Treatment of Nerve Injuries Resulting from Automobile Accidents

Nerve Injuries from Car Accidents: Causes, Treatment, and Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s Expertise
Introduction
Car accidents happen in an instant, but their effects can last a lifetime. Among the many injuries sustained in motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), nerve injuries are particularly common and can significantly impact daily life. Research suggests that over 25% of nerve injury cases result from car and truck accidents, with motorcycle crashes contributing to 32.5% of peripheral nerve injuries (Miller & Zois, 2024). These injuries often lead to peripheral neuropathy, a condition where nerves outside the brain and spinal cord are damaged, causing symptoms like pain, numbness, and weakness. In El Paso, TX, Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a chiropractor and board-certified nurse practitioner, stands out as a leading clinician helping victims recover from such injuries while supporting their personal injury cases. This comprehensive guide explores the medical causes of nerve injuries, their role in peripheral neuropathy, and how Dr. Jimenez’s unique approach aids recovery and legal processes.
References
- Miller & Zois. (2024). Nerve injuries in auto accident lawsuits. Retrieved from Miller & Zois
Understanding Nerve Injuries
Nerves are the body’s communication network, transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts. Injuries to the nerves can disrupt this communication, leading to a range of symptoms. Nerve injuries from MVAs typically fall into three categories:
- Compression: Nerves are pinched or pressed, often by swollen tissues or misaligned bones.
- Stretching: Nerves are overstretched, as seen in whiplash injuries.
- Severing: Nerves are partially or completely cut, often from severe trauma.
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when peripheral nerves—those outside the brain and spinal cord—are damaged. This condition can affect motor nerves (controlling movement), sensory nerves (responsible for sensation), or autonomic nerves (managing involuntary functions like heart rate). Symptoms vary depending on the nerve type affected, but common signs include pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness (Mayo Clinic, 2024).
Types of Nerve Injuries
| Type | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | The nerve is overstretched without tearing | The nerve is pinched by surrounding tissues |
| Stretching | Nerve is overstretched without tearing | Burning sensation, weakness |
| Severing | Numbness, tingling, and sharp pain | Loss of function, severe pain, paralysis |
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Peripheral nerve injuries: Symptoms and causes. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
Causes of Nerve Injuries in MVAs
Car accidents subject the body to sudden, violent forces that can damage nerves in various ways. The following are the primary causes of nerve injuries in MVAs:
Whiplash
Whiplash, one of the most common MVA injuries, occurs when the head and neck are jerked forward and backward rapidly. This motion can overstretch nerves in the neck and shoulders, leading to inflammation and compression. Whiplash is a significant contributor to nerve injuries, often causing symptoms like neck pain, tingling in the arms, and headaches (AICA Orthopedics, 2021).
Direct Trauma
The impact of a car accident can cause direct trauma to nerves. For example, hitting a steering wheel or being struck by debris can crush or sever nerves. Blunt force trauma is a leading cause of nerve damage, particularly in high-impact collisions (Singleton Schreiber).
Secondary Injuries
After an accident, swelling, inflammation, or scar tissue can compress nerves, leading to delayed symptoms. Herniated discs or spinal misalignments can also exert pressure on nerve roots, leading to radiculopathy, a related condition characterized by nerve root irritation (Fletcher Law Office, 2023).
Common MVA Scenarios Leading to Nerve Injuries
| Scenario | Mechanism of Injury | Potential Nerve Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Rear-end collision | Whiplash from sudden neck movement | Cervical nerve stretching |
| Head-on collision | Blunt force trauma to chest or limbs | Peripheral nerve compression |
| Rollover accident | Blunt force trauma to the chest or limbs | Severe nerve severing or compression |
References
- AICA Orthopedics. (2021). Can you get nerve damage from a car accident? Retrieved from AICA Orthopedics
- Singleton Schreiber. (n.d.). Nerve damage from car accidents in California. Retrieved from Singleton Schreiber
- Fletcher Law Office. (2023). What is radiculopathy vs. neuropathy from a Texas car accident? Retrieved from Fletcher Law Office
Symptoms of Nerve Injuries
Nerve injuries present a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type and severity of the damage. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for seeking timely treatment.
Motor Nerve Damage
Motor nerves control muscle movement. Damage can lead to:
- Muscle weakness or difficulty with tasks like gripping or walking.
- Loss of coordination or balance.
- In severe cases, paralysis (HM Attorneys, 2022).
Sensory Nerve Damage
Sensory nerves are responsible for detecting sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain. Symptoms include:
- Numbness or tingling, often described as “pins and needles.”
- Sharp, burning, or shooting pain radiating along nerve pathways.
- Hypersensitivity to touch or temperature changes (Bensinger Legal).
Autonomic Nerve Damage
Autonomic nerves regulate involuntary functions. Damage may cause:
- Irregular heart rate or blood pressure.
- Digestive issues, such as nausea or constipation.
- Excessive sweating or inability to sweat (The Russo Firm).
Common Symptoms by Nerve Type
| Nerve Type | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Motor | Weakness, coordination loss, paralysis |
| Sensory | Numbness, tingling, burning pain, hypersensitivity |
| Autonomic | Heart rate changes, digestive issues, sweating abnormalities |
Delayed Symptoms
Some nerve injuries may not be immediately apparent. Swelling or scar tissue can develop days or weeks after an accident, leading to symptoms that worsen over time. This underscores the importance of medical evaluation even if you feel fine initially (Houston Pain Specialists).
References
- HM Attorneys. (2022). Can a car accident cause nerve damage? Retrieved from HM Attorneys
- Bensinger Legal. (n.d.). Signs of nerve damage after a car accident. Retrieved from Bensinger Legal
- The Russo Firm. (n.d.). Neurological issues caused by car accidents. Retrieved from The Russo Firm
- Houston Pain Specialists. (n.d.). Why some auto accident injuries lead to chronic nerve pain. Retrieved from Houston Pain Specialists
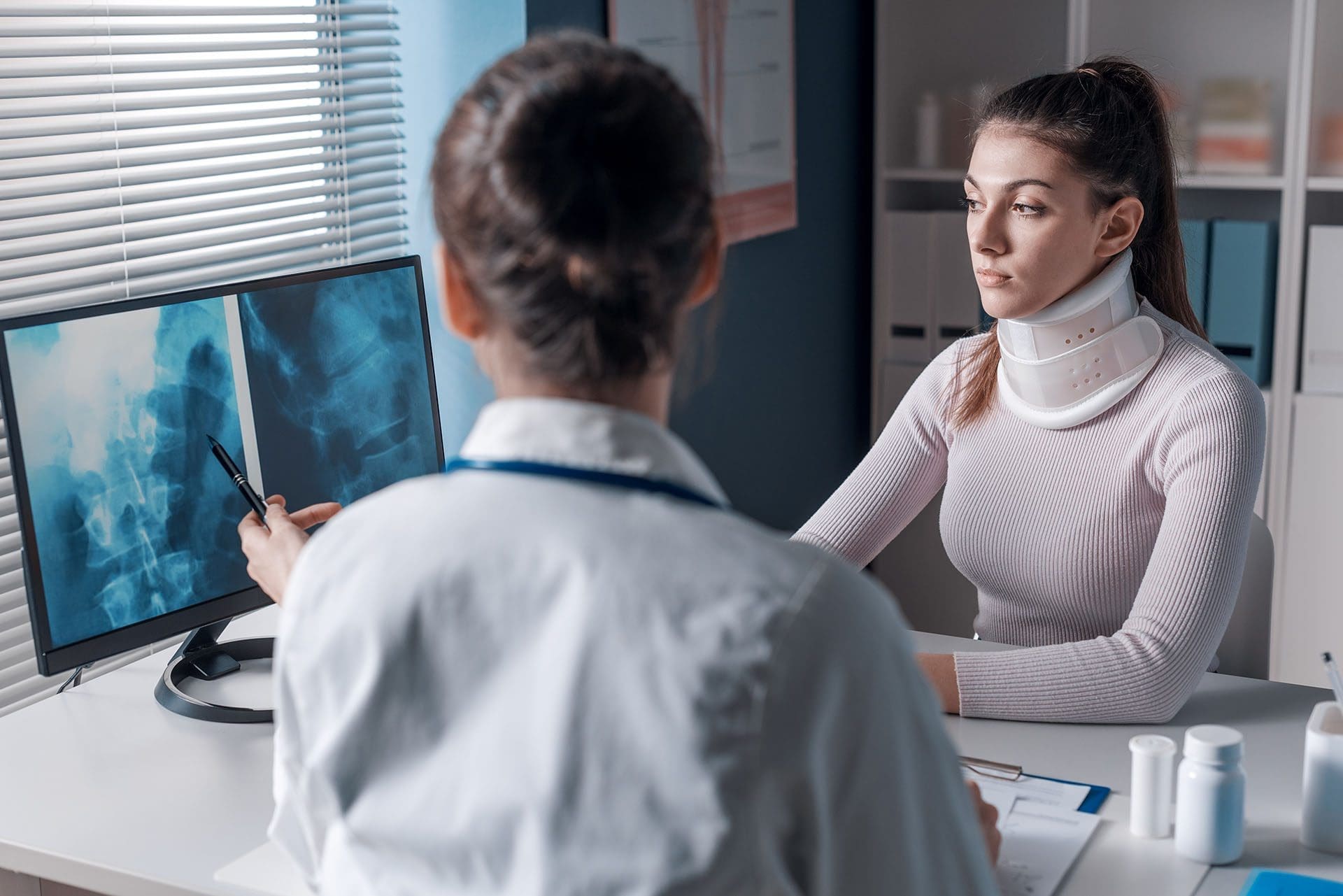
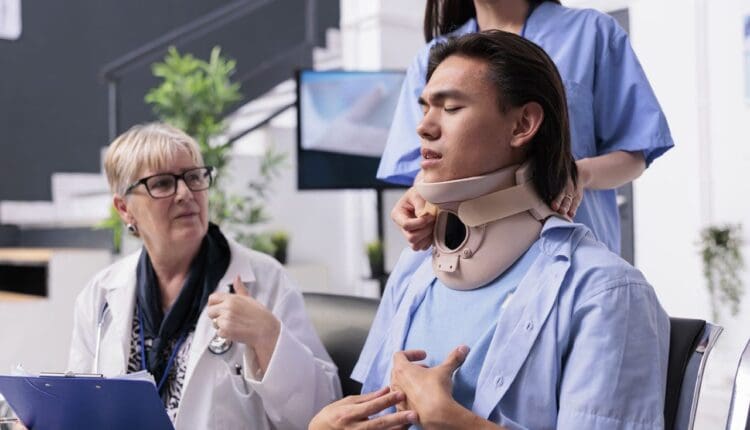
Diagnosis of Nerve Injuries
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Doctors use a combination of physical examinations, imaging techniques, and specialized tests to diagnose nerve injuries.
Physical Examination
A doctor will:
- Test reflexes using a reflex hammer to check for hyporeflexia (reduced reflexes) or hyperreflexia (overactive reflexes).
- Assess sensation using tools such as a pinprick or cotton swab to detect sensory abnormalities.
- Evaluate muscle strength and coordination (Spine Universe, 2018).
Diagnostic Imaging
Imaging helps identify structural issues causing nerve compression.
- X-rays: Detect bone fractures or misalignments.
- MRI: Shows soft tissue damage, such as herniated discs or nerve compression.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed views of bones and tissues (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2018).
Nerve Conduction Studies
These tests measure how well nerves transmit electrical signals, helping pinpoint the location and extent of damage. Electromyography (EMG) may be used alongside to assess muscle response.
Diagnostic Methods
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Exam | Assess reflexes, sensation, and strength |
| X-ray | Identify bone fractures or misalignments |
| MRI | Detect soft tissue and nerve compression |
| Nerve Conduction Study | Measure nerve signal transmission |
References
- Spine Universe. (2018). Neurological exams: Sensory nerves and deep tendon reflexes. Retrieved from Spine Universe
- Dr. Alex Jimenez. (2018). The abdomen: Diagnostic imaging approach. Retrieved from Dr. Alex Jimenez
Treatment Options
Treatment for nerve injuries aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent the development of chronic conditions. Options range from non-invasive therapies to surgical interventions.
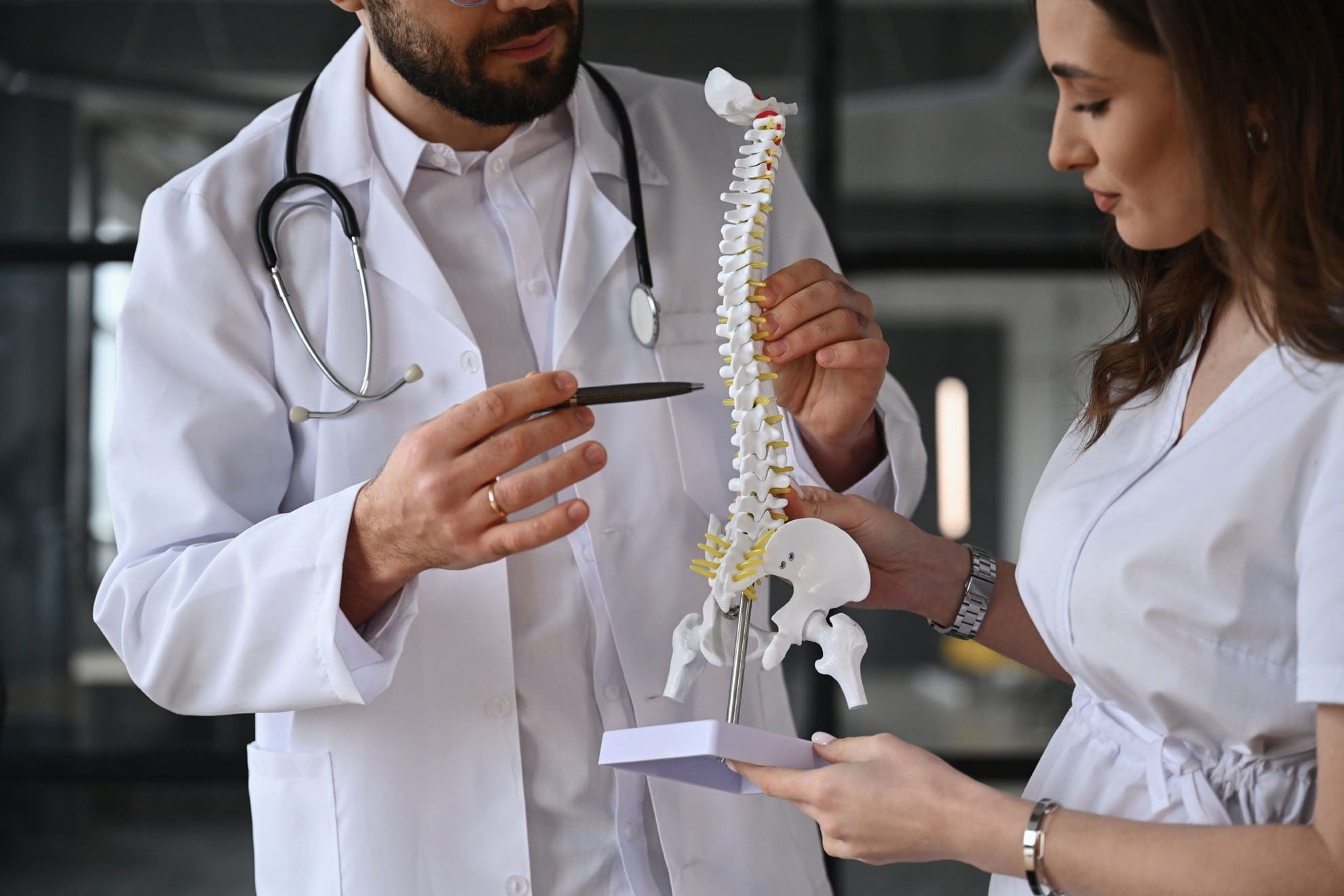
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments realign the spine and joints, reducing nerve compression. This approach is effective for whiplash, pinched nerves, and herniated discs. Chiropractors also provide soft tissue therapy to reduce inflammation (PrimeCare Chiropractic).
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises and stretches improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and reduce nerve pressure. For optimal results, Houston Pain Specialists often combine physical therapy with chiropractic care.
Medication
Medications may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce swelling.
- Nerve pain medications, such as gabapentin.
- Muscle relaxants are used to alleviate spasms.
Surgery
Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to repair severed nerves or relieve compression from herniated discs or fractures. Surgery is typically considered a last resort (Dolman Law, 2022).
Treatment Options Overview
| Treatment | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chiropractic Care | Spinal adjustments, soft tissue therapy | Whiplash, pinched nerves |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to improve mobility and strength | Muscle weakness, mobility issues |
| Medication | Pain relief and inflammation reduction | Acute pain, inflammation |
| Surgery | Repair severe nerve damage or compression | Severed nerves, severe compression |
References
- PrimeCare Chiropractic. (n.d.). Chiropractic care for personal injury recovery. Retrieved from PrimeCare Chiropractic
- Houston Pain Specialists. (n.d.). Why some auto accident injuries lead to chronic nerve pain. Retrieved from Houston Pain Specialists
- Dolman Law. (2022). Neurological issues from a car accident. Retrieved from Dolman Law
The Role of Chiropractic Care in Recovery
Chiropractic care plays a vital role in recovering from MVA-related nerve injuries. By addressing spinal misalignments and reducing nerve pressure, chiropractors help restore function and alleviate pain.
Benefits of Chiropractic Care
- Pain Relief: Adjustments reduce nerve compression, easing pain without relying heavily on medications.
- Improved Mobility: Realigning the spine enhances range of motion, aiding daily activities.
- Non-Invasive: Chiropractic care avoids surgery, making it a safer option for many patients (Aventura Wellness, 2023).
Supporting Personal Injury Claims
Chiropractors provide detailed documentation of injuries, treatment plans, and progress, which is crucial for personal injury lawsuits. This evidence links the accident to the injury, supporting compensation claims. Chiropractors may also testify in court to explain the extent of injuries (Comfort Rehab, 2024).
Early Intervention
Seeking chiropractic care soon after an accident can prevent chronic conditions. Delayed treatment may allow scar tissue or inflammation to worsen nerve damage, leading to persistent pain (Hensley Legal, 2024).
References
- Aventura Wellness. (2023). The role of chiropractic care in personal injury recovery. Retrieved from Aventura Wellness
- Comfort Rehab. (2024). Role of chiropractic in personal injury lawsuits. Retrieved from Comfort Rehab
- Hensley Legal. (2024). Can a personal injury chiropractor help your case? Retrieved from Hensley Legal
Dr. Alexander Jimenez: A Leading Expert in El Paso
In El Paso, TX, Dr. Alexander Jimenez is a prominent clinician for MVA victims, offering a unique blend of chiropractic and medical expertise. With over 25 years of experience, he leads Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic, specializing in injury rehabilitation, functional medicine, and personal injury care (A4M, n.d.).
Background and Credentials
Dr. Jimenez holds dual licensure as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) and a board-certified Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC). He is also certified in functional medicine, allowing him to address both biomechanical and systemic health issues. His education includes training from the National University of Health Sciences, and he has been recognized as a top-rated chiropractor in El Paso from 2015 to 2024 (Healthgrades).
Clinical Approach
Dr. Jimenez employs a comprehensive approach to treat nerve injuries:
- Advanced Diagnostics: He utilizes imaging techniques (X-rays, MRIs) and the Living Matrix Functional Medicine Assessment to pinpoint the underlying causes of nerve damage (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2025).
- Dual-Scope Interventions: Combining chiropractic adjustments with medical management, he addresses both structural and physiological aspects of injuries.
- Each patient receives a personalized treatment plan that prioritizes pain relief, mobility recovery, and long-term wellness.
Role in Personal Injury Cases
Dr. Jimenez acts as an intermediary between medical care and legal processes. His clinic provides detailed medical records, diagnostic imaging results, and treatment summaries that support personal injury claims. These documents help establish the link between the accident and the injury, which is crucial for securing compensation. His expertise also allows him to collaborate with attorneys, providing expert testimony when needed (Dr. Alex Jimenez, 2017).
Community Impact
Dr. Jimenez’s commitment to El Paso extends beyond his clinic. He engages in community outreach, such as the “Tell A Veteran” program, offering chiropractic care to disabled veterans. His Health Voice 360 Podcast educates the public on various health issues, including nerve injuries and recovery, as well as other related topics (LinkedIn).
Why Choose Dr. Jimenez?
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dual Licensure | Combines chiropractic and medical expertise |
| Advanced Diagnostics | Pinpoints injury causes with precision |
| Legal Support | Provides documentation for personal injury claims |
| Holistic Approach | Addresses physical, nutritional, and emotional health |
References
- A4M. (n.d.). Dr. Alex Jimenez: Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic. Retrieved from A4M
- Healthgrades. (n.d.). Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC. Retrieved from Healthgrades
- Dr. Alex Jimenez. (2025). Why choose Dr. Jimenez and clinical team. Retrieved from Dr. Alex Jimenez
- Dr. Alex Jimenez. (2017). Personal injury doctor. Retrieved from Dr. Alex Jimenez
- LinkedIn. (n.d.). Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s profile. Retrieved from LinkedIn
Conclusion
Nerve injuries from car accidents, including compression injuries and whiplash, can lead to peripheral neuropathy, causing significant physical and emotional challenges. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent chronic pain and restore quality of life. Dr. Alexander Jimenez, located in El Paso, TX, provides MVA victims with hope by integrating advanced diagnostics, chiropractic care, and functional medicine to facilitate their recovery. His role in personal injury cases ensures patients receive both medical care and legal support, helping them navigate the aftermath of an accident. If you’ve been in a car accident, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen—seek expert care to start your journey to healing.
References
- Nerve injuries in auto accident lawsuits
- Peripheral nerve injuries: Symptoms and causes
- Can you get nerve damage from a car accident?
- Nerve damage from car accidents in California
- What is radiculopathy vs. neuropathy from a Texas car accident?
- Can a car accident cause nerve damage?
- Signs of nerve damage after a car accident
- Neurological issues caused by car accidents
- Why some auto accident injuries lead to chronic nerve pain
- Neurological exams: Sensory nerves and deep tendon reflexes
- The abdomen: Diagnostic imaging approach
- Chiropractic care for personal injury recovery
- Neurological issues from a car accident
- The role of chiropractic care in personal injury recovery
- Role of chiropractic in personal injury lawsuits
- Can a personal injury chiropractor help your case?
- Dr. Alex Jimenez: Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic
- Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC
- Why choose Dr. Jimenez and clinical team
- Personal injury doctor
- Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s profile