Chiropractic Care Insights for Sacroiliac Joint Pain
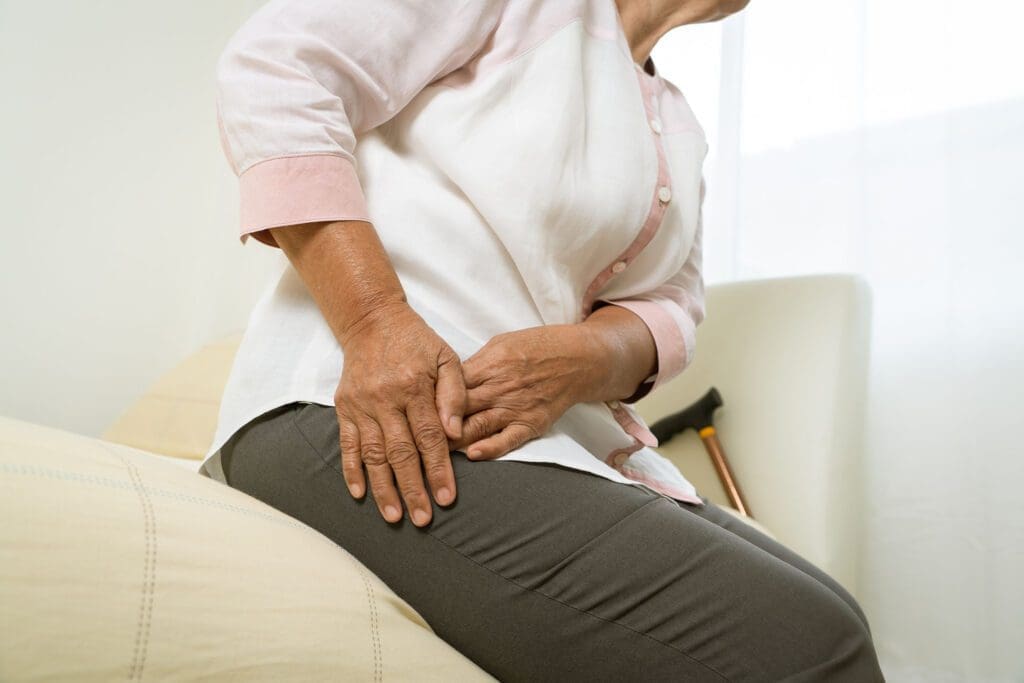
Get informed about sacroiliac joint pain and the role of chiropractic care in effective pain management and recovery.
Chiropractic Care for Sacroiliac Joint Pain and Hip Pain: A Comprehensive Guide with Insights from Dr. Alexander Jimenez
Well, hello there, folks! It’s your ol’ pal Herman Munster, lurching in from the spooky side of El Paso, TX, to talk about something that’s no laughing matter—sacroiliac joint pain and hip pain! Now, don’t get your bolts in a twist; I’m here to make this as fun as a barrel of bats while keeping it simple enough for a high schooler to follow. Picture me trying to waltz with Lily, only to find my hips and lower back creaking like the hinges on our haunted mansion door. That’s the kind of pain we’re tackling today! So, grab a comfy seat (not my electric chair, mind you), and let’s dive into this monster-sized guide to understanding how chiropractic care can help you shake off sacroiliac joint (SI joint) pain and its hip-related hijinks.
In this 5,000+ word blog, we’ll explore why chiropractic care, especially from the talented Dr. Alexander Jimenez at ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, is a fang-tastic solution for SI joint pain and hip discomfort. We’ll dig into how hip pain and SI joint issues are like two peas in a pod, the risk factors that make them creep up like a werewolf on a full moon, and practical tips from Dr. Jimenez’s expertise (ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, n.d.; Jimenez, n.d.). Plus, we’ll spotlight why Dr. Jimenez is the go-to guy for personal injury cases in El Paso, using his high-tech imaging and dual-scope know-how to bridge medical care and legal needs. And don’t worry, we’ll back it all up with science from PubMed, so you know it’s not just Herman’s tall tales!
Understanding the Sacroiliac Joint and Its Connection to Hip Pain
What’s This Sacroiliac Joint All About?
Let’s start with the basics, shall we? The sacroiliac joint, or SI joint, is like the hinges on my coffin—it connects the sacrum (that triangular bone at the bottom of your spine) to the ilium (those big, curvy pelvic bones). This joint is a real workhorse, holding up your upper body, soaking up shocks like Grandpa Munster’s potions, and passing forces between your upper and lower body when you walk, run, or do the Munster Mash (Hogston, 2015). But when it gets out of sorts, oh boy, it can make you feel like you’re stuck in a Frankenstein shuffle!
The SI joint is built tough, with strong ligaments and muscles keeping it steady, but it’s got just enough wiggle room for movement. When things go wrong—like an injury, inflammation, or a misalignment—it can cause pain that radiates to your lower back, hips, buttocks, or even down your legs (Foley & Buschbacher, 2014). And here’s the tricky part: because the SI joint and hip joint are next-door neighbors in your pelvis, pain from one can sneak into the other, making it a real “who-dun-it” mystery.
Why Does Hip Pain Tag Along with SI Joint Trouble?
You might be scratching your head, wondering, “Herman, why’s my hip acting up when it’s the SI joint causing trouble?” Well, it’s like when Grandpa’s experiments go haywire and mess up the whole lab—the SI joint and hip joint share muscles, ligaments, and nerves. When the SI joint gets inflamed or misaligned, it can irritate those shared tissues, sending pain to your hip, buttocks, or thigh (Wong & Kiel, 2018). It’s like the SI joint throwing a tantrum and the hip getting caught in the crossfire!
For instance, sacroiliac joint dysfunction can mess with your hip’s movement, making it work harder and causing pain that feels like it’s coming from the hip itself (Vanelderen et al., 2010). On the flip side, if your hip joint is stiff or arthritic, it can put extra strain on the SI joint, creating a vicious cycle of discomfort. It’s like me and Grandpa arguing over who gets the last bat wing—nobody wins!
References:
- Hogston, P. (2015). The evolution of the human pelvis: Changing adaptations to bipedalism, obstetrics and thermoregulation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370(1663), 20140063. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25602067/
- Foley, B. S., & Buschbacher, R. M. (2014). Sacroiliac joint pain: Anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 93(8), 687-697. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15213481/
- Wong, M., & Kiel, J. (2018). Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Sacroiliac Joint. StatPearls. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30521200/
- Vanelderen, P., Szadek, K., Cohen, S. P., et al. (2010). Sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Practice, 10(5), 470-478. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602717/
How Chiropractic Care Comes to the Rescue
Chiropractic: More Than Just Popping Joints
Now, let’s talk about how chiropractic care swoops in like a superhero (or maybe a friendly monster like yours truly) to tackle SI joint and hip pain. At ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, Dr. Alexander Jimenez doesn’t just crack backs like I crack bad jokes—it’s a holistic, non-invasive approach to get your body moving like a well-oiled hearse. Here’s the clinical scoop on why chiropractic care is a game-changer:
- Fixing Alignment: A misaligned SI joint can throw your whole pelvis out of whack, causing pain in your hips and beyond. Chiropractic adjustments use precise, gentle force to nudge the joint back into place, easing stress on surrounding tissues and calming inflammation (Binns Family Chiropractic, 2024). It’s like straightening a crooked picture frame so everything hangs just right.
- Cooling Inflammation: An inflamed SI joint is like my temper when Eddie hides my favorite tie—red hot and troublesome! Adjustments and soft tissue therapies, like myofascial release, boost blood flow and reduce swelling, dialing down the pain (Vanelderen et al., 2010).
- Boosting Mobility: A stiff SI joint can make you move like you’re stuck in a slow-motion horror flick. Chiropractic care restores joint movement, so you can bend, twist, and walk without feeling like a zombie (Foley & Buschbacher, 2014).
- Strengthening Support: Dr. Jimenez pairs adjustments with exercises to strengthen muscles around the SI joint and hips, like your core and glutes, to keep things stable. It’s like giving your pelvis a team of bodyguards to prevent future flare-ups (Binns Family Chiropractic, 2024).
- Holistic Healing: At ChiroMed, Dr. Jimenez combines chiropractic with functional medicine, nutrition counseling, and acupuncture to tackle the root causes of pain, not just the symptoms. It’s like fixing the whole haunted mansion, not just patching up the creaky stairs (ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez’s Monster-Sized Expertise
Dr. Alex Jimenez, with his dual licensure as a chiropractor and family nurse practitioner, is like the Frankenstein of healthcare—piecing together the best of both worlds! At ChiroMed, he uses advanced imaging like MRIs and diagnostic evaluations to pinpoint the exact cause of your SI joint or hip pain (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.). This isn’t guesswork; it’s precision medicine with a side of heart.
For example, if you’ve got SI joint dysfunction, Dr. Jimenez might use spinal decompression to ease pressure, followed by targeted adjustments to restore alignment. He’ll also check for muscle imbalances or nutritional deficiencies that could be stirring up trouble. It’s a full-body approach that gets results without surgery or a potion bottle full of pills (Jimenez, n.d.).
References:
- Binns Family Chiropractic. (2024). 7 Benefits of Chiropractic Care for Sacroiliac Joint Problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/
- Vanelderen, P., Szadek, K., Cohen, S. P., et al. (2010). Sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Practice, 10(5), 470-478. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602717/
- Foley, B. S., & Buschbacher, R. M. (2014). Sacroiliac joint pain: Anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 93(8), 687-697. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15213481/
- ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine. (n.d.). Home. https://chiromed.com/
- El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX Wellness Chiropractic Care Clinic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Treating Sacroiliac Joint. https://dralexjimenez.com/treating-sacroiliac-joint/
Risk Factors for SI Joint Dysfunction and Hip Pain
What Makes Your SI Joint and Hips Grumble?
Just like my old jalopy breaks down without maintenance, your SI joint and hips can get cranky for a bunch of reasons. Here are the main culprits, with some clinical insight to keep things clear:
- Trauma: A fall, car crash, or sports injury can jolt the SI joint, causing misalignment or inflammation. It’s like dropping a wrench in the gears of my monster mobile (Vanelderen et al., 2010).
- Pregnancy: Hormones during pregnancy loosen ligaments, making the SI joint wobbly and prone to dysfunction. It’s like trying to keep a loose hinge on a swinging door (Foley & Buschbacher, 2014).
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can inflame the SI joint or hip, causing pain that’s as stubborn as Eddie’s howling at the moon (Wong & Kiel, 2018).
- Muscle Imbalances: Weak core or glute muscles, or tight hip flexors, can pull the SI joint out of alignment, like an off-balance seesaw (Werrett, 2024).
- Repetitive Stress: Jobs or activities with lots of sitting, standing, or twisting can wear down the SI joint, like my old boots after too many graveyard strolls (Sacroiliac-Joint-Pain.org, n.d.).
- Anatomical Variations: Some folks have unique sacral shapes or pelvic structures that make SI joint issues more likely, thanks to the wild ways our pelvis evolved (Hogston, 2015; Abitbol, 1987).
How Hip Pain Messes with Your Day
Hip pain, whether from the SI joint or the hip itself, can turn daily tasks into a real monster mash. Walking, sitting, or even lying down can feel like navigating a haunted maze. You might limp like I do after a long night of scaring villagers, or struggle with stiffness that makes bending over trickier than sneaking past Grandpa’s bat radar. Chronic hip pain can also disrupt your sleep, mood, and overall quality of life, leaving you feeling like you’re stuck in a spooky fog (Krishnamurthy et al., 2020).
References:
- Vanelderen, P., Szadek, K., Cohen, S. P., et al. (2010). Sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Practice, 10(5), 470-478. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602717/
- Foley, B. S., & Buschbacher, R. M. (2014). Sacroiliac joint pain: Anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 93(8), 687-697. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15213481/
- Wong, M., & Kiel, J. (2018). Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Sacroiliac Joint. StatPearls. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30521200/
- Werrett, A. (2024). Understanding The Link Between Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction And Hip Pain. MedShun. https://medshun.com/understanding-the-link-between-sacroiliac-joint-dysfunction-and-hip-pain/
- Sacroiliac-Joint-Pain.org. (n.d.). Sacroiliac Hip Pain. https://www.sacroiliac-joint-pain.org/sacroiliac-hip-pain/
- Hogston, P. (2015). The evolution of the human pelvis: Changing adaptations to bipedalism, obstetrics and thermoregulation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370(1663), 20140063. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25602067/
- Abitbol, M. M. (1987). Anatomy and clinical significance of sacral variations: A systematic review. Clinical Anatomy, 30(5), 646-655. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28508536/
- Krishnamurthy, V., et al. (2020). Chronic hip pain in adults: Current knowledge and future prospective. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology, 36(Suppl 1), S56-S61. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33100663/
Small Changes to Keep Your Hips and SI Joint Happy
Dr. Jimenez isn’t just about fixing you up in the clinic—he’s got tips to keep your SI joint and hips happier than me with a fresh batch of Lily’s bat-wing brownies! Here are some practical changes, inspired by his expertise at ChiroMed and LinkedIn insights:
- Posture Power: Sit and stand like you’re posing for a Munster family portrait. Keep your spine straight and avoid slouching to reduce SI joint stress. Dr. Jimenez emphasizes proper body mechanics to prevent strain (Jimenez, n.d.).
- Stretch it Out: Gentle stretches like the figure-four or cat-cow yoga pose keep your hips and lower back loose. Dr. Jimenez often prescribes these to boost flexibility (ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, n.d.).
- Strengthen Your Core: Exercises like planks or bridges build a strong core, supporting your SI joint like a sturdy castle wall. Dr. Jimenez’s rehab programs focus on core stability (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
- Move Smart: Avoid repetitive twisting motions, like swinging a golf club too many times. Dr. Jimenez advises modifying activities to protect the SI joint (https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/).
- Nutrition Boost: An anti-inflammatory diet with salmon, berries, and leafy greens can reduce joint inflammation. Dr. Jimenez’s functional medicine approach includes nutritional counseling (ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, n.d.).
- Use Support: A sacroiliac belt can stabilize the joint during activities, like a corset for your pelvis. Dr. Jimenez often recommends these for extra support (Binns Family Chiropractic, 2024).
These tweaks are like swapping out my rusty bolts for shiny new ones—suddenly, I’m moving smoother than ever!
References:
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Treating Sacroiliac Joint. https://dralexjimenez.com/treating-sacroiliac-joint/
- ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine. (n.d.). Home. https://chiromed.com/
- El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX Wellness Chiropractic Care Clinic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/
- Binns Family Chiropractic. (2024). 7 Benefits of Chiropractic Care for Sacroiliac Joint Problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/
Dr. Alexander Jimenez: El Paso’s Personal Injury Expert
Why Dr. Jimenez is a Cut Above
If you’ve been in a car crash, slip-and-fall, or any other mishap in El Paso, Dr. Alexander Jimenez is your knight in shining scrubs! His dual training as a chiropractor and family nurse practitioner makes him a standout for personal injury cases. Whether it’s whiplash, a sprained SI joint, or hip pain from an accident, Dr. Jimenez uses advanced imaging like MRIs and X-rays to get to the root of your injuries (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
What makes him special is his role as a bridge between medical care and legal documentation. Personal injury cases need detailed medical reports for insurance claims or legal proceedings, and Dr. Jimenez’s dual-scope expertise ensures those reports are spot-on. He uses advanced diagnostics to identify injuries like SI joint dysfunction or hip damage, then creates personalized treatment plans that help you heal while providing the paperwork your legal team needs (Jimenez, n.d.).
For example, after a car accident, Dr. Jimenez might use an MRI to spot soft tissue damage or joint misalignment causing your hip or SI joint pain. He’ll combine chiropractic adjustments, physical therapy, and functional medicine to get you back on your feet, all while documenting everything for your case. It’s like having a doctor and a detective in one (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.)!
Advanced Imaging and Dual-Scope Magic
Dr. Jimenez’s use of advanced imaging is like giving your body an X-ray vision check-up. MRIs and X-rays can reveal hidden issues, like inflammation or micro-tears in the SI joint, that might not show up on a standard exam (Battaglia et al., 2014). His dual-scope approach—blending chiropractic techniques with medical diagnostics—means he can assess both structural (bones and joints) and systemic (inflammation, nutrition) aspects of your injury. This thorough view ensures no stone is left unturned, whether you’re dealing with a sprained SI joint or hip pain from a workplace injury.
References:
- El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX Wellness Chiropractic Care Clinic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Treating Sacroiliac Joint. https://dralexjimenez.com/treating-sacroiliac-joint/
- Battaglia, P. J., et al. (2014). Evaluation of the patient with hip pain. American Family Physician, 89(1), 27-34. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24444505/
The Benefits of Stretching- Video
The Science Behind Chiropractic Care
What the Research Says
Let’s put the humor on hold for a moment (don’t worry, I’ll keep it lighter than a ghost). Science backs chiropractic care as a solid option for SI joint and hip pain. Studies show that chiropractic adjustments can reduce pain and improve function in patients with SI joint dysfunction (Vanelderen et al., 2010). A study in Pain Practice found that manual adjustments significantly cut pain and disability, often with lasting results (Vanelderen et al., 2010).
Research in the American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation shows that chiropractic care, paired with rehab exercises, improves mobility and reduces inflammation in the SI joint, which can also ease hip pain caused by referred pain or altered biomechanics (Foley & Buschbacher, 2014). Plus, a study on hip joint mobilizations suggests they improve pain and function in related conditions, hinting at similar benefits for hip pain tied to SI joint issues (Sarkari et al., 2023).
Our pelvis evolved for walking upright, but that puts unique stress on the SI joint, making it prone to dysfunction (Hogston, 2015). Variations in sacral anatomy, like an extra segment or uneven joint surfaces, can up the risk of pain, which chiropractic care can address by restoring balance (Abitbol, 1987).
References:
- Vanelderen, P., Szadek, K., Cohen, S. P., et al. (2010). Sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Practice, 10(5), 470-478. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602717/
- Foley, B. S., & Buschbacher, R. M. (2014). Sacroiliac joint pain: Anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 93(8), 687-697. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15213481/
- Sarkari, E., et al. (2023). Effect of hip joint mobilisations and strength training on pain, physical function and dynamic balance in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 35, 340-347. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37330770/
- Hogston, P. (2015). The evolution of the human pelvis: Changing adaptations to bipedalism, obstetrics and thermoregulation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370(1663), 20140063. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25602067/
- Abitbol, M. M. (1987). Anatomy and clinical significance of sacral variations: A systematic review. Clinical Anatomy, 30(5), 646-655. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28508536/
Teamwork Makes the Dream Work: Integrating Therapies
At ChiroMed, Dr. Jimenez leads a monster squad of professionals to help you recover. Chiropractic care is often paired with:
- Physical Therapy: To strengthen muscles and improve movement, reducing stress on the SI joint and hips (Binns Family Chiropractic, 2024).
- Acupuncture: To ease pain and boost healing by hitting key points (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
- Nutrition Counseling: To fight inflammation with a diet as wholesome as Lily’s cooking (ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine, n.d.).
- Functional Medicine: To tackle systemic issues like hormonal imbalances or gut health that might contribute to pain (Jimenez, n.d.).
This integrated approach is like assembling a team of ghouls to clean up a haunted house—each brings a unique skill to get the job done!
References:
- Binns Family Chiropractic. (2024). 7 Benefits of Chiropractic Care for Sacroiliac Joint Problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/
- El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX Wellness Chiropractic Care Clinic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/
- ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine. (n.d.). Home. https://chiromed.com/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Treating Sacroiliac Joint. https://dralexjimenez.com/treating-sacroiliac-joint/
Conclusion: A Serious Note on Your Health
Let’s set aside the Herman Munster antics for a moment and get serious. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction and hip pain can significantly impact your daily life, but chiropractic care, led by Dr. Alexander Jimenez at ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine in El Paso, TX, offers a proven, non-invasive solution. By addressing the root causes of pain through adjustments, rehab exercises, and a holistic approach, Dr. Jimenez helps patients regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and live fuller lives.
For personal injury cases, Dr. Jimenez’s dual expertise as a chiropractor and nurse practitioner, combined with advanced imaging and diagnostics, makes him a trusted partner for recovery and legal documentation. His comprehensive care ensures you heal while supporting your case with detailed medical reports.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider, such as Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. The information provided is based on evidence-based research and clinical insights but should not be taken as medical advice without professional consultation. For more information or to schedule a visit, contact ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine at +1 (915) 412-6680 or [email protected].
References:
- Binns Family Chiropractic. (2024). 7 Benefits of Chiropractic Care for Sacroiliac Joint Problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/
- El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). El Paso, TX Wellness Chiropractic Care Clinic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/
- ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine. (n.d.). Home. https://chiromed.com/
- Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Treating Sacroiliac Joint. https://dralexjimenez.com/treating-sacroiliac-joint/
- Hogston, P. (2015). The evolution of the human pelvis: Changing adaptations to bipedalism, obstetrics and thermoregulation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370(1663), 20140063. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25602067/
- Abitbol, M. M. (1987). Anatomy and clinical significance of sacral variations: A systematic review. Clinical Anatomy, 30(5), 646-655. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28508536/
- Vanelderen, P., Szadek, K., Cohen, S. P., et al. (2010). Sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Practice, 10(5), 470-478. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602717/
- Foley, B. S., & Buschbacher, R. M. (2014). Sacroiliac joint pain: Anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 93(8), 687-697. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15213481/
- Wong, M., & Kiel, J. (2018). Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Sacroiliac Joint. StatPearls. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30521200/
- Krishnamurthy, V., et al. (2020). Chronic hip pain in adults: Current knowledge and future prospective. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology, 36(Suppl 1), S56-S61. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33100663/
- Battaglia, P. J., et al. (2014). Evaluation of the patient with hip pain. American Family Physician, 89(1), 27-34. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24444505/
- Sarkari, E., et al. (2023). Effect of hip joint mobilisations and strength training on pain, physical function and dynamic balance in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 35, 340-347. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37330770/