Chiropractic Care: A Comprehensive Guide for The Gluteus Medius Muscle
Discover the advantages of chiropractic care for alleviating discomfort in the gluteus medius muscle and improving movement function.
Chiropractic Care for Gluteus Medius Injuries: A Comprehensive Guide to Hip Pain Relief
Greetings, weary traveler of the musculoskeletal realm, where the gluteus medius lurks like a brooding specter, ready to haunt your hips with every misstep. Picture your pelvis as a gothic mansion, its stability resting on this unassuming muscle, which, when neglected, throws tantrums in the form of hip pain. Fear not, for chiropractic care, led by the expertise of Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, offers a lantern in this fog of discomfort. With a dash of Wednesday Addams’ dark humor, we’ll unravel the clinical rationale behind chiropractic care for gluteus medius injuries, explore environmental culprits behind hip pain, and reveal how small lifestyle changes and non-surgical treatments can banish the pain. This 5,000-word odyssey, crafted for high school readers and seasoned professionals alike, will also spotlight Dr. Jimenez’s role in El Paso’s personal injury cases, where his diagnostic prowess bridges the fields of medicine and law. Let’s dive into the abyss.
The Gluteus Medius: The Silent Guardian of Your Lower Extremities
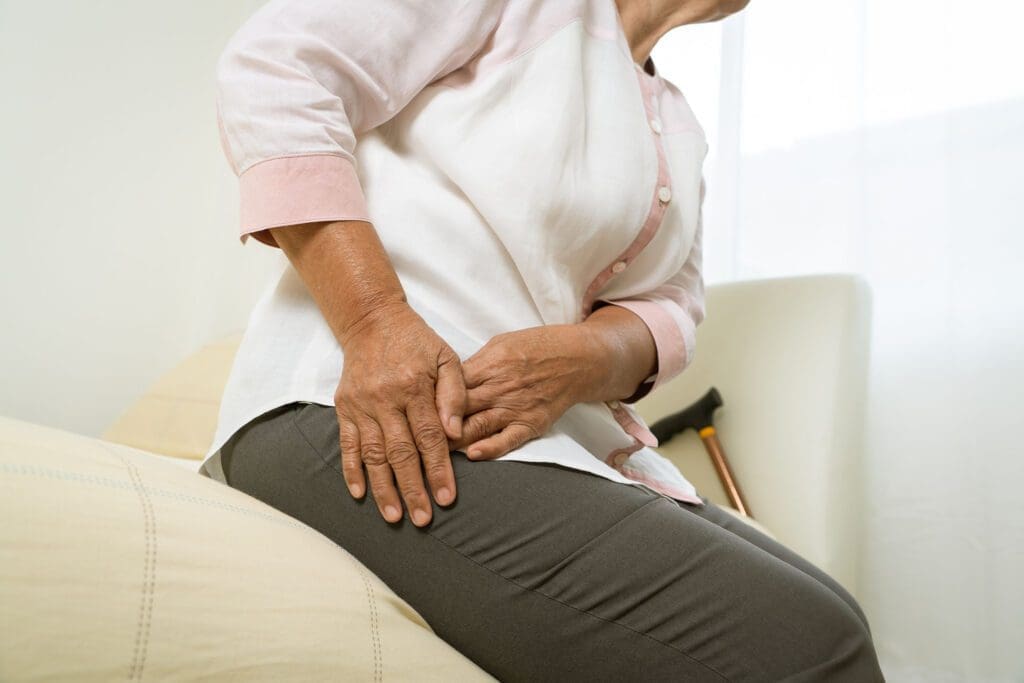
The gluteus medius, tucked away in the upper outer buttocks, is the unsung hero of your hips, much like a loyal butler in a haunted estate. While the gluteus maximus steals the limelight with its size, the medius quietly ensures you don’t topple over like a poorly balanced skeleton. This muscle stabilizes the pelvis during walking, running, or standing on one leg, abducts the hip (lifting your leg sideways), and aids in internal and external rotation (Foley & Bulbrook, 2019). Without it, your gait would resemble a drunken ghoul stumbling through a graveyard.
When the gluteus medius weakens or tears, chaos ensues. Lateral hip pain, a limp, or even lower back discomfort can emerge as the body compensates for the instability (Khamis & Yizhar, 2021). Its role in the lower extremities is pivotal: it links the hips to the knees and ankles, ensuring smooth coordination. A compromised gluteus medius can trigger a cascade of issues, like patellofemoral pain syndrome (knee pain) or shin splints, as your body scrambles to maintain balance (Semple et al., 2020). Think of it as the keystone in an arch—remove it, and the whole structure crumbles.
References
Foley, B. T., & Bulbrook, B. D. (2019). Gluteus Medius Muscle Function in People with and without Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 20(1), 463. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31623534/
Khamis, S., & Yizhar, Z. (2021). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, 14(6), 432–439. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34734776/
Semple, R., et al. (2020). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 29(6), 811–819. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31995322/
Environmental Villains: Why Your Hips Are Haunted by Pain
Hip pain doesn’t materialize out of thin air—it’s conjured by environmental factors that creep up like shadows in a storm. Let’s unmask these culprits, each contributing to the gluteus medius’s misery:
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Hours spent glued to a chair, whether studying or binge-watching a grim series, weaken the gluteus medius. Prolonged sitting tightens hip flexors and stifles blood flow, leaving the muscle as irritable as a ghost trapped in a dusty attic (El Paso Chiropractor, 2016).
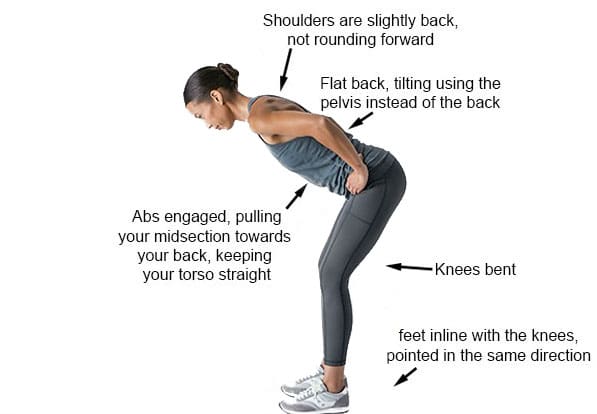
- Poor Posture: Slouching or leaning on one leg is like inviting a poltergeist to wreak havoc on your pelvis. It strains the gluteus medius, leading to pain and instability (Wong & Lee, 2023).
- Unsuitable Footwear: Those trendy but flimsy shoes? They’re as supportive as an Ouija board in a windstorm. Flat feet or overpronation misalign the lower extremities, stressing the gluteus medius (Kibler et al., 2020).
- Overuse Injuries: Runners, dancers, or athletes who push too hard without proper form are practically begging for a gluteus medius meltdown. Repetitive stress without rest is like a horror movie marathon—exhausting and painful (Santos et al., 2020).
- Trauma from Personal Injury: In El Paso, car accidents or falls are as common as tumbleweeds. These traumas can directly injure the gluteus medius or cause compensatory issues, disrupting its function (Jimenez, n.d.).
These factors create a vicious cycle: a weakened gluteus medius leads to instability, which invites more pain. It’s like a haunted house where every creak triggers another fright.
References
El Paso Chiropractor. (2016). Strengthening the gluteus medius after injury. El Paso Chiropractor Blog. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on chiropractic care. ChiroMed. https://chiromed.com/
Kibler, W. B., et al. (2020). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(12), 1271–1287. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303311/
Santos, T. R., et al. (2020). Core stability and hip exercises improve physical function and activity in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 36(8), 903–910. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32208190/
Wong, C. K., & Lee, J. (2023). Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. American Family Physician, 107(1), 27–36. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36661418/
Chiropractic Care for Leg Instability- Video
The Chiropractic Exorcism: Dr. Jimenez’s Clinical Rationale
Enter Dr. Alexander Jimenez, El Paso’s chiropractic maestro, wielding adjustments like a sorcerer banishing demons. His approach to gluteus medius injuries is rooted in restoring alignment and function to the musculoskeletal system, offering relief where pills and scalpels fall short. With credentials as a Doctor of Chiropractic, Advanced Practice Registered Nurse, and Family Nurse Practitioner, Dr. Jimenez is a triple threat against hip pain (Jimenez, n.d.).
How Chiropractic Care Saves Your Hips
Chiropractic adjustments target misalignments in the spine and pelvis that overstress the gluteus medius. A tilted pelvis can pull on the muscle like a cruel puppeteer, causing pain or tears (Foley & Bulbrook, 2019). By realigning these structures, chiropractic care reduces tension, improves blood flow, and restores nerve function, allowing the gluteus medius to heal. It’s like resetting a cursed grandfather clock—suddenly, everything ticks in harmony.
Dr. Jimenez enhances this with advanced diagnostics, using X-rays, MRIs, or functional assessments to pinpoint the root of hip pain (Kibler et al., 2020). His dual-scope approach—combining chiropractic adjustments with detailed evaluations—ensures a tailored treatment plan. For personal injury cases, common in El Paso, he bridges the gap between medical care and legal documentation, providing detailed reports to support claims while guiding patients toward recovery (Jimenez, n.d.).
Non-Surgical Allies in the Fight Against Hip Pain
Chiropractic care is the conductor of a grimly effective orchestra, with non-surgical treatments playing key roles:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises such as side-lying leg lifts or clamshells strengthen the gluteus medius, fortifying it against future strains (Semple et al., 2020).
- Dry Needling: This technique, like acupuncture with a sinister twist, inserts needles into trigger points to release muscle tension. Research supports its efficacy for gluteus medius-related pain (Navarro-Santana et al., 2021).
- Massage Therapy: Deep tissue massage boosts circulation and eases tightness, like soothing a restless spirit in your hips (El Paso Chiropractor, 2016).
- Core Stability Training: Strengthening the core and hips together reduces stress on the gluteus medius, improving overall function (Santos et al., 2020).
This multi-faceted approach tackles the overlapping risk profiles of hip pain, from muscle weakness to biomechanical imbalances, ensuring a comprehensive recovery.
References
El Paso Chiropractor. (2016). Strengthening the gluteus medius after injury. El Paso Chiropractor Blog. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
Foley, B. T., & Bulbrook, B. D. (2019). Gluteus Medius Muscle Function in People with and without Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 20(1), 463. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31623534/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on chiropractic care. ChiroMed. https://chiromed.com/
Navarro-Santana, M. J., et al. (2021). Effectiveness of dry needling and ischemic trigger point compression in the gluteus medius in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized short-term clinical trial. Pain Medicine, 22(10), 2232–2241. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34474445/
Santos, T. R., et al. (2020). Core stability and hip exercises improve physical function and activity in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 36(8), 903–910. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32208190/
Kibler, W. B., et al. (2020). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(12), 1271–1287. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303311/
Personal Injury in El Paso: Dr. Jimenez’s Dual Role
In El Paso, personal injury cases—car crashes, slip-and-falls, or workplace accidents—are as frequent as storms in a desert. These incidents often injure the gluteus medius, either directly through trauma or indirectly via compensatory movements. Dr. Jimenez shines as a distinguished practitioner, guiding victims through recovery while supporting their legal battles (Jimenez, n.d.).
His approach is meticulous: advanced imaging (X-rays, MRIs) and functional tests reveal the extent of gluteus medius damage, while dual-scope procedures combine clinical treatment with precise documentation (Kibler et al., 2020). This makes him a vital liaison between medical care and legal systems, ensuring injuries are thoroughly assessed and reported for claims. Picture a patient limping into his office post-accident: Dr. Jimenez uses adjustments, dry needling, and exercises to restore their hip function, while his detailed reports fortify their legal case, cutting through bureaucratic fog like a well-aimed dagger.
References
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on chiropractic care. ChiroMed. https://chiromed.com/
Kibler, W. B., et al. (2020). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(12), 1271–1287. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303311/
Small Changes for Big Relief: Practical Tips from Dr. Jimenez
Dr. Jimenez’s wisdom extends beyond the clinic, offering practical tweaks to keep your gluteus medius from staging a revolt. Channeling Wednesday Addams’ grim efficiency, here are tips to fortify your hips:
- Break the Sitting Curse: Stand and stretch every 30 minutes to free your gluteus medius from the shackles of your chair (El Paso Chiropractor, 2016).
- Strengthen Strategically: Exercises like side-lying leg lifts or clamshells build gluteus medius strength, like arming your muscle against unseen foes (Semple et al., 2020).
- Choose Wise Footwear: Opt for shoes with arch support to align your lower extremities. Ditch flimsy flats—they’re as useless as a broken pentagram (Kibler et al., 2020).
- Posture Vigilance: Stand evenly, shoulders back, like a statue in a haunted manor. Good posture keeps your pelvis balanced (Wong & Lee, 2023).
- Sleep with Care: Place a pillow between your knees when side-sleeping to align your hips, like tucking them into a cozy crypt (El Paso Chiropractor, 2016).
These small changes, paired with chiropractic care, can prevent hip pain from returning like an unwanted specter.
References
El Paso Chiropractor. (2016). Strengthening the gluteus medius after injury. El Paso Chiropractor Blog. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
Kibler, W. B., et al. (2020). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(12), 1271–1287. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303311/
Semple, R., et al. (2020). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 29(6), 811–819. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31995322/
Wong, C. K., & Lee, J. (2023). Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. American Family Physician, 107(1), 27–36. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36661418/
A Touch of Dark Humor
Let’s pause for a moment of morbid levity. Imagine your gluteus medius as a grumpy ghoul, muttering curses every time you sit too long or wear those treacherous flip-flops. It’s not just a muscle—it’s a diva, throwing fits in the form of hip pain. Chiropractic care, under Dr. Jimenez’s steady hand, is like Wednesday Addams glaring at the muscle and saying, “Calm down, or I’ll make you do clamshells until you’re silent.” His adjustments and treatments banish the pain with the precision of a guillotine, leaving your hips grateful and quiet.
Conclusion: A Serious Note
While we’ve woven a thread of dark humor to lighten this journey, hip pain and gluteus medius injuries are serious matters that can disrupt mobility and quality of life. Chiropractic care, as practiced by Dr. Alexander Jimenez in El Paso, offers a clinically proven, non-surgical path to relief. By addressing environmental triggers, integrating complementary treatments, and adopting small lifestyle changes, you can reclaim your hip health. For personal injury victims, Dr. Jimenez’s expertise ensures both physical recovery and robust legal support, making him a beacon of hope in a challenging landscape.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any treatment. The information provided is based on credible sources but does not replace a medical evaluation.
References
El Paso Chiropractor. (2016). Strengthening gluteus medius after injury. El Paso Chiropractor Blog. https://www.elpasochiropractorblog.com/2016/10/strengthening-gluteus-medius-after.html
Foley, B. T., & Bulbrook, B. D. (2019). Gluteus Medius Muscle Function in People with and without Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 20(1), 463. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31623534/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Clinical insights on chiropractic care. ChiroMed. https://chiromed.com/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Professional profile. LinkedIn. https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Khamis, S., & Yizhar, Z. (2021). Lateral hip pain: Relation to greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, 14(6), 432–439. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34734776/
Kibler, W. B., et al. (2020). Posterior, lateral, and anterior hip pain due to musculoskeletal origin: A narrative literature review of history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(12), 1271–1287. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303311/
Navarro-Santana, M. J., et al. (2021). Effectiveness of dry needling and ischemic trigger point compression in the gluteus medius in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized short-term clinical trial. Pain Medicine, 22(10), 2232–2241. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34474445/
Santos, T. R., et al. (2020). Core stability and hip exercises improve physical function and activity in patients with non-specific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 36(8), 903–910. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32208190/
Semple, R., et al. (2020). A systematic review of rehabilitation exercises to progressively load the gluteus medius. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 29(6), 811–819. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31995322/
Wong, C. K., & Lee, J. (2023). Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. American Family Physician, 107(1), 27–36. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36661418/