiplash can lead to chronic pain or nerve damage. Over 80,000 neck injuries from car crashes are reported yearly in the U.S., many untreated (Integrity Spine & Orthopedics, 2024).
Why Seek Care: Symptoms may be delayed due to adrenaline masking pain. Early diagnosis with X-rays or MRIs can prevent long-term issues (Stridewell, 2023).
References
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2024, March 10). Whiplash injury. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/whiplash-injury
- Integrity Spine & Orthopedics. (2024, August 11). What neck injuries do car accidents cause? https://www.integrityspineortho.com/post/what-neck-injuries-do-car-accidents-cause/
- Stridewell. (2023, August 23). Delayed neck pain after a car accident. https://stridewell.com/managing-pain/delayed-neck-pain-after-a-car-accident/
The Road To Recovery- Video
Prevention Strategies
Wearing a seatbelt is the top way to prevent auto injuries. Texas law requires all passengers to buckle up, with fines up to $200 for violations (TxDOT). Other strategies include:
- Proper Headrest Adjustment: Position the headrest so it touches the back of your head to reduce whiplash risk (Driving.ca, 2018).
- Safe Driving: Avoid distractions and follow speed limits.
- Vehicle Safety Features: Airbags and anti-lock brakes add protection (ChiroSport Specialists, 2017).
Herman’s Tip: If Herman Munster can remember to buckle up in his creaky old car, so can you! It’s a small step for big safety.
References
- Texas Department of Transportation. (n.d.). Click it or ticket. https://www.txdot.gov/safety/traffic-safety-campaigns/click-it-or-ticket.html
- Driving.ca. (2018, November 21). How it works: Preventing whiplash. https://driving.ca/auto-news/news/how-it-works-preventing-whiplash
- ChiroSport Specialists of Dallas. (2017, February 1). A 3-step safety check to avoid whiplash. https://www.chirosportspecialists.com/news/3-step-safety-check-whiplash/
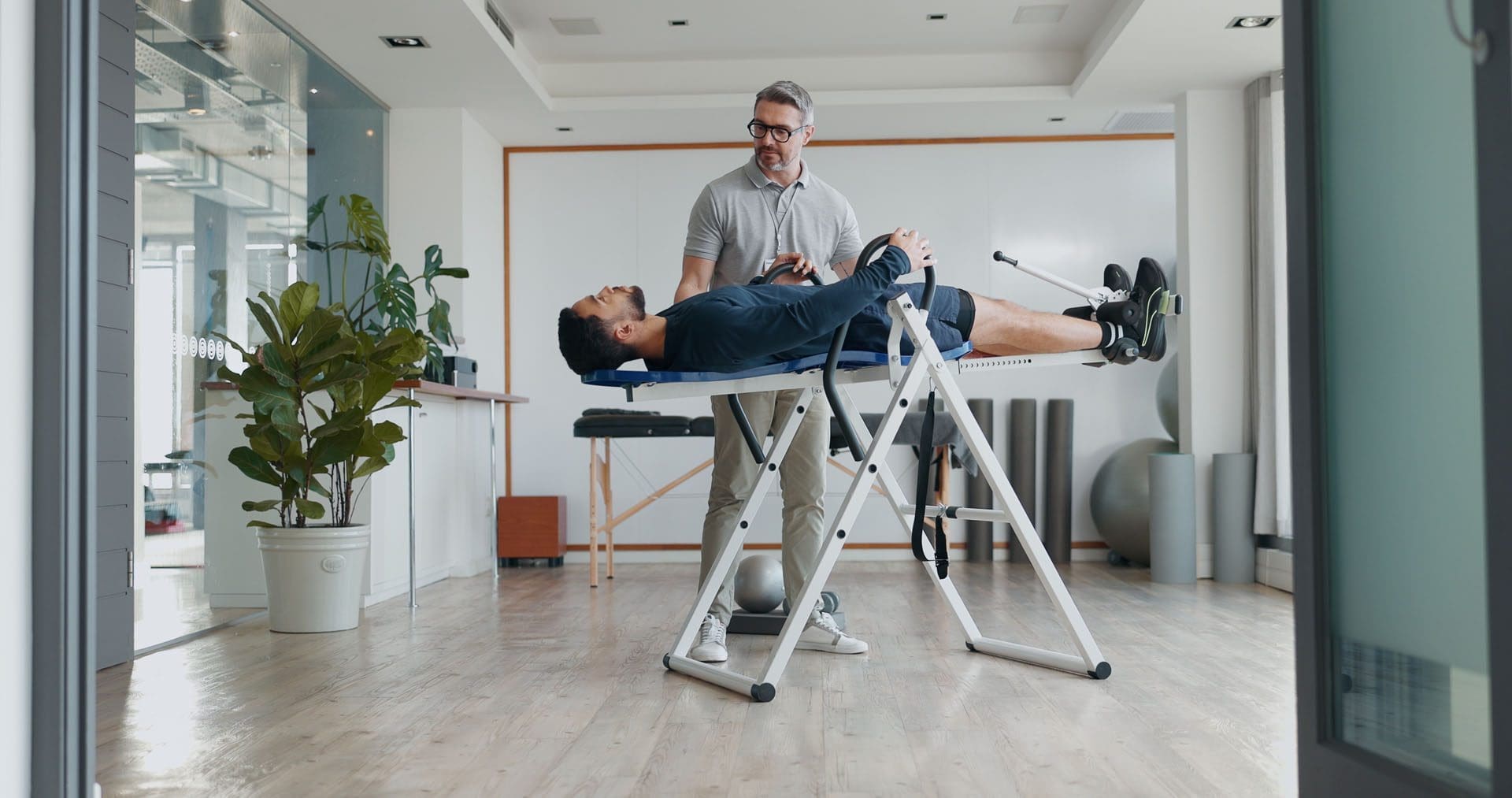
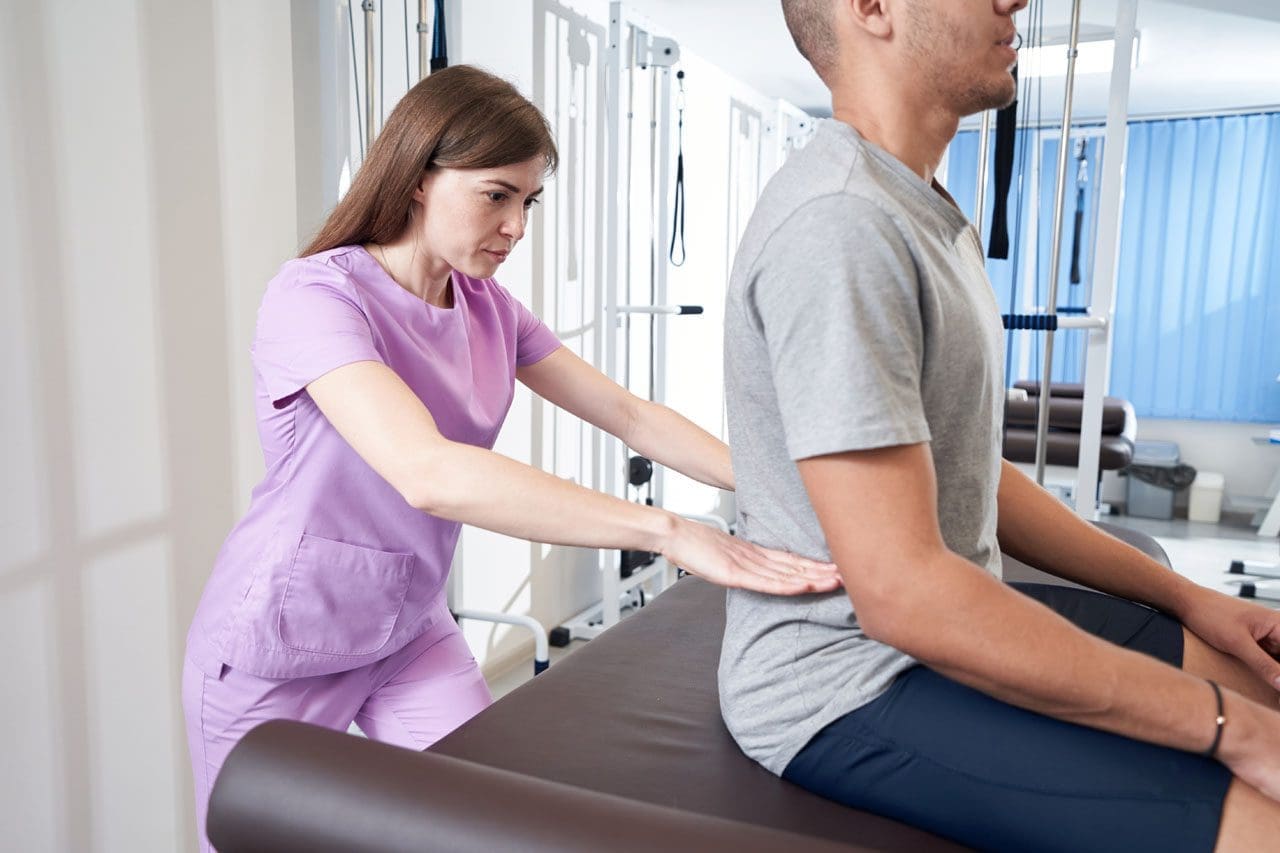
Chiropractic Care for Auto Injury Recovery
Chiropractic care is a non-invasive way to treat auto injuries, focusing on the spine and muscles. Dr. Alexander Jimenez, based in El Paso, uses techniques like:
- Spinal Manipulation: Realigns the spine to reduce pain.
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Strengthens injured areas.
- Therapy Modalities: Uses ultrasound or ice to reduce inflammation.
For whiplash, Dr. Jimenez may use gentle stretching or muscle stimulation to ease neck pain. He also orders X-rays or MRIs to diagnose injuries accurately, ensuring tailored treatment plans (Dr. Alex Jimenez).
Benefits:
- Pain relief without surgery
- Faster recovery
- Improved mobility
References
- Dr. Alex Jimenez. (n.d.). Personal injury doctor. https://www.dralexjimenez.com/personal-injury-doctor/
Personal Injury Cases in El Paso
After an MVA, personal injury claims help victims cover medical bills, lost wages, and pain. In El Paso, with 16,232 crashes in 2022, these cases are common (Thompson Law, 2021). Texas follows a “fault” system, meaning the at-fault driver’s insurance pays for damages (Nix Patterson, LLP).
Dr. Jimenez plays a vital role by:
- Documenting Injuries: Provides detailed medical reports.
- Using Advanced Diagnostics: Orders imaging to confirm injuries.
- Liaising with Attorneys: Works with lawyers to support claims, sometimes testifying in court.
Why Act Fast: Immediate medical care strengthens your claim and health. Delays can weaken legal cases or worsen injuries (Cesar Ornelas Injury Law, 2022).
References
- Thompson Law. (2021, November 17). El Paso car accident lawyers. https://1800lionlaw.com/el-paso-car-accident-lawyer/
- Nix Patterson, LLP. (n.d.). El Paso personal injury lawyers. https://nixlaw.com/el-paso/personal-injury-lawyers/
- Cesar Ornelas Injury Law. (2022, November 26). El Paso personal injury lawyer. https://cesarornelaslaw.com/el-paso-personal-injury-lawyer/
Conclusion
Motor vehicle accidents can cause serious injuries, but seatbelts significantly reduce the risk, saving thousands of lives yearly. Cervical pain from whiplash is common, but early care from experts like Dr. Alexander Jimenez in El Paso can make a difference. His chiropractic treatments and legal support help victims recover physically and financially. Always buckle up, seek medical care after a crash, and consult a lawyer for personal injury claims.
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical or legal advice. Consult a qualified healthcare provider or attorney for personalized guidance.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2025, January 30). Facts about seat belt use. https://www.cdc.gov/seat-belts/facts/index.html
- Mayo Clinic. (2024, February 16). Whiplash – Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/whiplash/symptoms-causes/syc-20378921
- Alexander Orthopaedics. (2024, December 6). Common neck injuries from a car accident. https://alexanderorthopaedics.com/blog/common-neck-injuries-from-a-car-accident/
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. (n.d.). Seat belt safety: Buckle up America. https://www.nhtsa.gov/vehicle-safety/seat-belts
- The Zebra. (2023, January 30). Seat belt statistics in 2025. https://www.thezebra.com/resources/research/seat-belt-statistics/
- For the People. (2025, January 22). The role of seat belts in preventing serious injuries: Expert insights. https://www.forthepeople.com/blog/role-seat-belts-preventing-serious-injuries-expert-insights/
- Thompson Law. (2021, May 24). Texas seat belt law. https://1800lionlaw.com/texas-seat-belt-law/
- Cooney & Conway. (2021, August 9). How seat belts may help prevent fatalities. https://www.cooneyconway.com/blog/how-seat-belts-prevent-fatalities/
- BMC Public Health. (2018, December 28). Seatbelt use and risk of major injuries sustained by vehicle occupants. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-818-6280-1
- Kaizo Health. (2022, January 17). What is whiplash? How seat belt injuries can affect the neck and spine. https://www.kaizo-health.com/what-is-whiplash-how-seat-belt-injuries-can-affect-the-neck-and-spine/
- Consumer Reports. (2021, September 20). Protection against whiplash injuries. https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/2012/12/how-to-save-your-neck-in-a-rear-end-crash/index.htm
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2024, March 10). Whiplash injury. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/whiplash-injury
- Integrity Spine & Orthopedics. (2024, August 11). What neck injuries do car accidents cause? https://www.integrityspineortho.com/post/what-neck-injuries-do-car-accidents-cause/
- Stridewell. (2023, August 23). Delayed neck pain after a car accident. https://stridewell.com/managing-pain/delayed-neck-pain-after-a-car-accident/
- Texas Department of Transportation. (n.d.). Click it or ticket. https://www.txdot.gov/safety/traffic-safety-campaigns/click-it-or-ticket.html
- Driving. (2018, November 21). How it works: Preventing whiplash. https://driving.ca/auto-news/news/how-it-works-preventing-whiplash
- ChiroSport Specialists of Dallas. (2017, February 1). A 3-step safety check to avoid whiplash. https://www.chirosportspecialists.com/news/3-step-safety-check-whiplash/
- Dr. Alex Jimenez. (n.d.). Personal injury doctor. https://www.dralexjimenez.com/personal-injury-doctor/
- Thompson Law. (2021, November 17). El Paso car accident lawyers. https://1800lionlaw.com/el-paso-car-accident-lawyer/
- Nix Patterson, LLP. (2023). El Paso personal injury lawyers. https://nixlaw.com/el-paso/personal-injury-lawyers/
- Cesar Ornelas Injury Law. (2022, November 26). El Paso personal injury lawyer. https://cesarornelaslaw.com/el-paso-personal-injury-lawyer/