Brain Health Tips and Strategies Using Functional Wellness
Discover the benefits of functional wellness for brain health for maintaining peak cognitive performance and overall mental wellness.
Introduction
The brain is responsible for all the body’s functions. It controls a complex network of communication between nerves, muscles, joints, and organs. This remarkable organ, which weighs approximately three pounds, contains billions of neurons that continually work to regulate functions such as breathing, heart rate, movement, thought, and emotion (Cleveland Clinic, 2025). Learning how the brain talks to the rest of the body can help you stay healthy and deal with neurological problems without surgery.
The nervous system is like the body’s information superhighway. The brain sends and gets millions of signals every second (Cancer Canada, 2020). People have the best health, clear thinking, coordinated movement, and balanced emotions when this communication flows smoothly. But when interference gets in the way of these pathways, different symptoms can show up that make life harder and affect your health. This article examines the brain’s fundamental functions, its connections to other parts of the body, the impact of environmental factors on neurological health, and natural treatments supported by research that promote the nervous system’s healing and optimal functioning.
The Brain’s Essential Functions for the Body
Central Command and Control
As the primary command center for all body processes, the brain integrates sensory data and triggers the right reactions (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024). The central nervous system, comprising the brain and spinal cord, controls critical activities such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. Automatic processes, including respiration, heart rate regulation, and blood vessel width, are managed by the brainstem, which is situated at the base of the brain (National Institutes of Health, 2022). The survival of humans would be impossible without these vital factors.
A crucial junction between the neurological and endocrine systems is the hypothalamus (National Institutes of Health, 2022). This small yet powerful part of the brain detects changes in the body and responds by stimulating glands and organs to produce more hormones. In addition to managing bodily temperature and emotions, the hypothalamus also governs eating and sleeping patterns (Mayo Clinic, 2024). The brain maintains homeostasis through these processes, which stabilize the internal environment of the body despite changes outside.
Processing and Integration
The brain interprets sensory data from the surroundings and converts it into experiences that have value beyond fundamental survival needs (Cleveland Clinic, 2025). By directing communications between the cerebrum and the spinal cord, the thalamus serves as a gatekeeper. The hippocampus, on the other hand, transmits information to be stored in different parts of the cerebrum and is responsible for memory creation and retrieval. Humans are able to learn, remember, and adjust to their environment because of this ongoing processing.
The brain’s extraordinary capability for integration is shown by its ability to coordinate intricate motions. Voluntary motions are planned, coordinated, and carried out by the motor cortex, which is situated in the rear of the frontal lobe (TutorChase, 2023). It instructs muscles to contract or relax in certain patterns by sending signals down the spinal cord. The cerebellum, situated in the rear of the brain, controls these motions, maintaining balance and posture while ensuring fluid and accurate movements. These areas work together to allow people to do a variety of tasks, from basic hand motions to intricate sports movements.
Brain-Muscle-Joint-Nerve Correlation
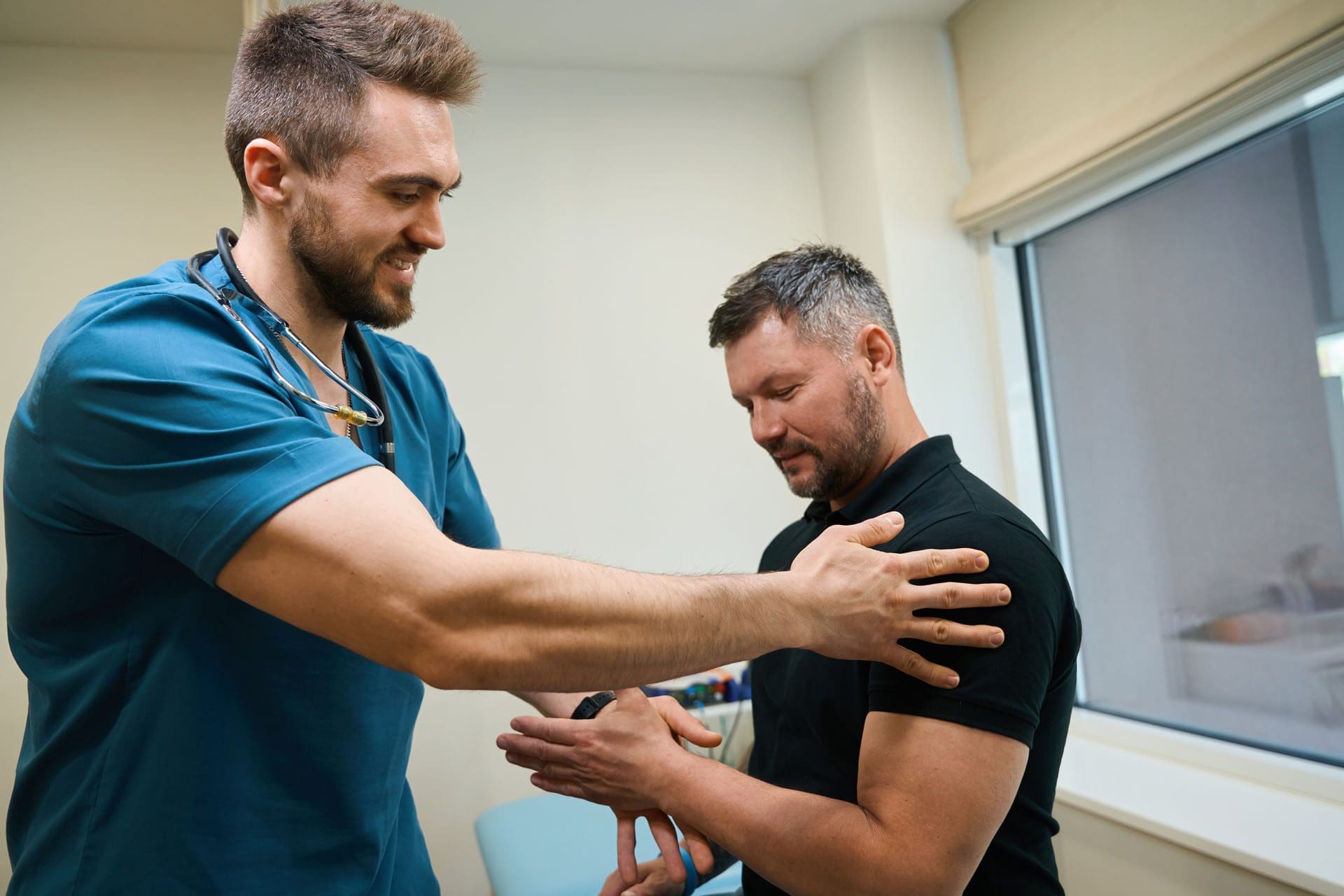
The Neuromuscular Connection
The brain controls muscle coordination and movement through an intricate network that connects the central nervous system to every muscle in the body (TutorChase, 2023). Motor neurons serve as the primary communication pathway, transmitting electrical signals from the brain through the spinal cord to the muscle fibers. This process begins in the motor cortex, where neurons send signals down the corticospinal tract to lower motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord. From there, acetylcholine is released at the neuromuscular junction, triggering muscle contraction (Wikipedia, 2003).
This neuromuscular coordination involves both voluntary and involuntary movements (Orlando Health, 2021). While skeletal muscles respond to conscious commands for movements such as walking or reaching, smooth muscles in organs like the heart, lungs, and intestines function automatically. The nervous system coordinates both types, ensuring that breathing continues during sleep and the heart beats steadily without conscious effort. When neuromuscular communication functions properly, movements flow smoothly, muscles respond appropriately to signals, and the body maintains balance and coordination.
Joint Mechanics and Proprioception
Joints represent critical points where bones meet, providing the body with a wide range of motion (Orlando Health, 2021). The brain continuously monitors joint position and movement through specialized sensory receptors called mechanoreceptors. These receptors send constant feedback to the brain about the body’s position in space, a sense known as proprioception. This information allows the brain to coordinate movements precisely, maintain balance, and adjust posture automatically.
The relationship between the spine and nervous system deserves special attention. The spinal column protects the delicate spinal cord while providing structural support and allowing movement (True Wellness Chiropractic, 2025). When vertebrae maintain proper alignment, nerve signals travel freely between the brain and body. However, misalignments can create pressure on nerves, disrupting communication and potentially causing pain, dysfunction, or altered sensation. This connection explains why spinal health plays such a crucial role in overall nervous system function.
Neural Pathways and Signal Transmission
The nervous system relies on neural pathways to carry information throughout the body (Wikipedia, 2004). Ascending sensory pathways transmit information from the periphery to the brain, while descending motor pathways carry commands from the brain to muscles and organs. These pathways use both electrical signals within neurons and chemical messengers called neurotransmitters at synapses, the tiny gaps between neurons.
The efficiency of signal transmission affects every aspect of health and function (Paris Brain Institute, 2025). Nerve impulses travel along axons, triggering the release of neurotransmitters at synaptic knobs. These chemical messengers cross the synapse and either activate or inhibit the next neuron in the pathway. The frequency of these signals determines the intensity of the response. When pathways function optimally, the brain receives accurate sensory information and delivers precise motor commands. Disruptions in these pathways can lead to sensory changes, motor difficulties, or impaired coordination.
Brain Communication with Vital Organs
The Vagus Nerve: The Body’s Information Superhighway
The vagus nerve represents one of the most important communication pathways between the brain and body (Yale Medicine, 2022). This massive, meandering network contains more than 100,000 nerve fibers that travel from nearly every internal organ to the base of the brain and back again. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting the “rest and digest” response that enables the body to relax, recover, and maintain balance after stress.
Communication through the vagus nerve occurs bidirectionally (Yale Medicine, 2022). Signals from organs travel up to the brain, informing it about heart rate, blood pressure, digestive activity, and other vital functions. Simultaneously, the brain sends signals down through the vagus nerve to regulate these same functions. This constant feedback loop allows the brain to maintain homeostasis by adjusting organ function in response to changing conditions. High vagal tone, which indicates strong vagus nerve function, associates with better stress recovery, improved emotional regulation, and enhanced overall health (Mass General Hospital, 2024).
Cardiovascular Regulation
The brain exerts continuous control over cardiovascular function through multiple pathways (Science, 2021). The medulla oblongata, located in the brainstem, regulates heart rhythms and blood pressure automatically. Meanwhile, the hypothalamus coordinates responses to stress or exercise by activating the sympathetic nervous system, which increases heart rate and redirects blood flow to muscles. This dual control system enables the body to respond rapidly to changing demands while maintaining stable function during periods of rest.
The brain-heart connection extends beyond simple regulation of heartbeat (Wikipedia, 2024). Brain-heart interactions link cardiac physiology to activity in the central and peripheral nervous system, potentially explaining how cardiovascular arousal influences decision-making and emotional regulation. Research indicates that the brain continuously monitors cardiac signals, utilizing this information to adjust autonomic nervous system activity and maintain cardiovascular health.
Respiratory Control and Metabolism
Breathing represents another vital function under constant brain control (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 2024). The medulla oblongata contains specialized centers that monitor carbon dioxide levels in the blood and automatically adjust breathing rate and depth. This regulation occurs without conscious thought, yet people can also voluntarily control breathing, demonstrating the integration of automatic and voluntary nervous system functions.
The brain’s regulation extends to metabolic processes throughout the body. Through the endocrine system, the hypothalamus regulates thyroid function, which in turn controls metabolic rate (National Institutes of Health, 2022). It also regulates hunger, thirst, and body temperature. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” releases hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproductive function under the direction of the hypothalamus. This complex hormonal control system works in conjunction with neural pathways to maintain the body’s internal balance.
Environmental Factors Affecting Brain Activity and Body Function
Air Pollution and Neurological Impact
Environmental factors significantly influence brain health and function, with air pollution emerging as a major concern (Nature, 2022). Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) can travel deep into body tissues after inhalation due to its small size. These particles cause inflammation and damage to organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and brain. Research indicates that increased exposure to PM2.5 is linked to changes in brain structure in older adults, including brain atrophy, which often precedes the onset of dementia symptoms (UC Davis, 2025).
Air pollution affects brain function through multiple mechanisms (Lone Star Neurology, 2024). These particles trigger oxidative stress, which damages cells by producing harmful free radicals. Oxidative damage impairs memory and cognitive functions, leading to decreased mental clarity and impaired performance. Nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide also contribute to brain dysfunction, causing mood disorders, persistent depression, and poor cognitive function. The connection between air pollution and brain health highlights the importance of environmental quality for neurological wellbeing.
Stress and Neurological Function
Chronic stress has a profound impact on brain structure and function (Northwestern Medicine, 2022). When the body experiences stress, it releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, triggering the “fight or flight” response. While this response is helpful in acute situations, chronic activation can lead to lasting changes in the brain. Stress impacts areas responsible for memory, emotion regulation, and decision-making, including the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex (Neurology Center NJ, 2025).
The neurological impact of stress manifests in various ways (Foothills Neurology, n.d.). Chronic stress can cause difficulty concentrating, impaired memory, heightened emotional sensitivity, and increased risk of neurological disorders. Research identifies chronic stress as a potential risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions (Northwestern Medicine, 2022). The stress-inflammation connection also plays a role, as elevated stress increases inflammatory markers throughout the body, including the brain, potentially contributing to cognitive decline and mood disorders.
Nutrition and Brain Health
Dietary factors have a significant impact on brain function and cognitive abilities (NCBI, 2017). Multiple nutrients have been identified as having direct effects on cognitive processes and emotions by regulating neurotransmitter pathways, synaptic transmission, and membrane fluidity. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), represent essential components of neuronal membranes and play crucial roles in brain plasticity and cognition (NCBI, 1998). Dietary deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids has been associated with increased risk of attention-deficit disorder, dyslexia, dementia, depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Other nutrients contribute to cognitive health through various mechanisms (Harvard Health, 2024). Leafy greens, such as kale, spinach, and broccoli, contain brain-healthy nutrients, including vitamin K, lutein, folate, and beta-carotene, which may help slow cognitive decline. B vitamins, including B6, B12, and folate, support mood regulation and memory while promoting overall brain health. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, dark chocolate, and green tea, protect brain cells from oxidative damage. The connection between nutrition and brain function highlights the importance of making informed dietary choices to support neurological health throughout life.
Sleep Quality and Brain Restoration
Sleep plays a critical role in brain health and function (Professional Heart Association, 2024). During sleep, particularly deep sleep, the brain performs essential maintenance and repair processes. The glymphatic system, which becomes highly active during sleep, clears harmful waste products and toxins that accumulate during waking hours (UC Davis Medicine, 2023). This cleansing process helps remove proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases, thereby maintaining healthy brain function.
Sleep quality affects multiple aspects of brain health (NCBI, 2023). Memory consolidation occurs primarily during sleep, as the brain strengthens and integrates newly acquired information into long-term memory. Sleep also supports neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections and reorganize existing ones. Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep duration associates with increased risk of cognitive decline, mood disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases (UCSF, 2024). Sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea, can cause a disrupted oxygen supply to the brain, leading to oxidative stress and impaired brain function during sleep periods.
Neurological Disorders and Overlapping Risk Profiles
Understanding Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders represent conditions that affect how the nervous system functions, targeting the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body (Cleveland Clinic, 2024). These conditions can cause physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral symptoms that significantly impact quality of life. Hundreds of different neurological disorders exist, ranging from common conditions like migraines and epilepsy to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
The causes of neurological disorders vary widely (Cleveland Clinic, 2024). Some results stem from genetic factors, while others arise from infections, injuries, autoimmune responses, or degenerative processes. Environmental toxins, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, can impair brain function and contribute to the development of neurological diseases (NCBI, 2023). Many neurological conditions involve inflammation in the brain or nervous system, leading to progressive damage and functional decline. Understanding these diverse causes helps guide prevention strategies and treatment approaches.
Overlapping Symptoms and Risk Profiles
Many neurological and psychiatric disorders exhibit overlapping symptoms and shared brain mechanisms (NCBI, 2020). Research demonstrates that functional overlaps exist between conditions like mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and major depressive disorder, as well as between epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia. This overlap occurs because different disorders can affect similar brain regions and neural pathways, producing comparable symptoms despite distinct underlying causes.
The complexity of overlapping symptoms presents diagnostic challenges (Practical Neurology, 2025). Self-reported symptoms can result from multiple conditions, making it difficult to distinguish between different neurological or psychiatric disorders. For example, depression can contribute to diagnoses of major depressive disorder, adjustment disorder, and borderline personality disorder. Similarly, cognitive dysfunction may result from neuroinflammation, sleep disorders, hormonal imbalances, or neurodegenerative processes. Recognizing these overlaps helps healthcare providers develop more comprehensive and personalized treatment approaches.
Inflammation and Neurological Dysfunction
Neuroinflammation represents a common factor in many neurological conditions (Frontiers, 2024). Peripheral inflammation can trigger central nervous system inflammatory responses, contributing to cognitive dysfunction. The mechanisms involve the infiltration of peripheral immune cells into the central nervous system and the activation of microglia and astrocytes, the brain’s resident immune cells. This inflammatory cascade can damage neurons, impair neurotransmission, and disrupt normal brain function.
The relationship between inflammation and cognitive function appears bidirectional (Neurology, 2022). Chronic low-grade inflammation in midlife associates with poorer cognitive performance later in life, even when measured before obvious symptoms appear. Inflammatory markers, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and C-reactive protein (CRP), predict cognitive decline in the general population. Conversely, cognitive and emotional stress can increase inflammatory markers, creating a cycle that potentially accelerates neurological dysfunction.
Common Neurological Symptoms
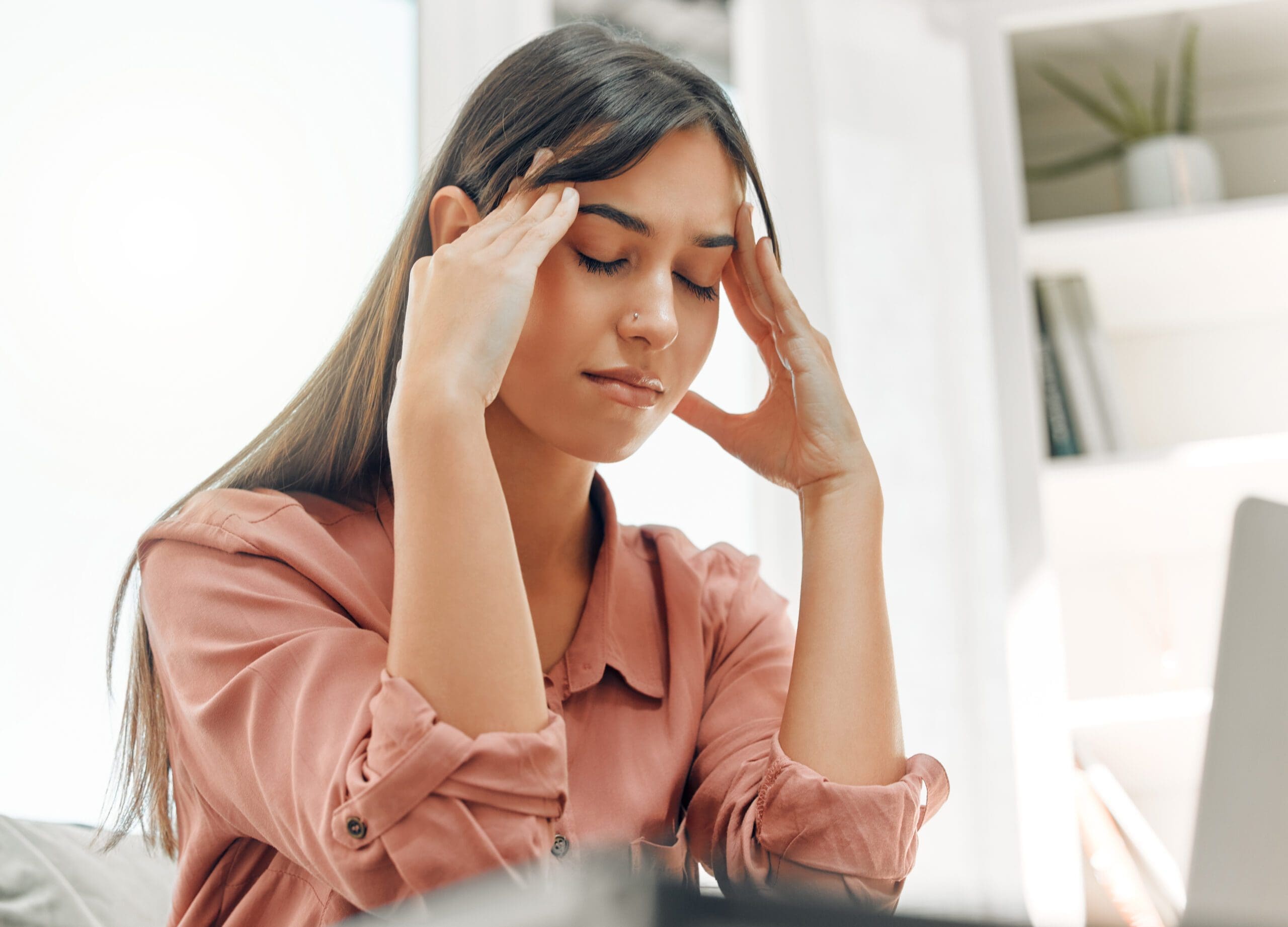
Headaches and Migraines
Headaches represent one of the most common neurological symptoms, ranging from mild tension headaches to severe migraines (NINDS, 2023). Primary headache disorders, including migraines, tension-type headaches, and cluster headaches, occur without another underlying condition. Secondary headaches result from other health issues that affect the brain, such as blood vessel disorders, infections, or structural abnormalities.
Migraines represent a neurological condition that extends beyond simple headaches (Yale Medicine, 2023). They often include a constellation of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual or sensory disturbances called auras. Genetics account for about half of all migraines, while changes in brainstem interactions with the trigeminal nerve and imbalances in brain chemicals like serotonin contribute to migraine development (Mayo Clinic, 2025). Understanding migraines as a neurological disorder rather than just a headache helps guide more effective treatment approaches.
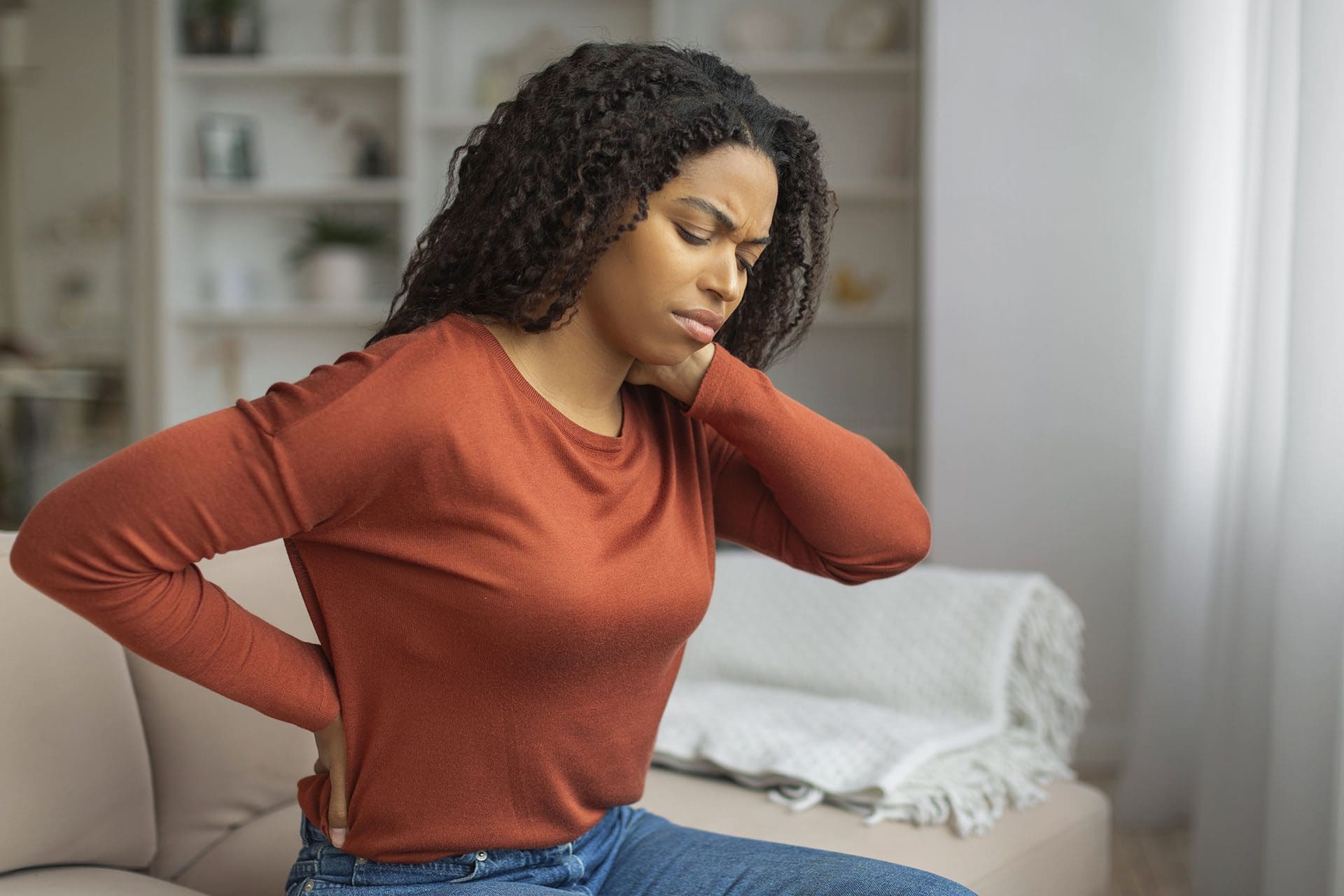
Inflammation and Pain
Neuroinflammation contributes to various pain syndromes and neurological symptoms (Harvard Magazine, 2025). Scientists have linked neuroinflammation with cognitive decline, higher risks for age-related cognitive impairment, and neurodegenerative diseases. Inflammation in the nervous system can cause pain through multiple mechanisms, including direct nerve irritation, increased sensitivity of pain receptors, and alterations in pain processing pathways in the brain and spinal cord.
Chronic pain often involves neurological changes that persist beyond the initial injury or illness (NCBI, 2019). Chiropractic care has been shown to impact the “pain matrix” in the brain, potentially providing pain relief through effects on central nervous system processing. This demonstrates how addressing nervous system function can influence pain perception and inflammatory responses throughout the body.
Fatigue and Energy Dysfunction
Fatigue represents a complex neurological symptom influenced by multiple factors (Frontiers, 2017). Neuroinflammation plays a significant role in the development of fatigue, particularly through its effects on basal ganglia function and dopamine pathways. Inflammatory cytokines influence dopamine function, resulting in reduced motivation and altered reward processing in the brain. This explains why fatigue often accompanies inflammatory conditions, even when physical demands remain minimal.
The connection between brain inflammation and muscle fatigue highlights the brain-body relationship (Washington University, 2016). Neuroinflammation can cause muscle weakness and fatigue by disrupting communication between the brain and muscles. This mechanism helps explain the severe fatigue experienced in conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and post-viral syndromes. Addressing neuroinflammation through natural approaches may help reduce fatigue and restore energy levels.
Cognitive Issues and Brain Fog
Cognitive dysfunction manifests in various ways, including memory problems, difficulty concentrating, slower processing speed, and reduced mental clarity, often called “brain fog” (Interactive Health Clinic, 2024). These symptoms can result from neuroinflammation, poor sleep, hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, or chronic stress. The multifactorial nature of cognitive dysfunction requires comprehensive assessment and treatment approaches.
Inflammation particularly impacts cognitive function through effects on brain areas involved in learning and memory (NCBI, 2010). Neuroinflammation leads to a significant reduction in genes involved in learning and memory processes. Additionally, inflammatory processes can affect neurotransmitter balance, blood flow to the brain, and neuronal energy metabolism. Peripheral inflammation, even when originating outside the brain, can trigger central nervous system inflammatory responses that impair cognitive abilities.
Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disorders frequently accompany neurological conditions and can themselves cause neurological symptoms (Professional Heart Association, 2024). Sleep-disordered breathing, insomnia, circadian rhythm disorders, and extreme sleep duration are all associated with adverse brain health outcomes. These sleep problems can contribute to stroke risk, subclinical cerebrovascular disease, and increased likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.
The relationship between sleep and brain function operates bidirectionally (Neurology Center NJ, 2025). Neurological conditions can disrupt sleep through effects on sleep-wake regulation, while poor sleep impairs brain function and may accelerate neurological decline. Symptoms indicating neurological causes of sleep problems include chronic fatigue despite adequate sleep time, frequent nighttime awakenings, unexplained daytime drowsiness, brain fog, and headaches or memory problems associated with poor sleep quality.
Muscle Instability and Weakness
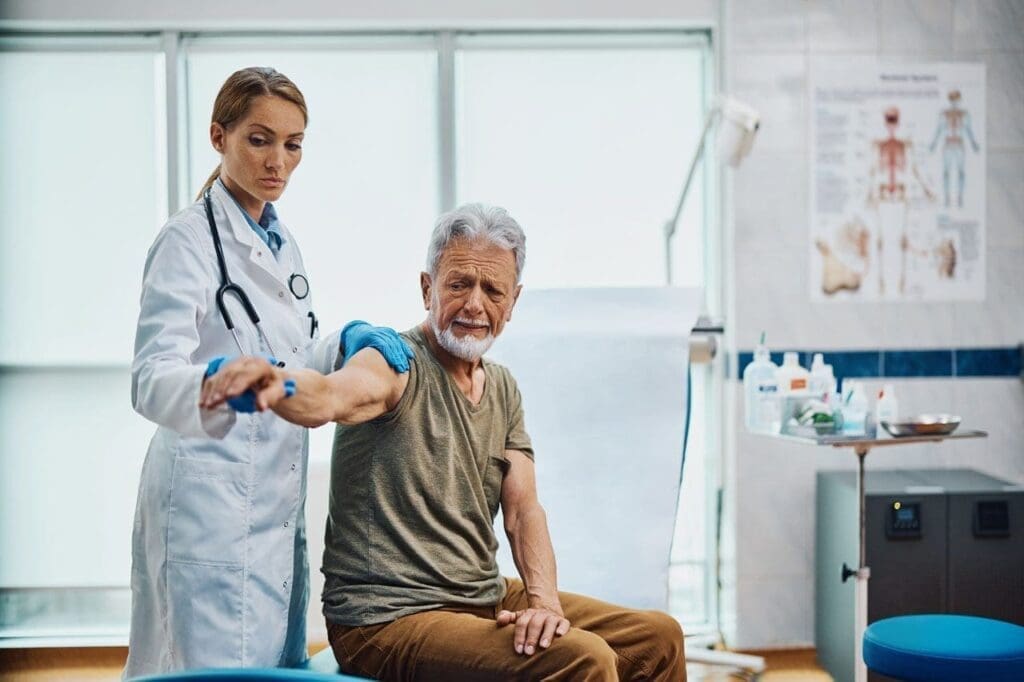
Neuromuscular disorders affect the communication between nerves and muscles, resulting in muscle weakness, fatigue, and instability (University of Michigan Health, 2004). These conditions can involve motor neurons in the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, the neuromuscular junction, or the muscles themselves. Common neuromuscular disorders include myasthenia gravis, where antibodies disrupt nerve-muscle communication, and various forms of neuropathy that affect peripheral nerves.
Muscle weakness and instability can significantly impair function and quality of life (NINDS, 2025). The symptoms may include difficulty walking, problems with balance and coordination, muscle cramps or spasms, and progressive weakness over time. Because these symptoms can result from multiple different neurological conditions, comprehensive evaluation by healthcare providers helps identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
The Power Of Chiropractic Care in Injury Rehabilitation- Video
Non-Surgical Treatments to Boost Neurological Health
Chiropractic Care and Nervous System Function
Chiropractic care focuses on optimizing nervous system function through spinal adjustments and other manual therapies (El Paso Injury Medical Clinic, 2025). According to Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, a board-certified family practice nurse practitioner and chiropractor in El Paso, Texas, chiropractic care benefits the central nervous system by reducing interference to nerve impulses traveling between the brain and body (EIHMD, 2022). This is accomplished by correcting vertebral subluxations, misalignments of the vertebrae that can put pressure on nerves and cause them to malfunction. Research demonstrates that chiropractic adjustments can alter brain function and processing (NCBI, 2019). A study has shown that chiropractic spinal manipulation alters pain perception and neural activity during pain experiences. The adjustments impact both the biomechanical movement patterns of the spine and proprioceptive processing while directly affecting the pain matrix in the brain. This multi-level effect explains how chiropractic care can provide relief for various conditions beyond simple back pain.
Dr. Jimenez’s clinical approach integrates chiropractic care with functional medicine principles (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). His practice emphasizes evidence-based treatment protocols that focus on restoring health naturally rather than relying on invasive procedures or addictive medications. By combining advanced medical expertise with chiropractic techniques, Dr. Jimenez addresses a wide range of conditions, including chronic pain, migraines, fibromyalgia, and neurological dysfunction. His holistic approach recognizes that optimal nervous system function requires addressing multiple factors, including spinal alignment, nutrition, stress management, and lifestyle behaviors.
Restoring Communication Between Brain and Body
Chiropractic adjustments enhance brain-body communication by improving the function of neural pathways (Camarata Chiropractic, 2023). When vertebrae shift out of proper alignment, they can compress or irritate nerves, disrupting signal transmission between the brain and body. Adjustments relieve this pressure, allowing clearer communication and optimizing the pathways nerves use to send motor commands and sensory feedback. This improved communication enhances coordination, reflexes, and overall nervous system efficiency. The neurological effects of chiropractic care extend beyond local spinal effects (Pure Well Chiropractic, 2025). Adjustments stimulate mechanoreceptors, specialized sensory receptors in the joints and muscles of the spine. This mechanoreceptor activity sends signals to the brain, providing valuable information about body position and movement. By improving mechanoreceptor activity, chiropractic care enhances proprioception and overall body awareness while reducing nociceptive input associated with pain.
Chiropractic care may influence neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections and adapt its function (IINN, 2023). When neuroplasticity is impaired, it can lead to symptoms such as brain fog, memory issues, difficulty with sensory processing, and impaired motor coordination. Chiropractic adjustments to the spine can positively influence neuroplasticity, potentially supporting the brain’s adaptive capacity and resilience. This influence on brain plasticity may explain some of the cognitive and emotional benefits patients report from chiropractic care.
Functional Wellness and Integrative Medicine
Functional medicine represents a patient-focused approach that treats the whole person, rather than focusing on isolated symptoms (NCBI, 2021). Dr. Jimenez incorporates functional medicine principles into his practice, conducting detailed health assessments that evaluate genetics, lifestyle, environmental exposures, and psychological factors (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). This comprehensive evaluation helps identify root causes of chronic conditions rather than simply managing symptoms. The functional medicine approach to neurological health addresses multiple physiological systems (Interactive Health Clinic, 2024). Rather than viewing brain-related symptoms in isolation, functional medicine practitioners consider factors like nutrition, gut health, hormone balance, and toxin exposure that can impact cognitive function. This holistic perspective recognizes that imbalances in one area can create ripple effects throughout the body, including the brain. Addressing these interconnected systems supports natural healing and optimal function.
According to Dr. Jimenez’s clinical observations, functional medicine assessments often reveal underlying factors contributing to neurological symptoms (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). These may include nutrient deficiencies affecting brain function, inflammatory processes triggered by food sensitivities, hormonal imbalances that disrupt cognitive performance, or toxic exposures that damage nervous tissue. By identifying and addressing these root causes through personalized treatment plans, functional medicine helps restore neurological health naturally and sustainably.
Acupuncture and Autonomic Nervous System Regulation
Acupuncture effectively regulates autonomic nervous system function through effects on central brain regions (Frontiers, 2022). Research demonstrates that acupuncture alleviates physical stress by regulating autonomic nervous system activity, with distinct effects observed across different acupuncture points. The practice increases overall activity of the vagus and autonomic nerves in real-time, with sustained effects continuing after treatment sessions. This regulation helps balance the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, promoting better stress management and overall health maintenance. The mechanisms through which acupuncture affects the brain involve activation of specific neural centers (NCBI, 2013). Acupuncture stimulates hypothalamic and midbrain nuclei associated with vagus nerve regulation, thereby influencing cardiovascular function, pain processing, and stress responses. This stimulation also activates centers that inhibit sympathetic nervous system overactivity, helping reduce excessive cardiovascular excitation and promoting relaxation. The neurobiological effects of acupuncture provide a foundation for its clinical efficacy in treating various conditions.
Clinical applications of acupuncture encompass a wide range of neurological and autonomic dysfunction-associated conditions (NCBI, 2022). Research shows acupuncture effectively alleviates symptoms in conditions including migraines, depression, insomnia, functional dyspepsia, and functional constipation. Dr. Jimenez incorporates acupuncture and electro-acupuncture into comprehensive treatment plans, recognizing these techniques as valuable tools for regulating nervous system function and supporting natural healing processes (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
Physical Therapy and Neurological Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in neurological rehabilitation by addressing movement, function, and independence following neurological injuries or conditions (UF Health Jacksonville, 2023). Neurologic physical therapy represents a specialty within physical therapy focused on the rehabilitation of the nervous system and the correlated musculoskeletal system. This specialty achieves rehabilitation through creating physiological changes that improve mobility, activities of daily living, balance, endurance, and cognition. Treatment approaches in neurological physical therapy target multiple functional areas (APT Clinics, 2023). These include restoring range of motion, improving functional movement and strength, gait training, postural realignment, improving safety of transfers and mobility, balance retraining to decrease fall risk, core stabilization, activities of daily living performance, visual perceptual skill retraining, cardiovascular endurance, improving motor planning and motor control, decreasing spasticity or tone, and prosthesis or orthosis training when needed.
Physical therapy interventions leverage neuroplasticity to promote recovery and functional improvement (NCBI, 2023). The brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections allows physical therapy to facilitate recovery even after significant neurological injuries. Through repetitive, task-specific training, physical therapy helps the brain create new neural pathways that compensate for damaged areas or restore lost functions. This plasticity-based approach has shown remarkable success in helping patients regain abilities after stroke, traumatic brain injury, and other neurological conditions.
Massage Therapy and Nervous System Benefits
Massage therapy has a significant impact on nervous system function by activating the parasympathetic nervous system (Elements Massage, 2023). This activation promotes the “rest and digest” response, counteracting the “fight or flight” mode triggered by stress. Through gentle, rhythmic movements, massage therapy encourages the body to shift into a relaxed state, lowering the heart rate, decreasing blood pressure, and promoting deep, rhythmic breathing. These physiological changes support nervous system balance and overall well-being. The neurological effects of massage extend beyond simple relaxation (Kinetic PT, 2025). Massage therapy helps reduce cortisol levels while boosting feel-good chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine. This creates a calming effect that can reduce symptoms of anxiety both immediately and over time. By stimulating nerve endings in the skin and muscles, massage sends signals through the nervous system that can interrupt pain cycles, reduce muscle tension, and promote healing. Regular massage sessions may improve sleep quality, a crucial factor for brain health and nervous system function.
Research demonstrates measurable effects of massage on autonomic nervous system regulation (NCBI, 2011). Studies show that heat and massage applications increase heart rate variability indices, indicating improved autonomic activity and balance. These changes suggest that massage therapy helps upregulate both sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system, promoting more flexible and adaptive nervous system responses to stress and environmental demands.
Improving Central Nervous System Function
Non-surgical treatments work synergistically to enhance central nervous system function through multiple mechanisms. Chiropractic adjustments reduce nerve interference, allowing signals to travel more freely between the brain and body (True Wellness Chiropractic, 2025). This improved signal transmission supports natural healing by enhancing communication between the brain and body systems. When the nervous system operates without interference, the body can better coordinate responses to internal and external stimuli. According to Dr. Jimenez’s clinical experience, combining multiple modalities often produces superior results compared to single-treatment approaches (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). His practice integrates chiropractic care, functional medicine, acupuncture, physical therapy, and massage therapy into comprehensive, personalized care plans that cater to each individual’s unique needs. This multimodal approach addresses nervous system function from multiple angles, supporting the body’s innate healing capacity while optimizing communication between the brain and all body systems.
Research supports the effectiveness of integrated treatment approaches for neurological conditions (NCBI, 2024). Multidisciplinary lifestyle interventions that incorporate physical activity, cognitive training, dietary modifications, and stress reduction techniques demonstrate clear benefits in slowing the progression of neurological disorders. These interventions can alleviate the impact of symptoms on quality of life, produce positive effects on behavioral, cognitive, and psychological symptoms, and potentially slow cognitive decline in pre-dementia stages.
Restoring Vagal Tone
Vagal tone refers to the activity level and function of the vagus nerve, which plays a central role in parasympathetic nervous system regulation (Mass General Hospital, 2024). High vagal tone associates with greater ability to recover from stress, better emotional regulation, and improved overall health. Various non-invasive techniques can enhance vagal tone, including specific breathing exercises, cold exposure, meditation, physical activity, and manual therapies. Auricular stimulation represents one approach to vagal tone enhancement (Herald Open Access, 2024). Gentle massage or pressure applied to specific points on the outer ear can activate vagal nerve fibers. When combined with diaphragmatic breathing exercises focusing on slow, deep breaths, this technique synergistically enhances vagal tone and reduces inflammation. The non-invasive nature of these approaches makes them accessible options for supporting nervous system health.
Dr. Jimenez’s functional medicine approach recognizes the importance of vagal tone for overall health and well-being (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). His clinical protocols often include interventions designed to support vagal nerve function, understanding that improved vagal tone can benefit multiple body systems simultaneously. By enhancing vagal tone, patients may experience improvements in stress resilience, digestive function, immune regulation, cardiovascular health, and emotional well-being.
Improving Somatic and Autonomic Systems
The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements and processes sensory input, while the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions (Simply Psychology, 2025). Both systems require optimal function for complete health and well-being. Natural therapies support both systems through different but complementary mechanisms. Chiropractic care directly impacts the somatic nervous system by improving spinal alignment and proprioceptive function (Active Family Health, 2025). Adjustments enhance motor control, coordination, and sensory processing. Simultaneously, chiropractic care influences the autonomic nervous system by reducing sympathetic hyperactivity and supporting parasympathetic function. This dual effect helps restore balance between the voluntary and involuntary aspects of nervous system function.
Manual therapies, including massage and specific forms of acupuncture, can shift autonomic nervous system balance toward parasympathetic dominance (Integrate Wellness Center, 2022). This shift enables the body to transition from a state of chronic stress activation to a calm, regenerative state, allowing for healing to occur. To achieve healthier nervous system regulation, the body requires time in a parasympathetic-dominant state, where repair and restoration processes can function optimally.
Exercise and Brain Health
Regular physical activity has a profound impact on brain health and function (American Psychological Association, 2020). Exercise triggers the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), increases cerebral blood flow, enhances synaptic plasticity, and reduces inflammation—all processes that support brain health. Aerobic exercise appears particularly beneficial, with research indicating that it can enhance the size of the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for verbal memory and learning (Harvard Health, 2014). The neuroprotective effects of exercise extend throughout the lifespan (NCBI, 2018). Exercise promotes trophic support to the brain vasculature, supports neurotransmission and neuronal survival, and enhances neurogenesis in the hippocampus. These effects contribute to improved cognitive function, better mood regulation, reduced anxiety and depression, and potentially lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Dr. Jimenez emphasizes the importance of physical activity in his comprehensive care plans, recognizing exercise as a powerful tool for supporting neurological health (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
The benefits of exercise for brain function include both immediate and long-term effects (Cleveland Clinic, 2025). Acute exercise sessions have been shown to improve attention, executive function, and processing speed. Over time, regular physical activity supports memory consolidation, enhances learning capacity, and may protect against cognitive decline. Exercise also improves sleep quality, which further benefits brain health through enhanced restoration and waste clearance during sleep periods.
Nutrition and Cognitive Support
Dietary interventions represent a fundamental component of neurological health support (NCBI, 2023). A functional medicine approach to nutrition considers individual needs, food sensitivities, nutrient deficiencies, and dietary patterns that support or impair brain function. Dr. Jimenez incorporates detailed nutritional assessments and personalized dietary recommendations into his treatment protocols, recognizing that proper nutrition forms the foundation for optimal nervous system function (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Specific dietary patterns show particular promise for brain health (UC Davis Health, 2025). The MIND diet, which combines elements of the Mediterranean diet with the DASH diet’s salt restrictions, has been associated with slower cognitive decline and reduced Alzheimer’s disease risk. This dietary pattern emphasizes green leafy vegetables, berries, nuts, whole grains, fish, and olive oil while limiting red meat, butter, cheese, pastries, and fried foods. These food choices provide antioxidants, healthy fats, and essential nutrients that support brain function and protect against neurodegeneration.
Nutritional supplementation may address specific deficiencies that impair neurological function (Oregon State University, n.d.). Omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, vitamin D, antioxidants, and other nutrients play crucial roles in brain health. However, supplementation should be guided by a comprehensive assessment of individual needs rather than generic recommendations. Dr. Jimenez’s functional medicine approach includes targeted nutritional testing to identify deficiencies and guide personalized supplementation strategies.
Stress Management and Mental Wellness
Chronic stress has a significant impact on neurological health, making stress management a crucial component of brain health protocols (Michigan Neurology, 2025). Effective stress reduction techniques include regular exercise to boost endorphins and reduce cortisol, a nutrient-rich diet with omega-3s and antioxidants, mindfulness and meditation practices to encourage present-moment awareness, and cognitive behavioral therapy when stress feels unmanageable or interferes with daily life. Mind-body therapies offer powerful tools for stress reduction and nervous system regulation (Ohio State Medical Center, n.d.). Techniques including meditation, yoga, tai chi, progressive muscle relaxation, and breathing exercises all demonstrate benefits for mental well-being and stress resilience. These practices work by activating the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing inflammatory responses, improving emotional regulation, and enhancing the brain’s ability to adapt. Dr. Jimenez’s holistic approach often incorporates stress management techniques as essential elements of comprehensive treatment plans (dralexjimenez.com, 2025).
The neurobiological effects of stress reduction practices include measurable changes in brain structure and function (NCBI, 2024). Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) enhances brain regions related to emotional processing and sensory perception while improving psychological outcomes like anxiety and depression. Regular meditation practice can reduce the size of the amygdala, the brain’s fear and stress center, while increasing activity in areas associated with attention and emotional regulation. These changes support better stress resilience and improved mental health outcomes.
Sleep Optimization
Sleep quality represents a critical but often overlooked factor in neurological health (Medicine, Utah, 2023). During sleep, the brain performs essential restoration and repair functions, clears metabolic waste through the glymphatic system, consolidates memories, and supports neuroplasticity. Healthcare providers should assess sleep quality as part of comprehensive neurological care and provide guidance for sleep optimization when problems are identified. Strategies for improving sleep quality include maintaining consistent sleep-wake schedules, creating a sleep-conducive environment (dark, cool, quiet), limiting screen time before bed, engaging in regular physical activity earlier in the day, managing stress through relaxation techniques, avoiding large meals and caffeine close to bedtime, and addressing underlying sleep disorders when present (Mayo Clinic Health System, 2022). Dr. Jimenez’s integrated approach recognizes that sleep problems often reflect underlying nervous system dysfunction and addresses both symptoms and root causes through comprehensive treatment protocols.
The relationship between sleep and neurological health operates in a bidirectional manner (Cereneo, 2024). Poor sleep can impair brain function and potentially accelerate neurological decline, while neurological conditions can also disrupt sleep quality. Addressing sleep problems may improve neurological symptoms, while treatments that enhance nervous system function often lead to better sleep. This bidirectional relationship highlights the importance of incorporating sleep optimization into comprehensive neurological health protocols.
Clinical Observations from Dr. Alexander Jimenez
Integrative Approach to Neurological Health
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s clinical practice in El Paso, Texas, demonstrates the effectiveness of combining conventional medical knowledge with natural, non-invasive therapeutic approaches (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). As both a board-certified family practice nurse practitioner and a doctor of chiropractic, Dr. Jimenez brings a unique perspective that bridges traditional and integrative medicine. His dual training allows him to evaluate patients comprehensively, addressing both conventional medical concerns and underlying functional imbalances that may contribute to neurological symptoms. Dr. Jimenez’s approach emphasizes evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by principles of integrative medicine (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Rather than relying solely on medications or surgical interventions, his practice focuses on restoring health naturally through addressing the root causes of dysfunction. This philosophy recognizes that the body possesses an innate healing capacity when provided with proper support through nutrition, structural alignment, stress management, and lifestyle optimization.
The multimodal treatment plans developed by Dr. Jimenez often combine chiropractic adjustments, functional medicine assessments, acupuncture, nutritional interventions, and physical rehabilitation (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). This integrated approach addresses nervous system health from multiple angles, supporting the body’s natural healing processes while optimizing communication between the brain and all body systems. Patients benefit from personalized care plans developed through detailed evaluation of their unique health history, current symptoms, and functional medicine assessments.
Patient-Centered Care Philosophy
Dr. Jimenez’s practice embodies a patient-centered philosophy that recognizes each individual as unique (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Rather than applying one-size-fits-all treatment protocols, his approach involves thorough assessment to understand each patient’s specific needs, challenges, and goals. This N-of-1 perspective aligns with core functional medicine principles that emphasize individualized care based on each person’s unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. The commitment to personalized care extends to collaborative decision-making about treatment approaches (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Dr. Jimenez educates patients about their conditions and treatment options, empowering them to participate actively in their health journey. When appropriate, he collaborates with other specialists, including surgeons, medical researchers, and rehabilitation experts, to ensure patients receive the best possible care tailored to their specific needs. This collaborative approach demonstrates the value of integrating different healthcare perspectives to achieve optimal outcomes.
Accessibility represents another key aspect of Dr. Jimenez’s practice philosophy (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Understanding that routine healthcare should be convenient and affordable for all, the practice offers multiple care plans without the hassles of insurance billing complexities when preferred. This commitment to accessibility ensures that more people can access the integrative care they need to address neurological symptoms and optimize nervous system function.
Clinical Success Through Comprehensive Care
Dr. Jimenez’s clinical experience demonstrates that addressing neurological health requires looking beyond isolated symptoms to underlying systemic imbalances (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Many patients present with complex, chronic conditions that have not responded adequately to conventional treatment approaches. Through comprehensive functional medicine assessments that evaluate nutrition, environmental exposures, stress factors, and lifestyle behaviors, Dr. Jimenez often identifies root causes that previous evaluations missed. The success of this comprehensive approach reflects the interconnected nature of body systems (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). Neurological symptoms often result from multiple contributing factors, including spinal misalignments that affect nerve function, nutritional deficiencies that impair neurotransmitter production, inflammatory processes triggered by food sensitivities or environmental toxins, hormonal imbalances that impact brain chemistry, chronic stress that dysregulates autonomic nervous system function, and sleep disturbances that prevent adequate brain restoration. Addressing these factors simultaneously often produces better results than targeting any single element alone.
Dr. Jimenez’s practice has treated thousands of patients in the El Paso community over more than two decades, refining treatment protocols based on clinical outcomes and ongoing research (dralexjimenez.com, 2025). This extensive clinical experience, combined with a commitment to evidence-based practice and integration of multiple therapeutic modalities, has established Dr. Jimenez as a trusted resource for people seeking natural approaches to neurological health. His work demonstrates that non-surgical, integrative treatments can effectively address even complex neurological conditions when applied comprehensively and personalized to individual needs.
Conclusion
The brain is the main control center for all of the body’s functions. It maintains contact with muscles, joints, nerves, and vital organs through a complex network of nerves. This communication system operates continuously to control everything, from basic survival functions like breathing and heartbeat to more complex tasks such as learning, memory, and regulating emotions. To stay healthy and manage neurological problems, it’s essential to understand how the brain connects to and controls the body. Air pollution, chronic stress, inadequate nutrition, and insufficient sleep are all environmental factors that significantly impact how the brain and nervous system function. These factors can cause a range of neurological symptoms, including headaches, inflammation, fatigue, cognitive difficulties, sleep disturbances, and muscle instability. Many neurological disorders share similar symptoms and risk factors. This illustrates the complexity and interconnection of the nervous system when it functions properly and when it malfunctions. Natural, non-surgical treatments are excellent ways to help your nervous system function optimally and maintain good neurological health. Dr. Alexander Jimenez and other integrative practitioners utilize chiropractic care to correct spinal misalignments, which reduces nerve interference and enhances communication between the brain and body. Functional wellness approaches address imbalances in nutrition, hormones, and metabolic function that may be contributing to neurological symptoms. Acupuncture regulates the activity of the autonomic nervous system, helping to restore balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic functions. Massage therapy and physical therapy help the nervous system by altering how it functions, including how it moves, processes pain, and responds to stress.
These therapeutic methods improve the function of the central nervous system, restore vagal tone, and improve the regulation of both the somatic and autonomic systems. Integrative treatments help the body heal itself by addressing the root causes of nervous system problems, rather than just masking the symptoms. Dr. Jimenez and other functional medicine practitioners have observed that comprehensive, personalized treatment plans that utilize multiple methods often yield better results than those that employ a single approach. The growing understanding of neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to change and form new neural connections throughout life, offers hope for recovery even after severe brain injuries or long-term illnesses. Natural therapies that enhance neuroplasticity, reduce inflammation, promote good nutrition, facilitate stress management, and encourage restful sleep enable the brain to heal and adapt. This neuroplasticity-based method recognizes that the nervous system can recover and heal itself effectively when it receives the right kind of support. In the future, combining natural therapies with standard medical care is the most effective way to manage your neurological health. This integration demonstrates that both traditional medical evaluation and diagnosis, as well as functional medicine’s focus on identifying the root causes of problems and treating them naturally, are important. Patients benefit from having access to the full range of treatment options, which enables doctors to create personalized treatment plans tailored to each person’s needs, wants, and situation. The field of neurological health is constantly evolving as new research sheds light on how the brain functions, how the nervous system communicates, and the mechanisms of various therapies. Staying up to date on new research while adhering to the fundamental principles of nervous system health—such as proper spinal alignment, good nutrition, stress management, adequate sleep, regular exercise, and social connection—is the most effective way to prevent and treat neurological conditions naturally. With this comprehensive, holistic approach, people of any age can enhance their overall quality of life, support their brain health, and optimize their nervous system function.
References
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons. (2024). Anatomy of the brain. https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Anatomy-of-the-Brain
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Working out boosts brain health. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2020/03/ce-corner-exercise
- Cancer Canada. (2020). Anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/brain-and-spinal-cord/what-is-brain-cancer/the-nervous-system
- Camarata Chiropractic. (2023). Unlocking the science behind chiropractic adjustments: Enhancing your brain-body connection. https://camaratachiropractic.com/blog/unlocking-the-science-behind-chiropractic-adjustments-enhancing-your-brain-body-connection/
- cereneo. (2024). The role of sleep in neurorehabilitation. https://www.cereneo.ch/en/news-events/the-role-of-sleep-in-neurorehabilitation
- Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Neurological disorders: What they are, symptoms & types. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/neurological-disorders
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025a). Brain: Parts, function, how it works & conditions. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23684-brain
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025b). How exercise improves your brain’s health. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/exercise-brain-health
- dralexjimenez.com. (2025). El Paso, TX, family practice nurse practitioner and chiropractor. https://dralexjimenez.com/
- EIHMD. (2022). How chiropractic care can benefit your nervous system. https://www.eihmd.com/how-chiropractic-care-can-benefit-your-nervous-system/
- Elements Massage. (2023). Massage therapy stimulates the nervous system. https://www.elementsmassage.com/needham/blog/massage-therapy-stimulates-the-nervous-system
- Foothills Neurology. (n.d.). Neurological impact of stress and management techniques. https://www.foothillsneurology.com/neurological-impact-of-stress-and-management-techniques/
- Frontiers. (2022). Regulation of the autonomic nervous system by acupuncture. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2022.882540/full
- Frontiers. (2024). Editorial: Neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1453772/full
- Harvard Health. (2014). Regular exercise changes the brain to improve memory, thinking skills. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/regular-exercise-changes-brain-improve-memory-thinking-skills-201404097110
- Harvard Health. (2024). Foods linked to better brainpower. https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/foods-linked-to-better-brainpower
- Harvard Magazine. (2025). Inflammation and brain health. https://magazine.hms.harvard.edu/articles/inflammation-and-brain-health
- Herald Open Access. (2024). A perspective on vagal tone via auricular stimulation and deep breathing. https://www.heraldopenaccess.us/openaccess/a-prospective-on-vagal-tone-via-auricular-stimulation-and-deep-breathing
- IINN. (2023). 4 ways chiropractic care can improve brain function. https://www.iinn.com/post/4-ways-chiropractic-care-can-improve-brain-function
- Integrate Wellness Center. (2022). The nervous system functions with chiropractic care. https://integratewellnesscenter.com/nervous-system-function-with-chiropractic-care/
- Interactive Health Clinic. (2024). How functional medicine can improve brain health. https://www.interactivehealthclinic.com/blog/how-functional-medicine-can-improve-brain-health/
- Kinetic PT. (2025). How massage therapy affects the nervous system. https://www.kineticptgreenville.com/how-massage-therapy-affects-the-nervous-system/
- Lone Star Neurology. (2024). Environmental influences on neurological disorders. https://lonestarneurology.net/environmental-influences-on-neurological-disorders/
- Mass General Hospital. (2024). The vagus nerve: A key player in your health and well-being. https://www.massgeneral.org/news/article/vagus-nerve-key-player-in-health-and-well-being
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). How your brain works. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/brain-tumor/multimedia/brain/vid-20084842
- Mayo Clinic. (2025). Migraine – Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20360201
- Mayo Clinic Health System. (2022). Tips to keep your brain healthy. https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/tips-to-keep-your-brain-healthy
- Michigan Neurology. (2025). The Connection Between Stress and Neurological Disorders. https://michiganneurologyassociates.com/the-connection-between-stress-and-neurological-disorders/
- National Institutes of Health. (2022). Major structures and functions of the brain. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279302/
- Nature. (2022). Residential green space and air pollution are associated with brain function. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13764-2
- NCBI. (1998). Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2805706/
- NCBI. (2010). Cognitive dysfunction with aging and the role of inflammation. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2888944/
- NCBI. (2011). The Effects of Heat and Massage Application on the Autonomic Nervous System. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3208934/
- NCBI. (2013). Acupuncture effect and central autonomic regulation. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3658605/
- NCBI. (2017). The role of diet and nutrition on mental health and well-being. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28707609/
- NCBI. (2018). The neuroprotective effects of exercise: Maintaining a healthy brain throughout life. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6296262/
- NCBI. (2019). The effects of chiropractic spinal manipulation on central processing of pain. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520945/
- NCBI. (2020). Functional overlaps exist in neurological and psychiatric disorders. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31926110/
- NCBI. (2021). Functional medicine past, present, and future. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8651258/
- NCBI. (2022). The autonomic nervous system: A potential link to the efficacy of acupuncture. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36452202/
- NCBI. (2023a). Adaptive neuroplasticity in brain injury recovery. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10515784/
- NCBI. (2023b). Editorial: Effects of environmental toxins on brain health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9945219/
- NCBI. (2023c). Physical Activity and Lifestyle Modifications in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10244289/
- NCBI. (2023d). Sleep disorders affect cognitive function in adults. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9843690/
- NCBI. (2024a). Multidisciplinary lifestyle interventions for neurological disorders. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11348753/
- NCBI. (2024b). Neurobiological changes induced by mindfulness and meditation. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11579371/
- Neurology. (2022). Association of midlife inflammatory markers with cognitive function. https://www.neurology.org/doi/10.1212/WNL.0000000000201429
- Neurology Center NJ. (2025). The connection between sleep disorders and neurological health. https://neurocenternj.com/the-connection-between-sleep-disorders-and-neurological-health/
- NINDS. (2023). Headache. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/headache
- NINDS. (2025). Myasthenia gravis. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/myasthenia-gravis
- Northwestern Medicine. (2022). Stress and the brain: Health implications. https://www.nm.org/healthbeat/healthy-tips/stress-and-the-brain
- Ohio State Medical Center. (n.d.). Mind-body therapies. https://wexnermedical.osu.edu/integrative-medicine/mind-body
- Oregon State University. (n.d.). Nutrition and cognitive function. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/cognitive-function
- Orlando Health. (2021). Joints, muscles, and nerves: Link between brain and body. https://www.orlandohealth.com/content-hub/joints-muscles-and-nerves-link-between-brain-and-body
- Paris Brain Institute. (2025). Understanding the brain. https://parisbraininstitute.org/en/understanding-the-brain/
- Practical Neurology. (2025). Psychiatric Comorbidities in Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder https://practicalneurology.com/articles/2025-mar/psychiatric-comorbidities-in-functional-neurologic-symptom-disorder
- Professional Heart Association. (2024). Impact of sleep disorders and disturbed sleep on brain health. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/impact-of-sleep-disorders-and-disturbed-sleep-on-brain-health
- Pure Well Chiropractic. (2025). What a chiropractic adjustment can do for your focus and clarity. https://purewellchiro.com/what-a-chiropractic-adjustment-can-do-for-your-focus-and-clarity/
- Science. (2021). Newly detailed nerve links between the brain and other organs shape emotions, memory, and more. https://www.science.org/content/article/newly-detailed-nerve-links-between-brain-and-other-organs-shape-emotions-memory-and-more
- Simply Psychology. (2025). Somatic nervous system: Definition, function, and examples. https://www.simplypsychology.org/somatic-nervous-system.html
- True Wellness Chiropractic. (2025). How the nervous system and chiropractic care go hand in hand. https://truewellnesschiro.com/how-the-nervous-system-and-chiropractic-care-go-hand-in-hand/
- TutorChase. (2023). How does the brain control muscle coordination and movement? https://www.tutorchase.com/answers/ib/biology/how-does-the-brain-control-muscle-coordination-and-movement
- UC Davis. (2025). Air pollution and brain health. https://environmentalhealth.ucdavis.edu/air-pollution-and-brain-health
- UC Davis Health. (2025). Lifestyle changes boost brain health. https://health.ucdavis.edu/news/headlines/lifestyle-changes-boost-brain-health-study-shows/2025/09
- UC Davis Medicine. (2023). Why is at least 7 hours of sleep essential for brain health? https://medicine.utah.edu/neurosciences/news/brain-health-blog/seven-hours-sleep
- UF Health Jacksonville. (2023). Neurological physical therapy. https://ufhealthjax.org/services/neurological-physical-therapy
- University of Michigan Health. (2004). Neuromuscular disorders. https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/brain-neurological-conditions/neuromuscular-disorders
- UCSF. (2024). Poor sleep in midlife is associated with accelerated brain atrophy. https://www.ucsf.edu/news/2024/10/428841/poor-sleep-midlife-linked-faster-brain-atrophy
- Washington University. (2016). Brain inflammation may be the reason behind muscle fatigue after viral infection. https://neuroscienceresearch.wustl.edu/brain-inflammation-may-be-the-reason-behind-muscle-fatigue-after-viral-infection/
- Wikipedia. (2003). Somatic nervous system. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatic_nervous_system
- Wikipedia. (2004). Neural pathway. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neural_pathway
- Wikipedia. (2024). Brain-body interaction. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain%E2%80%93body_interaction
- Yale Medicine. (2022). Revealing communications between brain and body. https://medicine.yale.edu/news-article/revealing-communications-between-brain-and-body/
- Yale Medicine. (2023). Migraine: A neurological condition. https://www.yalemedicine.org/news/migraine-neurological-condition