Bone Growth Stimulator in Post-Injury Healing
Can bone growth stimulators help promote bone healing in cases where fractures or fusions fail to heal properly?
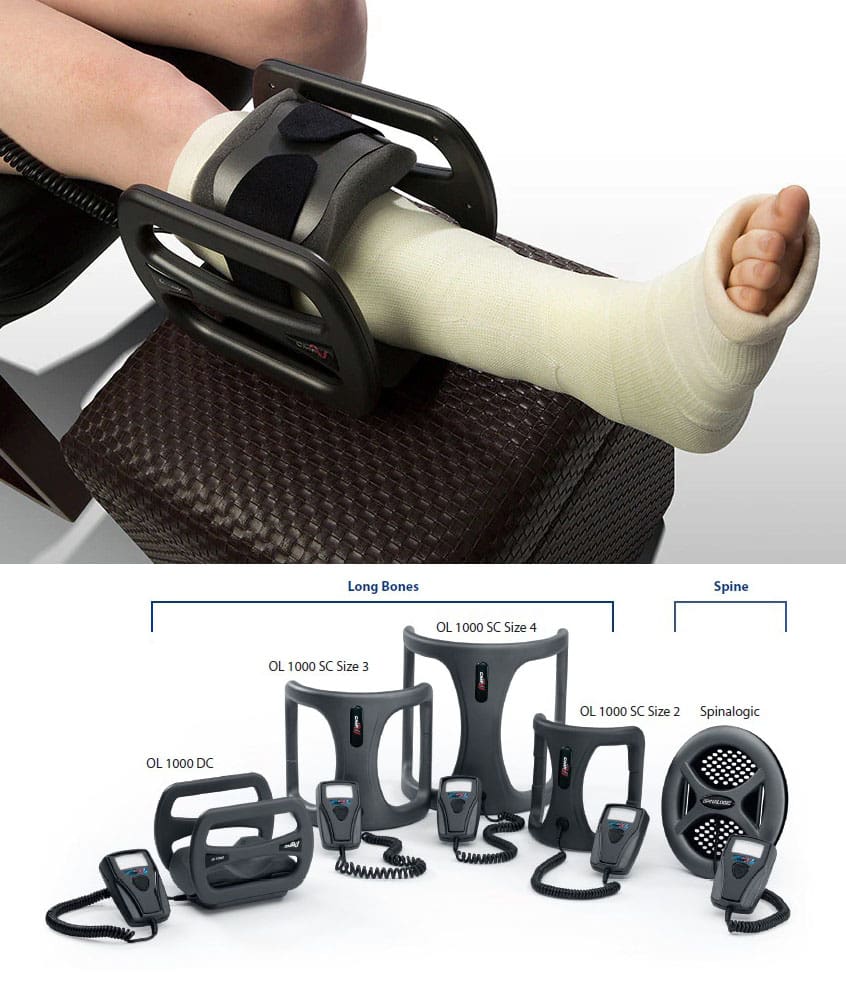
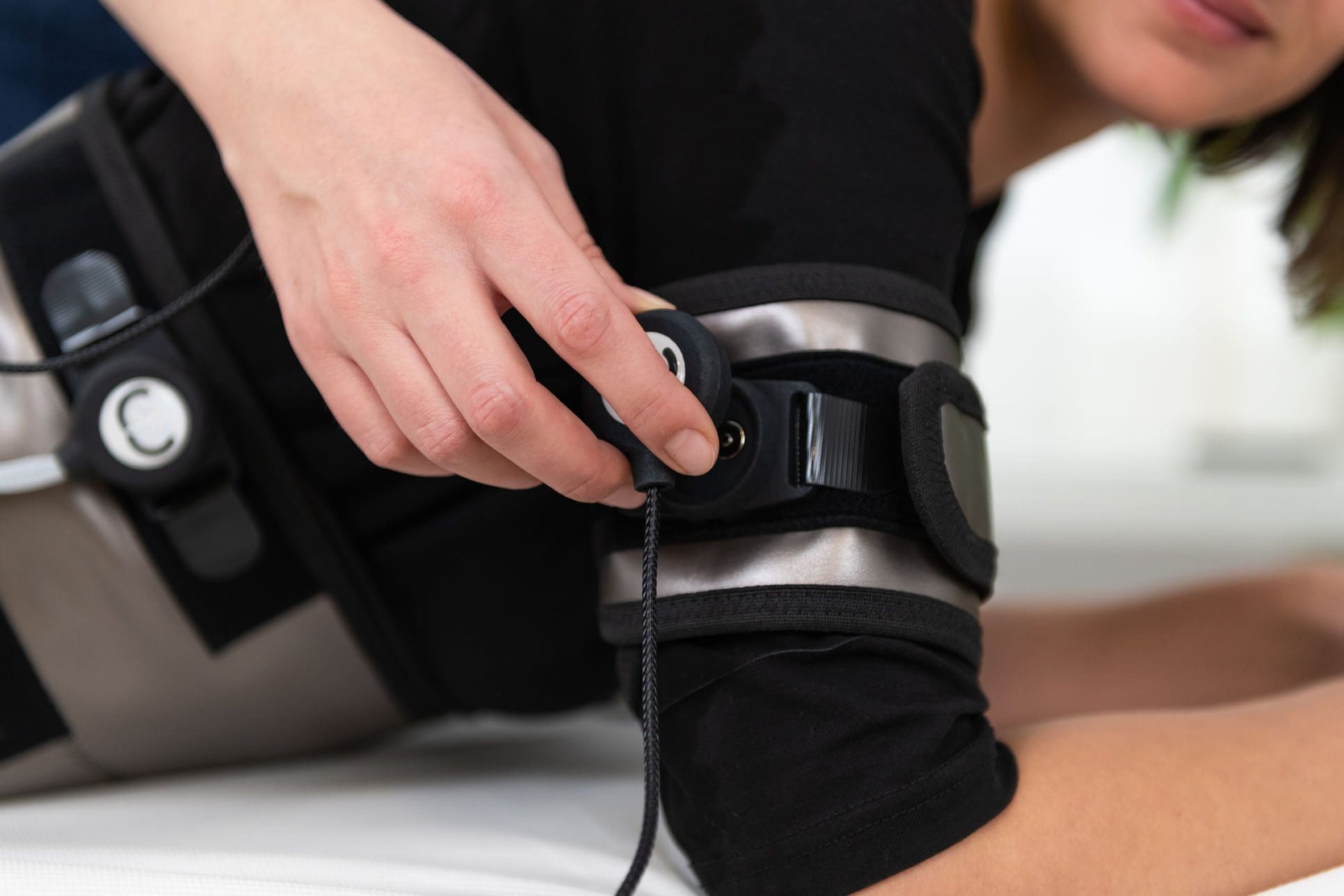
Bone Growth Stimulator
Individuals who sustain broken bones typically heal the fracture with appropriate treatment, which may include casts, realignment, and surgery. This type of surgery is performed on the spine and joints throughout the body; typically, the bone heals without a problem. Bone healing is a natural process, as bones are constantly replaced with new ones, and after an injury, the body can heal the damage to the bone. However, bone healing sometimes does not happen correctly and/or completely. Bone healing can take a long time, which is known as a delayed union, or it may not occur at all, or a nonunion. This is when a healthcare provider could recommend bone growth stimulation.
How They Work
Bone growth stimulators apply external or implanted electrical or ultrasonic energy to the fracture or fusion site, stimulating bone growth. These devices are often used when a fracture doesn’t heal within the expected timeframe (a nonunion fracture) or when a spinal fusion has not successfully fused. (FDA, 2022)
- They come in various shapes, sizes, and technologies depending on the location of the fracture.
- The most commonly used bone stimulators in orthopedics are electrical and ultrasound stimulators.
- The stimulator emits a pulsed electromagnetic or ultrasonic impulse to the area where bone healing should occur.
- Most modern bone stimulators are attached near the fracture site or fused with a small battery pack and worn for a period each day that may last minutes or hours.
Electrical Stimulation
- Devices deliver low-level electrical pulses to the fracture site, which can stimulate bone cells to create new bone tissue.
Ultrasound Stimulation
- They emit low-intensity pulsed ultrasound waves, which are absorbed by the bone and can promote bone healing.
Implantable vs. External
- Some stimulators are surgically implanted, providing constant stimulation directly at the fracture site, while others are external and worn over the skin or cast.
The goal is to activate a series of receptors in the body to encourage a healing response. (Childs, S. G. 2003) The stimulator activates a pathway that releases chemicals within the body to promote fracture healing. This type of process in the body is called a cascade, and it happens when one signal stimulates another method, and so on until healing is complete. The bone stimulator ensures this cascade continues until the healing process is complete.
Effectiveness
Studies of bone stimulator effectiveness suggest two benefits:
- Less pain is associated with the bone healing process.
- Faster fracture healing.
However, these studies haven’t shown that these differences lead to improved patient functional outcomes. It would seem that if there is less pain and faster healing, then the patient should recover without complications. However, some researchers have suggested this is probably because the differences in pain and healing times are small and not necessarily noticeable. (Aleem, I. S. et al., 2016)
- While bone growth stimulators can be effective, the results can vary, and their effectiveness is still under investigation.
- Some studies have shown that stimulators can reduce pain and speed up healing time, while others have shown mixed results.
- It’s important to discuss the benefits and risks of bone growth stimulation with a doctor to determine if it’s the right treatment option.
When Stimulation is Necessary
Bone stimulators are currently not used for routine fracture healing. It is certainly possible that bone healing stimulators will be used routinely in the future. They seem to show some benefit in non-healing fractures or fractures that are likely troublesome to heal. Some reasons individuals may have problems healing fractures are injuries to the blood supply to and around the fracture, injuries to specific bones, and overuse-related fractures. (Victoria, G. et al., 2009) These injuries may include (FDA, 2022)
Nonunion Fractures
- When a fracture doesn’t heal within the expected timeframe.
- Open fractures
- Stress fractures
- Scaphoid bone fractures
- Talus fractures
Failed Fusions
- When a spinal fusion hasn’t been successful.
High-Risk Patients
- For individuals with factors that can hinder bone healing, such as smoking, diabetes, or certain medications
Bone healing typically proceeds without much problem. However, there are situations where people have issues healing after fractures or surgery. Bone stimulators are not used for routine bone healing but in situations where steps may be needed to help stimulate the body. While the improvement may be small, it may be critical if it is the difference between healing and nonhealing.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
As a Family Practice Nurse Practitioner, Dr. Jimenez combines advanced medical expertise with chiropractic care to address various conditions. Our clinic integrates Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine to create customized care plans that promote natural healing, mobility, and long-term wellness. By focusing on flexibility, agility, and strength, we empower patients to thrive, regardless of age or health challenges. At El Paso’s Chiropractic Rehabilitation Clinic & Integrated Medicine Center, we passionately focus on treating patients after injuries and chronic pain syndromes. We focus on improving your ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored for all age groups and disabilities. We use in-person and virtual health coaching and comprehensive care plans to ensure every patient’s personalized care and wellness outcomes.
From Injury to Recovery with Chiropractic Care
References
U.S. Food & Drug Administration. (2022). AccelStim Bone Growth Stimulator – P210035. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/recently-approved-devices/accelstim-bone-growth-stimulator-p210035#:~:text=What%20is%20it?,the%20transducer%20to%20the%20fracture
Childs, S. G. (2003). Stimulators of bone healing. Biologic and biomechanical. Orthopedic nursing, 22(6), 421–428. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006416-200311000-00010
Aleem, I. S., Aleem, I., Evaniew, N., Busse, J. W., Yaszemski, M., Agarwal, A., Einhorn, T., & Bhandari, M. (2016). Efficacy of Electrical Stimulators for Bone Healing: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Sham-Controlled Trials. Scientific Reports, 6, 31724. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31724
Victoria, G., Petrisor, B., Drew, B., & Dick, D. (2009). Bone stimulation for fracture healing: What’s all the fuss?. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 43(2), 117–120. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.50844