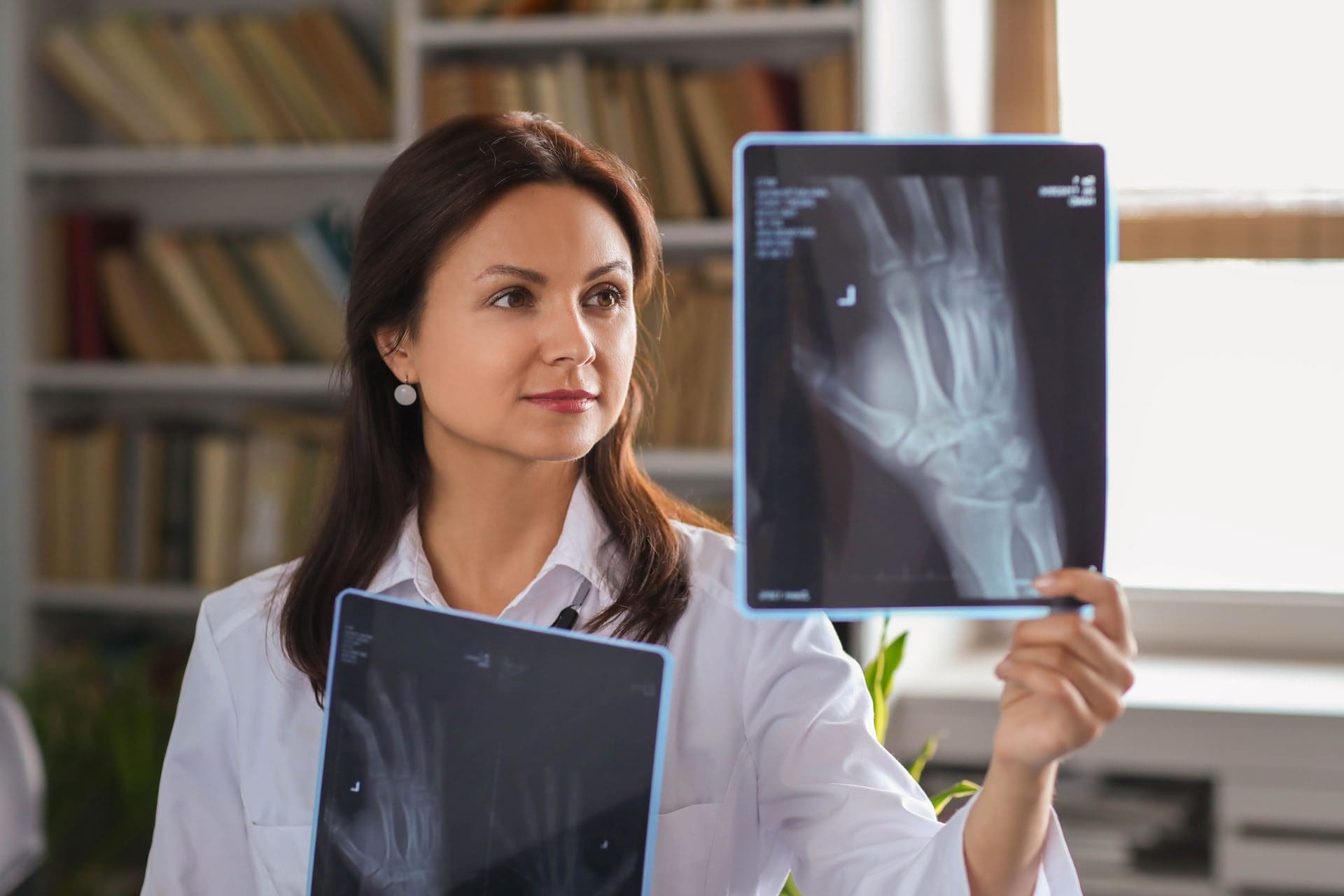
Auto Injuries: Understanding the Damage to The Rotator Cuffs
Get informed about auto injuries and rotator cuffs. Explore ways to protect your shoulders after an accident.
Shoulder Pain and Injuries in Motor Vehicle Accidents: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
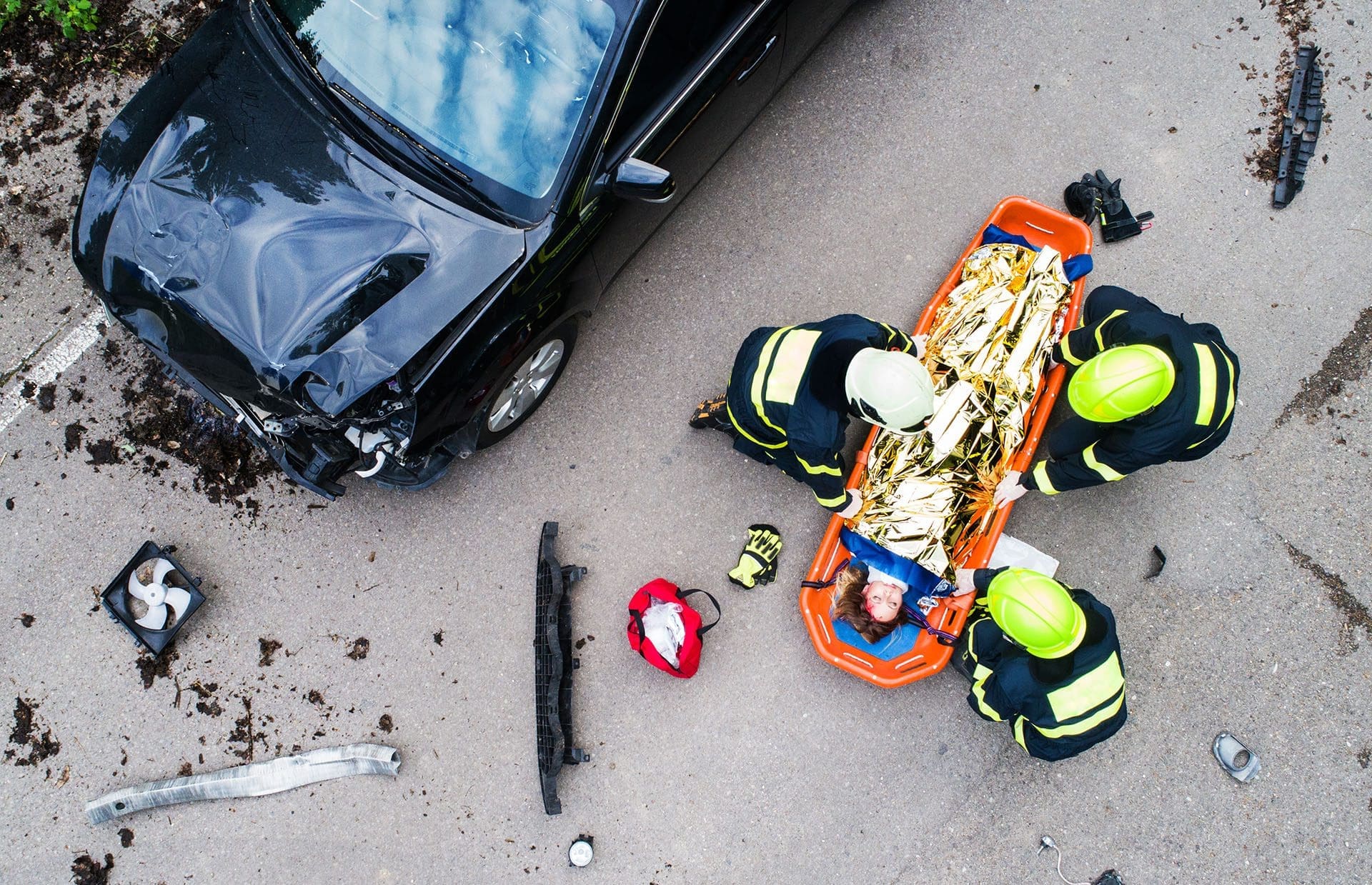
Shoulder injuries are a frequent consequence of motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), often resulting from the sudden and forceful impacts experienced during collisions. These injuries can range from minor sprains to severe conditions like rotator cuff tears, fractures, and nerve damage, significantly impacting daily life. While a sore shoulder might not earn you a starring role in a tragic drama, it can certainly feel like a grim plot twist in your day-to-day routine. Understanding the clinical reasons behind why shoulder pain and injuries are so closely linked to MVAs is essential for effective treatment and recovery. This blog post explores the mechanisms of shoulder injury in MVAs, their role in developing shoulder pain, and their specific impact on the rotator cuff. We also highlight the expertise of Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a distinguished chiropractor and nurse practitioner in El Paso, Texas, who specializes in treating personal injury cases with advanced diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is one of the most mobile joints in the human body, allowing for a wide range of movements, such as lifting, rotating, and reaching. This mobility, however, comes at the cost of stability, making the shoulder particularly vulnerable to injury. The shoulder joint comprises three main bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). The rotator cuff, a group of four muscles—supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis—and their tendons stabilize the shoulder joint and facilitate arm movements. These tendons connect the humerus to the scapula, and any damage to them can lead to significant pain and functional impairment. Ligaments, such as those connecting the clavicle to the scapula, also play a crucial role in maintaining joint stability but are susceptible to stretching or tearing during traumatic events like MVAs.
References
- Alexander Orthopaedics. (2023). 5 Common Shoulder Injuries from a Car Accident. https://alexanderorthopaedics.com/blog/shoulder-injury-car-accident-treatment/
Mechanisms of Shoulder Injury in MVAs
Shoulder injuries in MVAs typically result from the sudden and forceful movements experienced during a collision. Several mechanisms contribute to these injuries:
- Bracing Against the Steering Wheel: Drivers often instinctively brace themselves by pushing against the steering wheel during a crash, transmitting significant force to the shoulders. This action can overstretch or tear the rotator cuff tendons, especially in rear-end collisions (El Paso Chiropractor Blog, 2016).
- Seatbelt Restraint: While seatbelts are lifesaving, they can cause shoulder injuries if improperly positioned or if the impact force is excessive, leading to bruising, sprains, or fractures.
- Direct Impact: In side-impact or rollover accidents, the shoulder may strike the vehicle’s interior, such as the door or window, resulting in fractures or dislocations.
- Whiplash Effect: The rapid back-and-forth motion of the neck and upper body, commonly associated with whiplash, can strain shoulder muscles and ligaments, contributing to rotator cuff injuries.
These mechanisms highlight the shoulder’s vulnerability due to its complex structure and the intense forces involved in MVAs.
References
- El Paso Chiropractor Blog. (2016). Rotator Cuff Tears Resulting from Auto Injury. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/08/rotator-cuff-tears-resulting-from-auto.html
- Smith & Hassler, Attorneys At Law. (n.d.). Understanding Shoulder Injuries in Car Accidents. https://www.smithandhassler.com/articles/understanding-shoulder-injuries-in-car-accidents/
Chiropractic Care After Accidents and Injuries- Video
Common Shoulder Injuries from MVAs
Shoulder injuries from MVAs vary in severity, but the following are among the most common:
| Injury Type | Description | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Rotator Cuff Tears | Tears in one or more of the rotator cuff tendons, often due to overstretching or direct trauma. Common in rear-end collisions. | Radiating pain, restricted mobility, inflammation, swelling, popping/clicking, weakness. |
| Shoulder Sprains/Strains | Stretching or tearing of ligaments (sprains) or muscles (strains) around the shoulder joint. | Pain, instability, weakness, swelling. |
| Fractures/Dislocations | Breaks in the clavicle, scapula, or humerus, or dislocation of the shoulder joint due to impact. | Severe pain, swelling, bruising, limited movement. |
| Brachial Plexus Injuries | Damage to the nerve network supplying the shoulder, arm, and hand, often from forceful impact. | Numbness, weakness, burning pain, or paralysis in severe cases. |
Research suggests that shoulder injuries occur in approximately 27.9% of polytraumatized patients involved in MVAs, with 68.5% of these injuries attributed to traffic accidents, particularly motorbike, bicycle, and pedestrian incidents (TraumaRegister DGU®, n.d.). Additionally, over 2 million Americans experience whiplash injuries annually, many of which involve shoulder pain due to associated muscle and ligament strain (Atlanta Advocate, 2024).
References
- Atlanta Advocate. (2024). Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Injuries After a Georgia Car Wreck: Your Legal Options. https://atlantaadvocate.com/legal-guides/car-accidents/shoulder-injuries/
- El Paso Chiropractor Blog. (2016). Rotator Cuff Tears Resulting from Auto Injury. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/08/rotator-cuff-tears-resulting-from-auto.html
- TraumaRegister DGU®. (n.d.). Shoulder injuries in polytraumatized patients: an analysis of the TraumaRegister DGU®. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8629800/
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
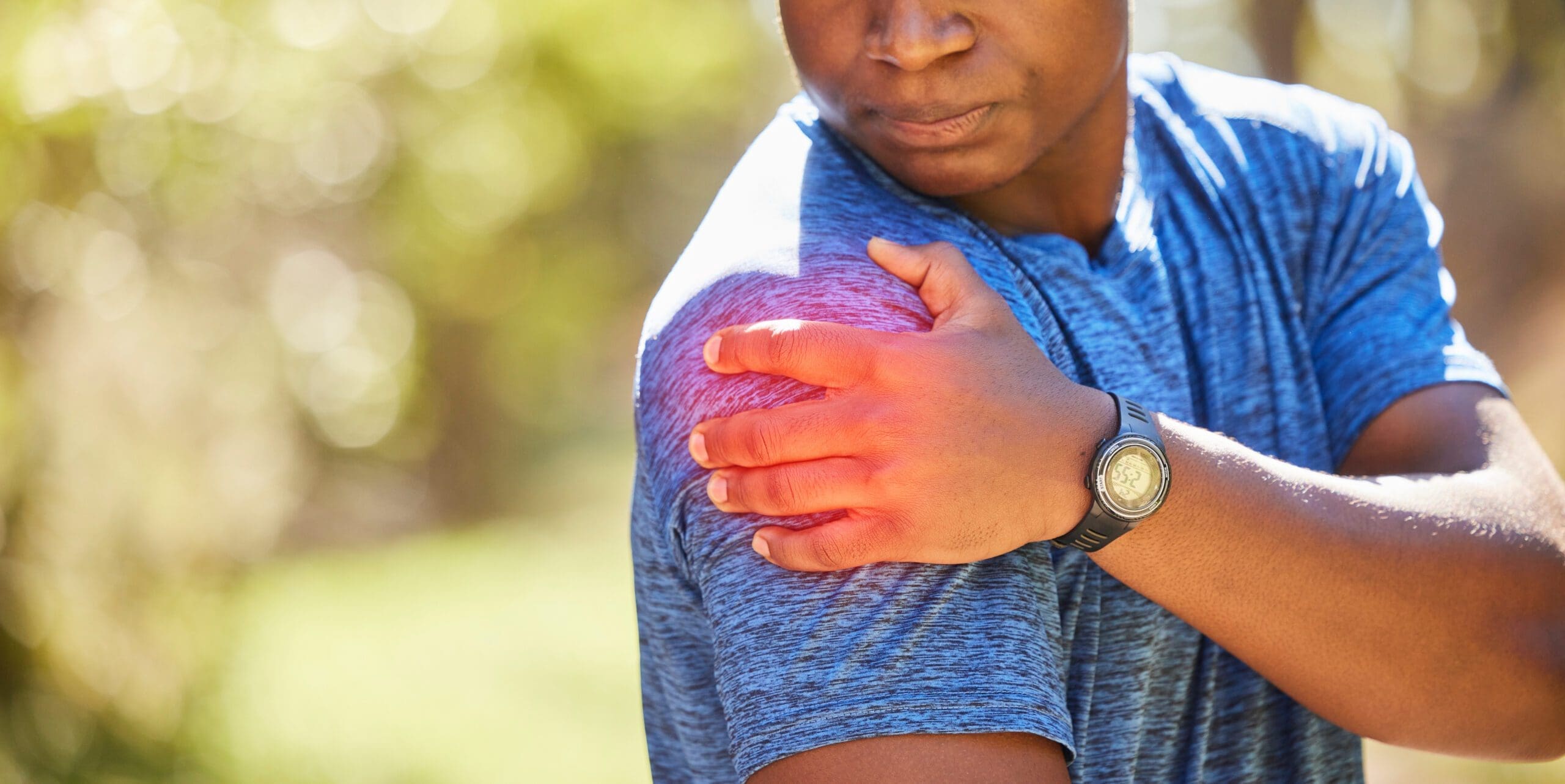
Individuals with shoulder injuries from MVAs may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Pain: Often severe, especially with movement, and may radiate to the arm or upper back.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty lifting or rotating the arm.
- Swelling or Bruising: Visible signs of trauma around the shoulder.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the arm, particularly with rotator cuff tears.
- Numbness or Tingling: Indicative of nerve involvement, such as brachial plexus injuries.
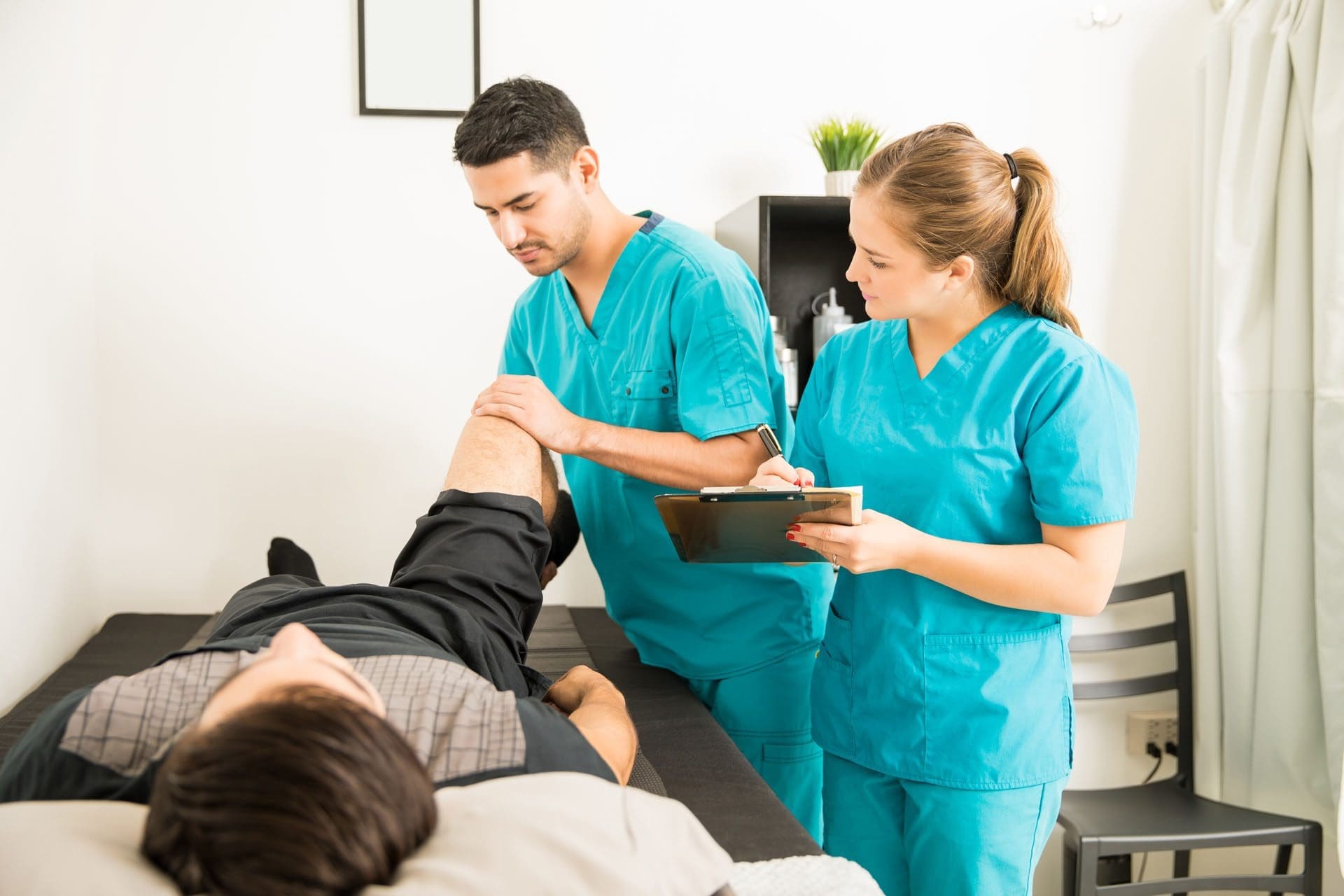
Diagnosis involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history and physical examination to assess pain, range of motion, and strength. Advanced imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, are often used to confirm the extent of damage. Dr. Alexander Jimenez, with his dual expertise as a chiropractor and a board-certified nurse practitioner, utilizes these diagnostic tools to identify shoulder injuries accurately. His approach integrates biomechanical assessments with medical diagnostics, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the injury’s scope (A4M, n.d.).
References
- A4M. (n.d.). Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic – Alex, Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP. https://www.a4m.com/alex-jimenez-injury-medical-amp-chiropractic-clinic-el-paso-tx.html
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Treatment for shoulder injuries from MVAs depends on the injury’s severity and type. Conservative approaches are often the first line of treatment and include:
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments and soft tissue manipulations to restore alignment and reduce pain.
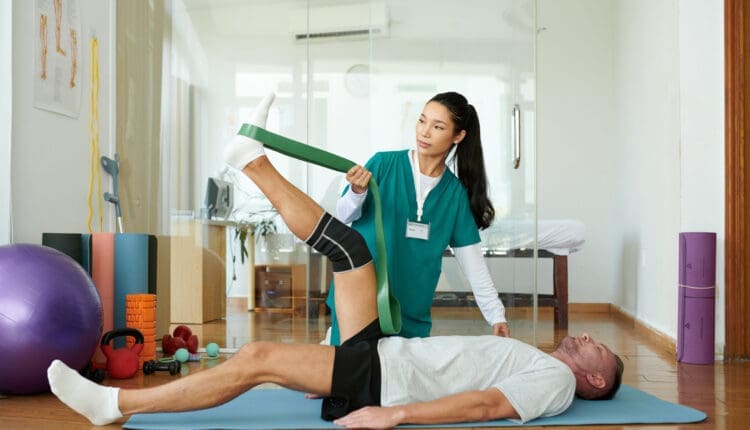
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff, improve flexibility, and restore function.
- Pain Management: Medications, acupuncture, or massage therapy to alleviate pain and inflammation.
For severe injuries, such as complete rotator cuff tears or complex fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary. Rehabilitation is critical, focusing on restoring strength and mobility and preventing chronic pain. Dr. Jimenez’s clinic emphasizes personalized rehabilitation plans, incorporating functional medicine to address underlying factors like inflammation or nutritional deficiencies (El Paso Back Clinic, 2025). Ligament injuries, common in shoulder trauma, heal through phases of inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling, but scar tissue may remain biomechanically inferior, necessitating careful rehabilitation to avoid long-term joint laxity.
References
- El Paso Back Clinic. (2025). Dr. Jimenez Injury Rehabilitation: Effective MVA Care. https://elpasobackclinic.com/dr-jimenez-injury-rehabilitation-effective-mva-care/
Role of Chiropractic Care in Shoulder Injury Recovery
Chiropractic care is a cornerstone of recovery for MVA-related shoulder injuries. Dr. Jimenez employs hands-on techniques, including spinal and joint manipulations, to address misalignments and alleviate pain. These adjustments improve joint mobility, relieve pressure on nerves, and enhance healing. His integrative approach combines chiropractic care with physical therapy, acupuncture, and nutritional counseling to promote holistic recovery. For instance, chiropractic adjustments can help realign the shoulder joint, while targeted exercises strengthen the rotator cuff, preventing future injuries. Dr. Jimenez’s dual licensure enables him to bridge chiropractic and medical care, providing a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each patient’s specific needs (A4M, n.d.).
References
- A4M. (n.d.). Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic – Alex, Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP. https://www.a4m.com/alex-jimenez-injury-medical-amp-chiropractic-clinic-el-paso-tx.html
Personal Injury Cases and Legal Aspects
In El Paso, Texas, personal injury cases related to MVAs are significant, as victims often seek compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering. Accurate documentation of injuries is crucial for these claims. Dr. Jimenez plays a pivotal role as a liaison between medical and legal services, providing detailed medical reports supported by advanced imaging and diagnostic evaluations. His expertise ensures that injuries are clinically linked to the accident, thereby strengthening legal claims. This dual role enhances patient care while supporting their pursuit of fair compensation (El Paso Back Clinic, 2025).
References
- El Paso Back Clinic. (2025). Dr. Jimenez Injury Rehabilitation: Effective MVA Care. https://elpasobackclinic.com/dr-jimenez-injury-rehabilitation-effective-mva-care/
Conclusion
Shoulder injuries from motor vehicle accidents, particularly rotator cuff tears, are a significant concern due to the shoulder’s complex anatomy and the intense forces involved in collisions. Research suggests that these injuries are common, with traffic accidents accounting for a substantial portion of shoulder trauma in polytraumatized patients. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s integrative approach, combining chiropractic care, advanced diagnostics, and personalized rehabilitation, offers a comprehensive recovery solution. His role in personal injury cases in El Paso underscores the importance of expert medical care in both healing and legal documentation. If you or a loved one has suffered a shoulder injury in an MVA, consulting a specialist like Dr. Jimenez can ensure optimal recovery and support for any legal claims.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
References
- A4M. (n.d.). Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic – Alex, Jimenez DC, APRN, FNP-BC, CFMP, IFMCP. https://www.a4m.com/alex-jimenez-injury-medical-amp-chiropractic-clinic-el-paso-tx.html
- Alexander Orthopaedics. (2023). 5 Common Shoulder Injuries from a Car Accident. https://alexanderorthopaedics.com/blog/shoulder-injury-car-accident-treatment/
- Atlanta Advocate. (2024). Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Injuries After a Georgia Car Wreck: Your Legal Options. https://atlantaadvocate.com/legal-guides/car-accidents/shoulder-injuries/
- El Paso Back Clinic. (2025). Dr. Jimenez Injury Rehabilitation: Effective MVA Care. https://elpasobackclinic.com/dr-jimenez-injury-rehabilitation-effective-mva-care/
- El Paso Chiropractor Blog. (2016). Rotator Cuff Tears Resulting from Auto Injury. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/08/rotator-cuff-tears-resulting-from-auto.html
- TraumaRegister DGU®. (n.d.). Shoulder injuries in polytraumatized patients: an analysis of the TraumaRegister DGU®. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8629800/







 Digital Pulleys
Digital Pulleys