Pregnancy Indoor Cycling: Stay Active and Strong
During pregnancy, is indoor cycling a safe and recommended way to maintain fitness?
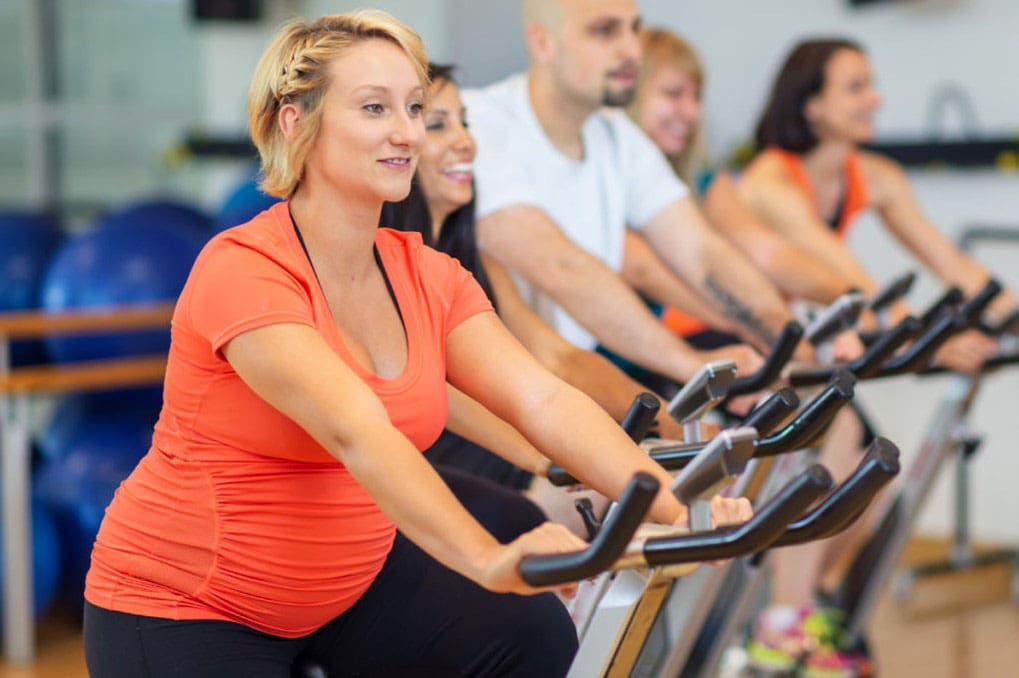

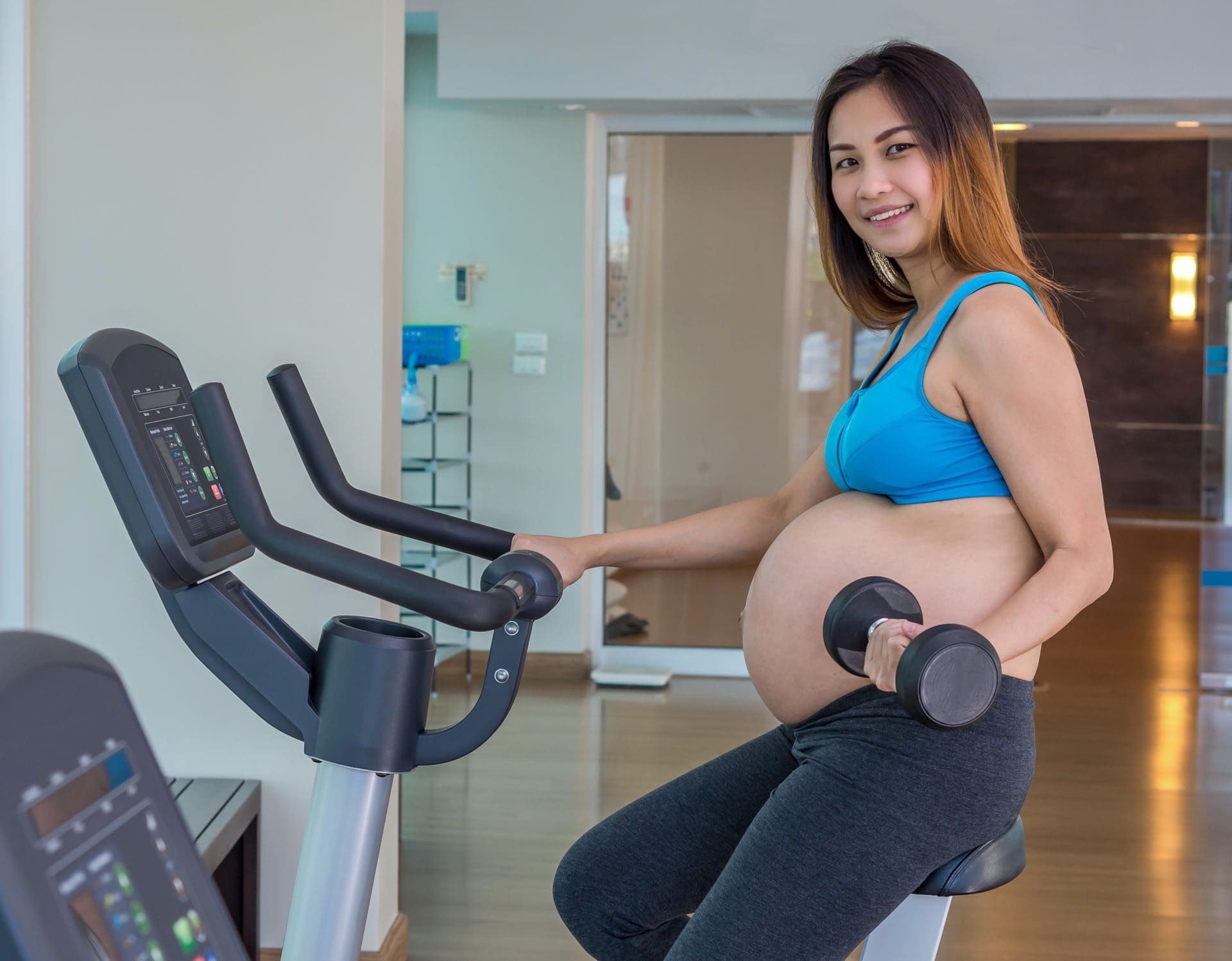
Pregnancy Indoor Cycling
Exercising during pregnancy is highly recommended for both the parent and the baby. Staying physically active can:
- Increase blood circulation
- Increase energy
- Reduce backaches
- Improve digestion and sleep
- Enhance mood
- Help manage weight
- Promote muscle tone, strength, and endurance. (Hinman, S. K. et al., 2015)
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, or ACOG, advises pregnant individuals to exercise regularly during pregnancy. (The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2024) The guidelines indicate that individuals who regularly engage in vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise before pregnancy should continue these activities during their pregnancy. (Syed H., Slayman T., & DuChene Thoma K. 2021) According to ACOG, observational studies of pregnant individuals who exercise show benefits such as:
- The reduced risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
- Cesarean birth
- Operative vaginal delivery
- Reduced postpartum recovery time
- Exercise can also help prevent postpartum depression. (Syed H., Slayman T., & DuChene Thoma K. 2021)
Stationary cycling has been extensively studied in pregnancy and found safe and beneficial (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2024).
Safety
Indoor cycling is ideal because individuals won’t have to deal with balance challenges or generate a heavy impact on their joints. There are many indoor cycling workouts to try, whether spin or on-demand classes. Indoor cycling is safer during pregnancy than outdoor cycling, which is not recommended because of the risk of falls from traffic and weather conditions. Although indoor cycling is generally considered safe during pregnancy, individuals should get clearance from their OB/GYN if they have any underlying medical conditions that might limit physical activity options.
Cycling Classes
Taking cycling classes during pregnancy is safe if a healthcare provider has no concerns. It’s important to take precautions.
- It’s recommended to continue with any exercise you were doing before pregnancy rather than start a new routine.
- Remember that this is an exercise for two, so the heart rate will elevate quickly and become overheated more easily.
- Take it easier on the bike, and don’t push too hard.
Consult With the Instructor
It’s recommended to seek out an instructor with some prenatal exercise training. Individuals may benefit from sticking with the same instructor whenever possible to get to know them and familiarize themselves with their modifications and needs. Whether or not you’re showing, tell the instructor that you’re pregnant before the class starts. This way, they can monitor progress and will not push too hard. The instructor can also give important pointers on modifying the ride to suit your needs.
Modify Bike Set-Up
Individuals may need to adjust the saddle position and raise the handlebars to stay comfortable as their bodies change. Sitting more upright is recommended to relieve strain on the lower back, and increasing the handlebars and bringing them closer instead of leaning forward is another goal. Another goal is to keep the weight more evenly distributed between the hands and body. Also, avoid movable indoor bikes that mimic outdoor riding. They can lean sideways, which might cause a fall.
Dial Down Intensity
With indoor cycling, it’s best to exercise moderately during pregnancy. Consider wearing a heart rate monitor to ensure a safe intensity. It’s also helpful to pay attention to the Rating of Perceived Exertion scale/RPE. Even if the heart rate isn’t too high, slow down or stop exercising immediately if you’re gasping for breath or feeling lightheaded. ACOG guidelines indicate that 13-14 “somewhat hard” on the Borg RPE scale is a safe and acceptable level of exertion. The guidelines also state that RPE is a better gauge of exertion than heart rate and that the talk test (holding a conversation while exercising) can indicate safe workout intensity.
Stay Cool and Properly Hydrated
Wear comfortable, breathable clothing to help you stay cool and a bra with plenty of support. Drink lots of water throughout the workout, actually more than usual. Overheating and dehydration are common during pregnancy and can be dangerous for both parents and babies. Carrying an extra 20 to 30 pounds and having 40% more blood pumping through the body toward the end of pregnancy makes you likely to sweat more and can easily lead to dehydration. Using a fan for home gyms is highly recommended.
Avoid Standing and Stay In a Seated Position
During the early months, you may be able to ride in a standing position without any problems. But as the belly grows, it changes the body’s center of gravity, putting more pressure on the joints and making it difficult to ride standing. Joints are looser or more flexible during pregnancy, which makes standing while cycling more difficult and risky. It is still a healthy workout if you stay seated the whole time—and, most importantly, avoid overdoing it or injuring yourself.
Body Signs
Listen to the body while exercising. If you get winded, dizzy, or unwell while riding, take a break or reduce your effort by a few notches. If a 45-to-60-minute class is too intense, feel free to depart early; just let the instructor know you’re OK. Energy will likely ebb and flow during pregnancy, so pay attention to the body’s signals and take care of them accordingly. Stop exercising if you experience any of the following (Syed H., Slayman T., & DuChene Thoma K. 2021)
- Abdominal pain
- Dyspnea: shortness of breath before exertion
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Calf pain or swelling
- Muscle weakness affects balance
- Chest pain
- Amniotic fluid leakage
- Regular painful contractions
- Vaginal bleeding
Call your doctor if you experience sharp pain, contractions, a surge of fluid, a sudden severe headache, prolonged swelling, or decreased baby movement.
Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic
It’s important to exercise wisely during the nine months to accommodate body changes, the extra weight, the increasingly relaxed ligaments, and the shift in the center of gravity. The stationary bike provides a personalized, low-impact workout. You get to control the intensity and the duration of the ride. Monitor your heart rate and/or RPE to avoid overdoing it. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Chiropractic Lower Back Pain Pregnancy Treatment
References
Hinman, S. K., Smith, K. B., Quillen, D. M., & Smith, M. S. (2015). Exercise in Pregnancy: A Clinical Review. Sports Health, 7(6), 527–531. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738115599358
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2024). Exercise during pregnancy. https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/exercise-during-pregnancy?utm_source=redirect&utm_medium=web&utm_campaign=int
Syed, H., Slayman, T., & DuChene Thoma, K. (2021). ACOG Committee Opinion No. 804: Physical Activity and Exercise During Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period. Obstetrics and gynecology, 137(2), 375–376. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004266