Chiropractic Spine Reduction and Integrated Care
Chiropractic spine reduction, also called a spinal adjustment or spinal manipulation, is a non-surgical treatment used to improve spinal mobility and function. During an adjustment, a chiropractor uses their hands or a specialized instrument to apply a quick, controlled force to a spinal joint that is not moving properly. This can help reduce joint restriction, lower tension in nearby muscles, and improve comfort during daily movement (Cleveland Clinic, 2022; National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health [NCCIH], 2025).
For clinics focused on integrated recovery care, chiropractic adjustments are often one part of a larger treatment strategy. Patients with back pain, neck pain, stiffness, headaches, whiplash, or poor mobility may benefit most when chiropractic care is combined with advanced clinical evaluation, rehabilitation support, and whole-person care. This kind of model fits well with a practice approach centered on musculoskeletal recovery, functional health, and coordinated medical oversight.
What is chiropractic spine reduction?
A chiropractic spine reduction is a targeted procedure used to restore motion to spinal joints that have become restricted or are not moving normally. These restrictions may develop after poor posture, repetitive strain, sports injuries, lifting injuries, car accidents, or prolonged inactivity. When spinal joints do not move the way they should, surrounding muscles may tighten, movement may become limited, and pain may increase.
The purpose of the adjustment is to improve joint mobility, reduce mechanical stress, and support improved function of the spine and surrounding tissues. According to the Cleveland Clinic, chiropractic adjustments are often used to address lower back pain, neck pain, muscle pain, headaches, stiffness, and conditions such as whiplash and sciatica (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). NCCIH also explains that spinal manipulation is a controlled technique in which a practitioner applies force to a spinal joint to move it beyond its passive range of motion, with the aim of improving function and reducing symptoms (NCCIH, 2025).
In simple terms, the adjustment is meant to help a stuck or irritated joint move more normally again.
What Happens During the Adjustment?
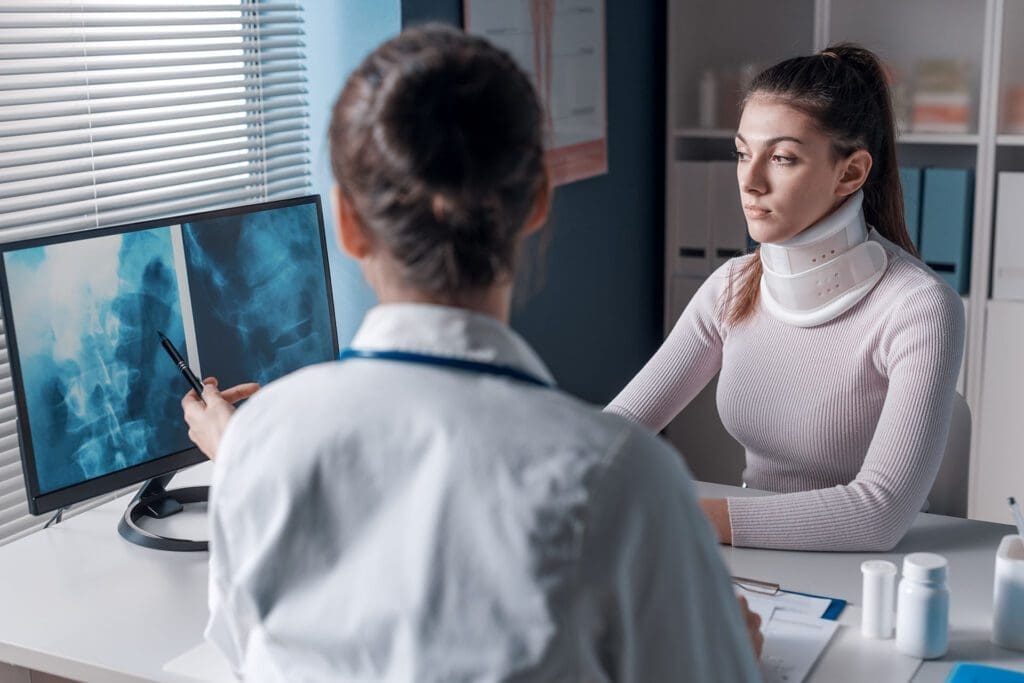
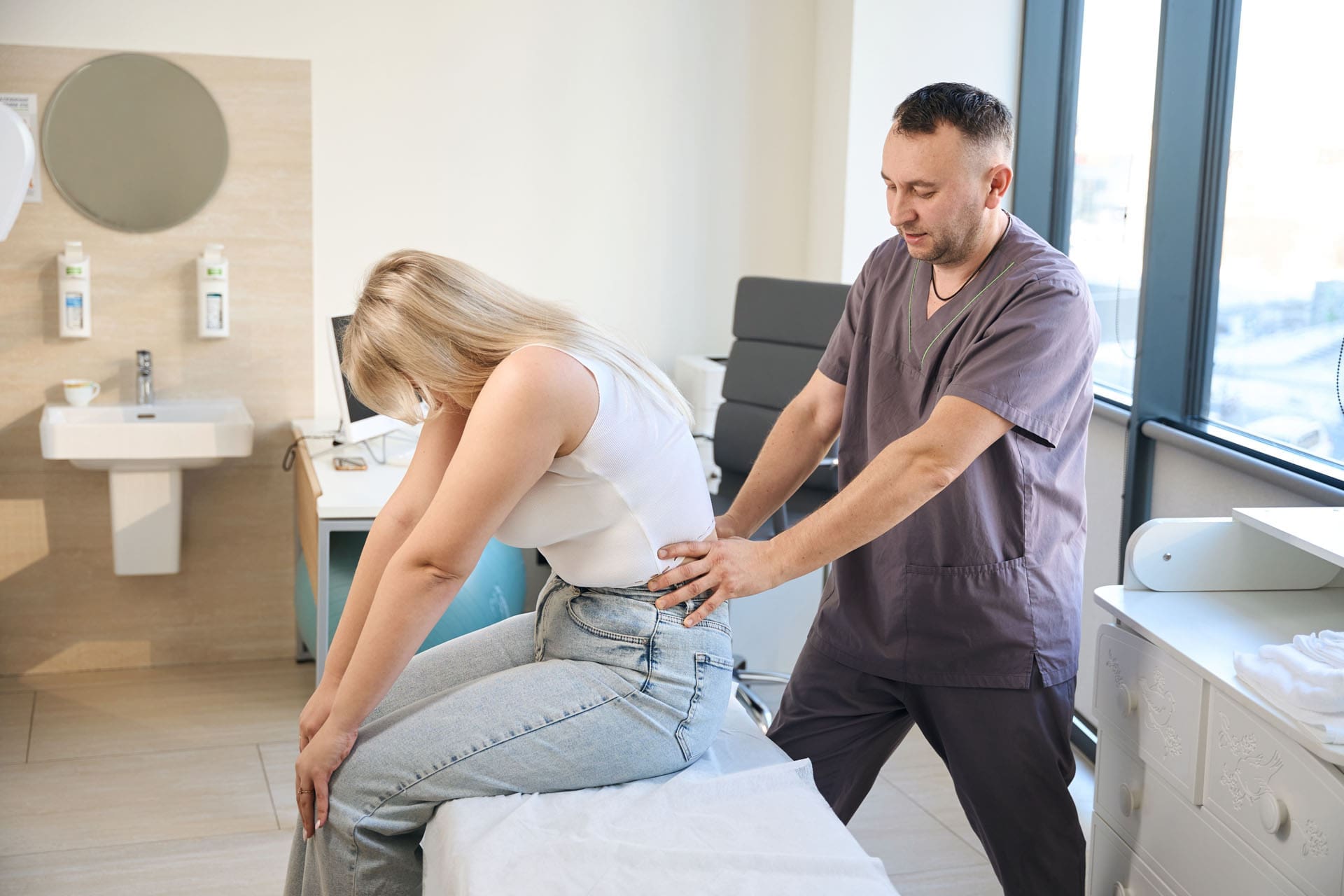
A chiropractic visit usually begins with an assessment. The clinician looks at posture, movement patterns, symptoms, health history, and the joints or tissues involved. In some cases, the patient may need additional medical review, imaging, or a broader workup if symptoms suggest something more than routine mechanical pain.
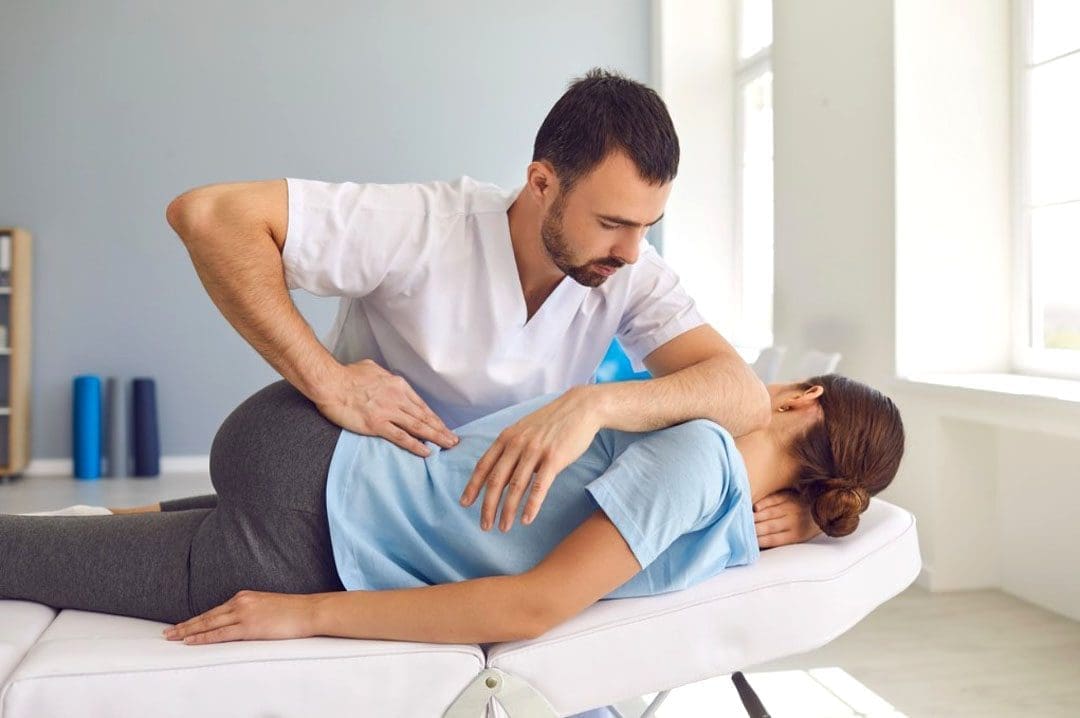
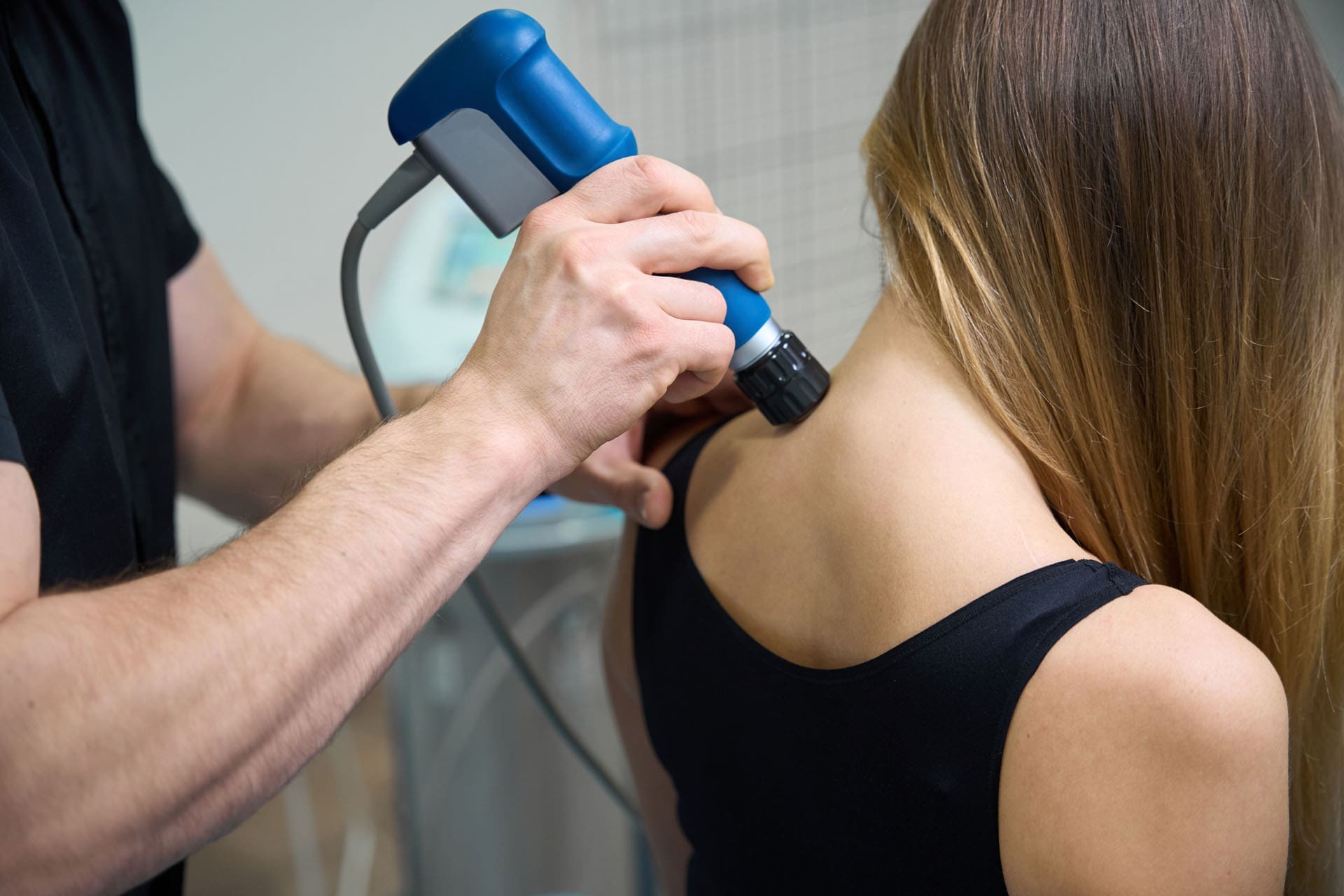
During the adjustment itself, the patient is positioned on a treatment table so the chiropractor can reach the affected area safely and accurately. Then a quick, controlled thrust is delivered to the spinal joint. Some chiropractors use their hands, while others use a specialized instrument designed to apply a precise force.
The adjustment is not random. It is a specific movement meant to improve joint mobility. For many patients, the procedure is brief and followed by a feeling of improved motion or reduced tightness.
Why Does It Make a Cracking Sound?
The sound heard during many adjustments is one of the most recognized parts of chiropractic care. However, it is often misunderstood. Cleveland Clinic explains that the cracking or popping sound is caused by gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide being released from the joint when pressure changes quickly during the adjustment (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). This is similar to the sound people hear when they crack their knuckles.
The sound is not bone breaking, bones rubbing together, or tissue tearing. It is simply a change in joint pressure. Also, a good adjustment does not always produce a sound. The real purpose is improved motion and function, not the pop itself.
How Chiropractic Adjustments May Help
Patients often seek chiropractic care because they want relief without surgery or long-term dependence on medication. Spinal adjustments may help reduce pain, improve movement, and support better function during work, exercise, and daily life.
Possible benefits of chiropractic spine reduction include:
- Less back or neck pain
- Better joint movement
- Reduced muscle tightness
- Improved flexibility and range of motion
- Easier movement during daily tasks
- Support for posture and spinal function
- Better tolerance for exercise and rehabilitation
Cleveland Clinic notes that chiropractic adjustments may help reduce pain and improve physical function (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). NCCIH adds that for acute and chronic low back pain, spinal manipulation can provide small to moderate improvements in pain and function for some patients (NCCIH, 2025).
For patients recovering from strain injuries, repetitive overuse, or accident-related trauma, better joint motion may also make it easier to progress into corrective exercise, rehab, and strengthening work.
Does a Chiropractic Adjustment Hurt?
Most chiropractic adjustments are not described as severely painful. Many patients feel pressure, movement, or a quick stretch. Some feel immediate relief, while others notice improvements over the next day or two. Cleveland Clinic reports that patients may experience mild soreness, stiffness, or fatigue after an adjustment, similar to what they might feel after exercise (Cleveland Clinic, 2022).
Common short-term effects may include:
- Mild soreness
- Temporary stiffness
- A feeling of tiredness
- A mild headache
- Temporary tenderness in the treated area
NCCIH states that these side effects are usually mild to moderate and often go away within about a day (NCCIH, 2025). While serious side effects are rare, a healthcare provider should immediately evaluate any unusual worsening of pain, weakness, numbness, or neurological symptoms.
Why Chiropractic Works Best as Part of Integrated Care
A spinal adjustment can help restore motion and reduce pain, but many patients need more than joint treatment alone. Real recovery often depends on addressing the full picture, including strength, posture, inflammation, work demands, prior injuries, sleep quality, stress load, and overall health status.
That is why an integrated clinical model can be so valuable. In a coordinated setting, chiropractic care may be combined with broader medical insight, patient education, and personalized recovery planning. This helps ensure that pain is not treated only as a simple joint problem when other factors may also be involved.
An integrated care strategy may include:
- Chiropractic adjustments
- Functional movement evaluation
- Soft-tissue therapies
- Home stretching and mobility plans
- Strengthening and rehabilitation exercises
- Clinical assessment of nerve or inflammatory symptoms
- Medical review of complex or persistent pain
- Lifestyle and recovery guidance
This kind of approach is especially helpful in practices that focus on musculoskeletal recovery and performance-based care.
The Role of APRN and FNP-BC Collaboration
An Advanced Practice Registered Nurse, or APRN, is a licensed advanced clinician with broad training in patient assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and care coordination. The American Nurses Association explains that APRNs include nurse practitioners and other advanced nursing roles that deliver patient-centered care in many settings (American Nurses Association, n.d.). A Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) is an APRN trained to treat patients across the lifespan (Goodwin University, 2021).
When chiropractic care is supported by APRN or FNP-BC involvement, patients may benefit from a more complete clinical picture. This matters when symptoms are not purely mechanical or when a patient has other issues affecting healing, such as inflammation, metabolic concerns, medication use, sleep disruption, or more complex injury patterns.
This collaborative model may help by offering:
- Better screening for conditions outside the routine chiropractic scope
- Improved care planning for complex recovery cases
- Closer monitoring of progress and symptom changes
- More complete patient education
- Easier coordination of imaging, referrals, or medical follow-up
- Greater confidence that structural and medical factors are both being addressed
Health Coach Clinic describes this kind of partnership as a way to combine spinal care, medical oversight, and patient education in support of stronger recovery outcomes (Health Coach Clinic, 2024).
The Value of Functional and Whole-Person Thinking
Some patients improve quickly with adjustments and exercise. Others continue to struggle because pain is being influenced by more than spinal mechanics alone. Sleep problems, chronic inflammation, poor nutrition, hormone imbalance, stress, and past trauma can all affect healing.
Dr. Alexander Jimenez has written about an integrative model that combines chiropractic care with functional medicine and advanced clinical assessment to better understand the whole patient rather than only focusing on symptoms (Jimenez, 2017; Jimenez, 2026). His clinical perspective supports the idea that musculoskeletal problems often connect to broader health patterns that require attention if long-term recovery is the goal.
In a clinically integrated setting, questions may include:
- Is the pain mainly joint-related, or are inflammatory factors also involved?
- Is the patient recovering well, or is something slowing healing?
- Does the patient need imaging or a deeper medical evaluation?
- Are posture, work habits, or training patterns part of the problem?
- Are nutrition, sleep, or stress affecting recovery?
This broader view can improve outcomes by guiding care based on what the patient actually needs, not just on what a single treatment can do.
A Recovery-Focused Approach for Modern Musculoskeletal Care
Chiropractic spine reduction is most effective when used as part of a broader treatment plan for musculoskeletal medicine and integrated recovery. The adjustment can help restore joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and improve overall movement. But lasting improvement often depends on combining that care with movement correction, strengthening, education, and medical insight when appropriate.
This kind of recovery-focused approach is useful for patients with:
- Neck and back pain
- Work-related strain
- Sports-related injuries
- Poor posture and spinal stiffness
- Mobility limitations
- Whiplash and minor accident-related injuries
- Recurrent musculoskeletal flare-ups
Chiropractic care may help the body move better. Integrated care helps patients function better over time.
Final Thoughts
Chiropractic spine reduction is a hands-on treatment designed to restore motion to restricted spinal joints. The quick thrust used during an adjustment may produce a popping sound because gases are released from the joint, but the real purpose is to improve movement, reduce pain, and support better function (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). For many patients, adjustments can be a helpful part of conservative care for spine-related pain and stiffness.
The strongest patient outcomes often happen when chiropractic care is paired with interdisciplinary support. When structural treatment is combined with APRN- or FNP-BC-led clinical insight, rehabilitation planning, and whole-person care, recovery can become more complete, more personalized, and more sustainable (American Nurses Association, n.d.; Health Coach Clinic, 2024). In a modern integrated setting, the goal is not only to help the spine move better but also to help the patient heal, function, and stay well.
References
American Nurses Association. (n.d.). Advanced practice registered nurses (APRN)
Cleveland Clinic. (2022, April 25). Chiropractic adjustment
Goodwin University. (2021, September 20). APRN vs. FNP: What is the difference?
Health Coach Clinic. (2024). Advantages of chiropractic and nurse practitioners in recovery
Jimenez, A. (2017, October 6). What is a functional medicine practitioner? | Functional chiropractor
Jimenez, A. (2026). Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CCST, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2025). Spinal manipulation: What you need to know