Chiropractic Care Explained For Reducing Chronic Inflammation
Find out how chiropractic care can support healing and enhance your daily wellbeing significantly from chronic inflammation.
Managing Inflammation Through Integrative Care for Optimal Health
Inflammation is a natural part of how the body protects and heals itself. However, when it becomes chronic, it can lead to serious health issues. This article explains the differences between acute and chronic inflammation, the roles inflammation plays in the body, and how environmental factors contribute to the development of chronic inflammation. It also explores non-surgical treatments, such as exercise, chiropractic care, and integrative therapies, that work together to reduce inflammation, support the body’s natural detoxification processes, and promote long-term health. Drawing on the clinical expertise of Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, a chiropractor and nurse practitioner, we’ll highlight how these approaches help manage injuries and enhance overall wellness.
Understanding Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s response to injury, infection, or harmful substances. It acts like a defense system, sending immune cells to repair damage or fight off germs. There are two main types of inflammation—acute and chronic—each with distinct causes, effects, and management strategies.
Acute Inflammation: A Short-Term Response
Acute inflammation is the body’s quick reaction to something like a cut, sprain, or infection. For instance, when you twist your ankle, the area becomes red, warm, and swollen. This happens because blood vessels dilate to allow immune cells, such as white blood cells, to reach the injury and initiate the healing process. The process typically lasts a few days and stops once the issue is resolved (Harvard Health, 2020).
Signs of acute inflammation include:
- Redness: Increased blood flow to the area.
- Warmth: The area feels hot due to increased blood flow.
- Swelling: Fluid builds up in the tissue.
- Pain: Nerves become sensitive, causing discomfort.
- Limited movement: Swelling or pain may restrict use of the area.
Acute inflammation is helpful because it protects the body and supports healing. For example, it helps fight off a virus during a cold, and once the virus is gone, the inflammation subsides (DifferenceBetween.net, n.d.).
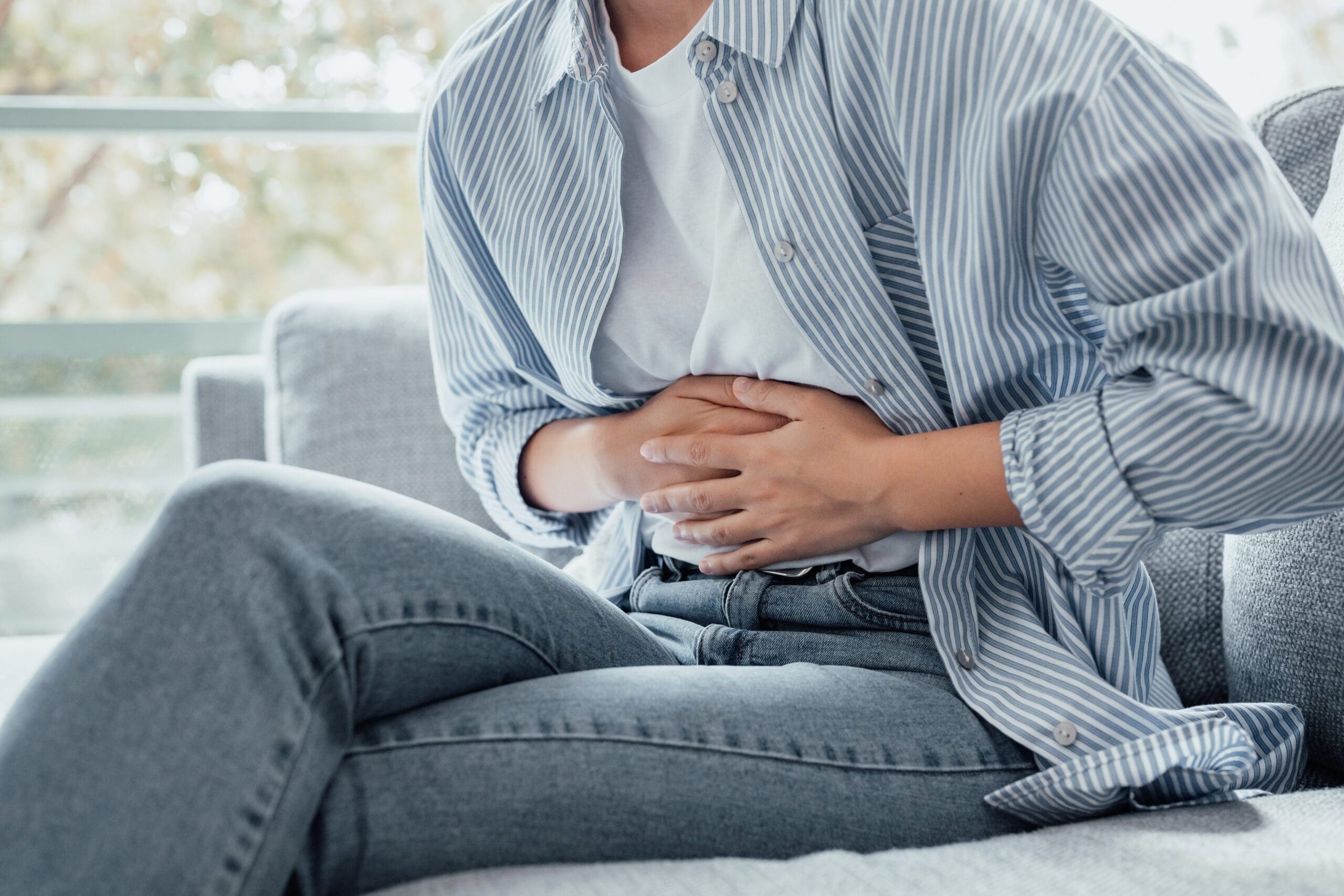
Chronic Inflammation: A Long-Term Issue
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, lasts for months or years and can harm the body. It occurs when the immune system stays active too long, attacking healthy tissues by mistake. This can lead to conditions like arthritis, heart disease, or diabetes. Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation may not have obvious symptoms, making it harder to detect. You might feel tired, have ongoing joint pain, or experience digestive problems (Shmerling, 2020).
Chronic inflammation is often referred to as “silent” because it can cause damage to organs over time without producing clear signs. For example, it can contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks (Furman et al., 2019).
The Role of Inflammation in the Body
Inflammation serves several important purposes:
- Fighting infections: It helps eliminate bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens.
- Healing injuries: It clears damaged tissue and supports repair, like when a wound heals.
- Clearing toxins: It removes harmful substances, such as chemicals or allergens.
However, chronic inflammation can cause harm. When the immune system remains active, it may mistakenly attack healthy cells, leading to issues such as joint damage in arthritis or an increased risk of chronic diseases (Furman et al., 2019).
Environmental Factors Driving Chronic Inflammation
Lifestyle and environmental factors can trigger or worsen chronic inflammation. Recognizing these can help you make changes to reduce inflammation and improve health.
Unhealthy Diet
Diets high in processed foods, sugar, or unhealthy fats can fuel chronic inflammation. For example, sugary snacks or fried foods can increase inflammatory chemicals in the body. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, also releases inflammatory substances, worsening the problem (Shmerling, 2020).
Chronic Stress
Ongoing stress from work, relationships, or other pressures can raise inflammation levels. Stress hormones, like cortisol, can disrupt the immune system when elevated for too long, leading to chronic inflammation (Liu et al., 2017).
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity is linked to higher inflammation. Sitting for long periods can increase inflammatory markers, while regular exercise helps reduce them by improving blood flow and supporting the body’s detox processes (Gleeson et al., 2011).
Exposure to Toxins
Pollutants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or pesticides can irritate the body and trigger chronic inflammation. These toxins keep the immune system in a constant state of alert (Mostafalou & Abdollahi, 2017).
Persistent Infections
Some infections, like hepatitis, can linger in the body and cause ongoing inflammation. Even low-grade infections without clear symptoms can contribute over time (Furman et al., 2019).
Poor Sleep
Lack of sleep or poor-quality sleep can lead to increased inflammation. Sleep is essential for the body to repair itself, and without it, inflammatory chemicals can build up (Irwin et al., 2016).
Non-Surgical Treatments to Manage Chronic Inflammation
Non-surgical treatments, such as exercise, chiropractic care, and integrative therapies, can effectively reduce chronic inflammation and support the body’s natural healing processes. These approaches work together to ease pain, improve function, and promote overall health without compromising the body’s natural detoxification systems.
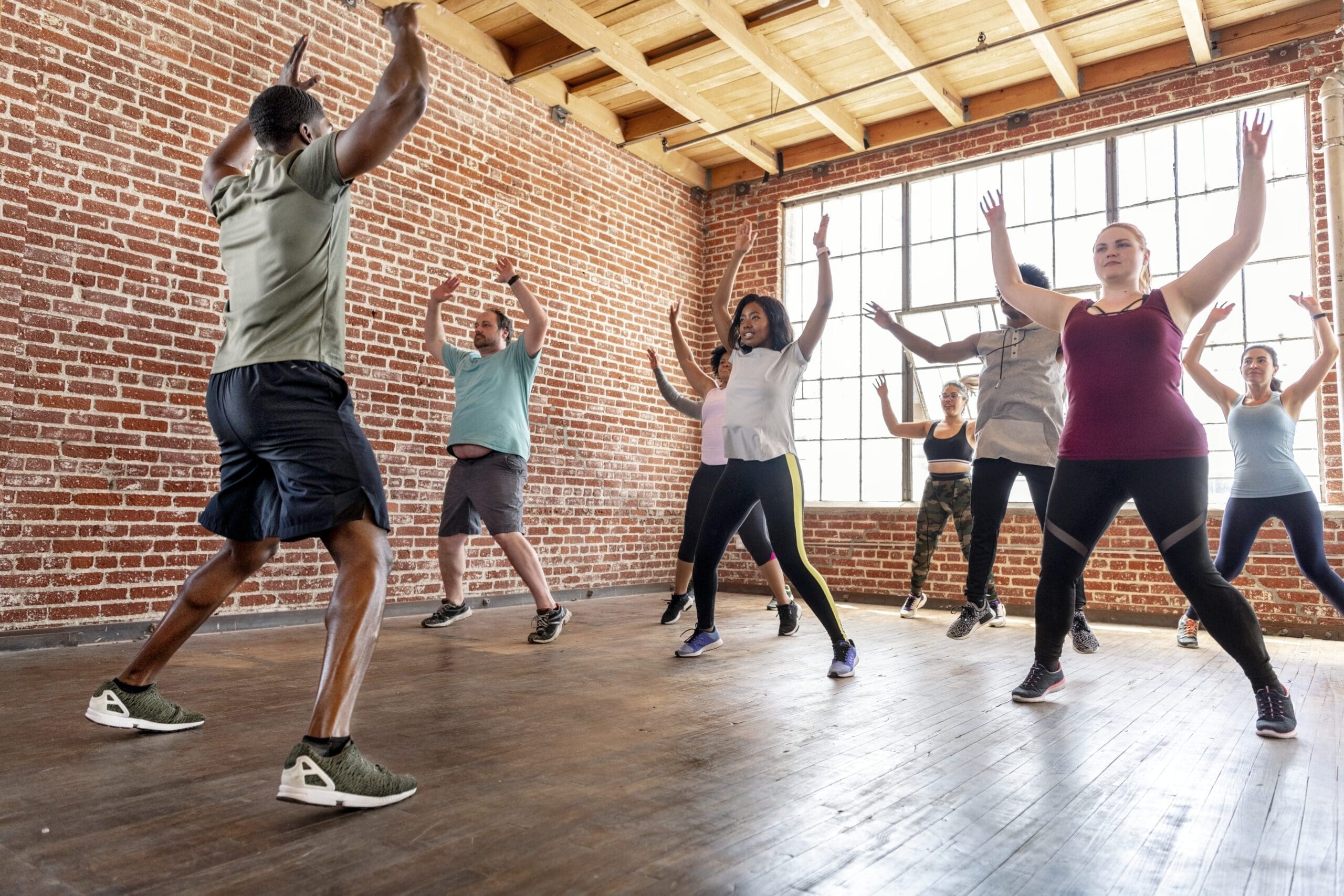
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is a powerful tool for reducing inflammation. It improves circulation, which helps the body clear inflammatory substances and deliver nutrients to tissues. Exercise also reduces stress and helps maintain a healthy weight, both of which lower inflammation.
- Aerobic Activities: Walking, running, swimming, or cycling can lower inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP). Regular aerobic exercise improves heart health and reduces inflammation (Gleeson et al., 2011).
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or doing resistance exercises strengthens muscles and supports joints, reducing inflammation in conditions like arthritis.
- Yoga and Stretching: These activities improve flexibility, reduce stress, and lower inflammation by calming the nervous system (West et al., 2021).
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a chiropractor and nurse practitioner, recommends personalized exercise plans to his patients to boost circulation and reduce inflammation, especially for those recovering from injuries (Jimenez, n.d.).
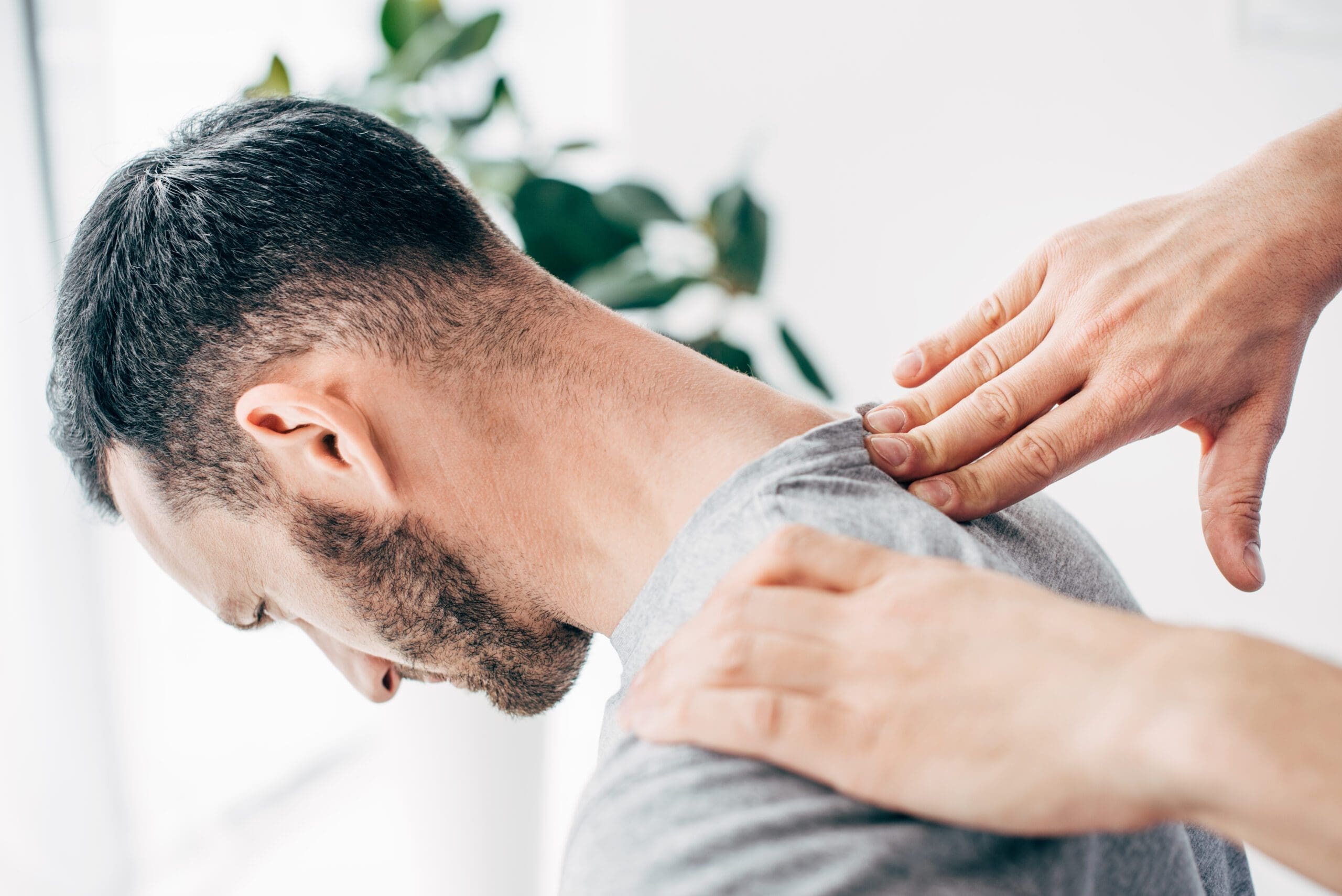
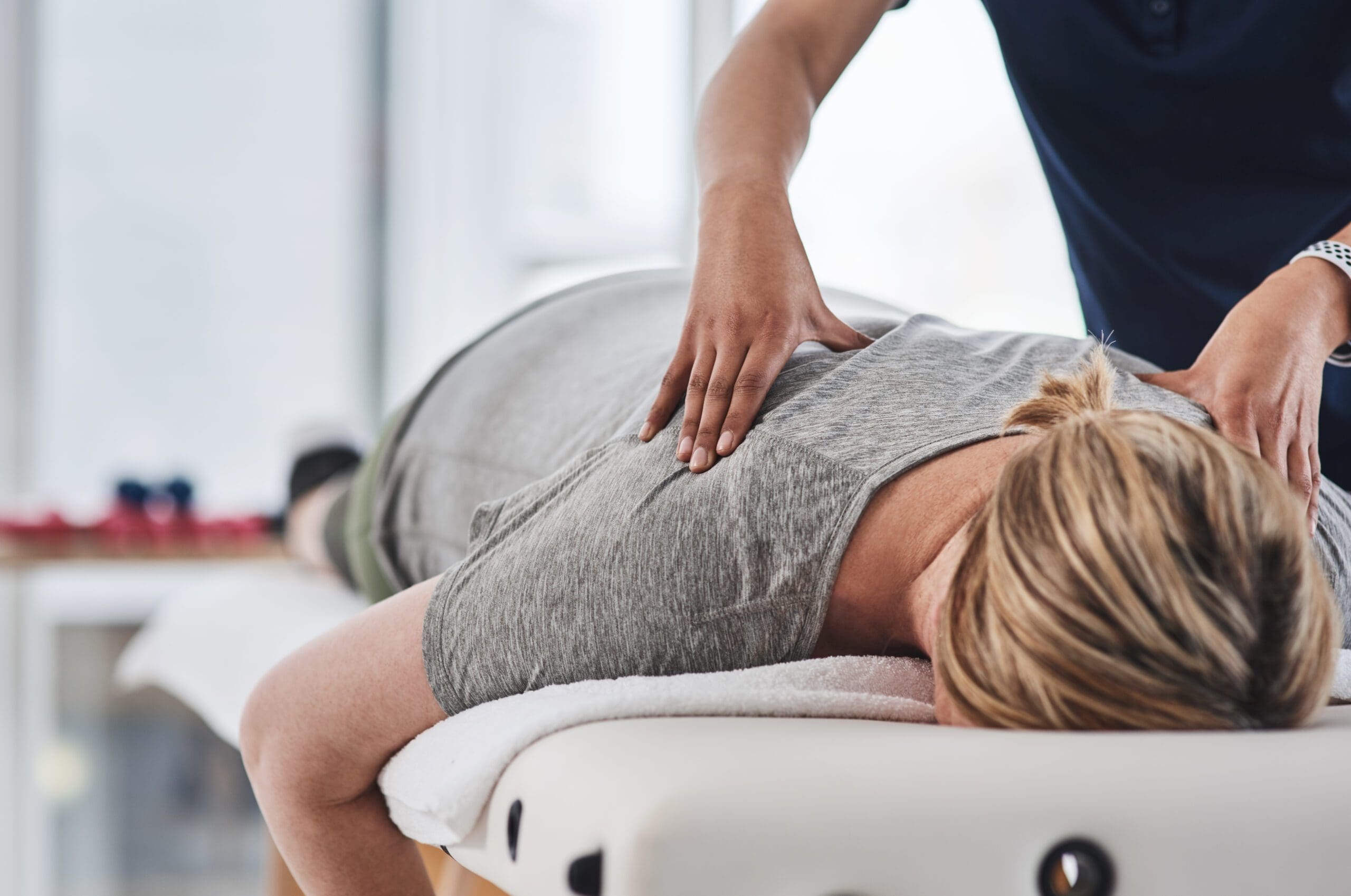
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care focuses on aligning the spine and optimizing the nervous system. Misalignments, or subluxations, can cause stress and inflammation in the body. Chiropractic adjustments restore alignment, reduce pain, and support natural healing.
Dr. Jimenez uses chiropractic care to treat inflammation caused by injuries from work, sports, or car accidents. Adjustments improve blood flow, reduce nerve pressure, and help the body manage inflammation more effectively (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
Integrative Therapies for Detoxification
Integrative care combines therapies to support the body’s natural detox systems, including the liver, kidneys, and lymphatic system. These systems remove toxins and waste, and chronic inflammation can strain them. Integrative therapies help without taking over their roles.
- Massage Therapy: Massage improves circulation, reduces muscle tension, and supports lymphatic drainage, helping the body clear toxins. It can also lower inflammatory markers and ease pain (Li et al., 2014).
- Acupuncture: This technique uses thin needles to stimulate specific points on the body, reducing inflammation by calming the nervous system and lowering stress hormones (Kavoussi & Ross, 2007).
- Nutrition Counseling: Eating anti-inflammatory foods, like vegetables, fruits, and omega-3-rich fish, supports detox processes. Supplements like turmeric or fish oil can further reduce inflammation (Calder, 2017).
Dr. Jimenez integrates these therapies into patient care, creating customized plans to reduce inflammation and support healing (Jimenez, n.d.).
Exploring Integrative Medicine- Video
Synergistic Effects of Combined Treatments
Exercise, chiropractic care, and integrative therapies work together to produce better results than any single treatment. For example:
- Exercise and Chiropractic Care: Exercise strengthens muscles and improves circulation, while chiropractic adjustments ensure proper spinal alignment, reducing inflammation and enhancing mobility.
- Massage and Acupuncture: Massage enhances lymphatic flow, and acupuncture reduces stress and inflammation, thereby amplifying the benefits of each.
- Nutrition and All Therapies: A healthy diet provides the nutrients needed for exercise, chiropractic care, and integrative therapies to work effectively, supporting the body’s healing processes.
These treatments support the body’s natural detox systems by improving circulation, reducing stress, and lowering inflammation, allowing the liver, kidneys, and lymphatic system to function optimally (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s Approach to Injury Management
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, based in El Paso, Texas, combines chiropractic care and nurse practitioner expertise to treat injuries from work, sports, personal accidents, and motor vehicle accidents (MVAs). His clinic uses a comprehensive approach to diagnose and treat injuries, focusing on long-term health.
Comprehensive Diagnosis
Dr. Jimenez employs a dual-scope approach, combining chiropractic evaluations with advanced medical diagnostics. For example, he assesses spinal alignment while using tools like MRI, X-rays, or ultrasound to examine soft tissue, bones, or swelling. This thorough process identifies the root cause of pain and inflammation (Jimenez, n.d.).
Tailored Treatment Plans
Treatment plans are personalized and may include:
- Chiropractic Adjustments: To correct spinal misalignments and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: To strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Massage Therapy: To relax muscles and improve circulation.
- Acupuncture: To reduce pain and inflammation.
These treatments target the cause of the injury, not just the symptoms, promoting lasting recovery (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
Managing Diverse Injuries
Dr. Jimenez treats a variety of injuries:
- Work Injuries: Repetitive strain or accidents, like back strains, are addressed with chiropractic care and therapy.
- Sports Injuries: Sprains or joint issues are treated with adjustments and exercise to restore function.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: Whiplash or back pain from MVAs is managed with imaging and targeted therapies (Jimenez, n.d.).
Medical and Legal Support
For injuries involving insurance or legal claims, Dr. Jimenez’s clinic provides detailed documentation, including:
- Diagnostic Results: Based on imaging and examination findings.
- Treatment Records: Outlining therapies and progress.
- Medical History: Detailing the patient’s condition before and after the injury.
This documentation supports patients in legal or insurance processes (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Dr. Jimenez uses advanced neuromusculoskeletal imaging, such as:
- MRI: To detect soft tissue damage.
- X-rays: To identify fractures or misalignments.
- Ultrasound: To assess swelling or fluid buildup.
These tools ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatments (Jimenez, n.d.).
Promoting Healing and Preventing Long-Term Issues
Dr. Jimenez’s integrative approach helps the body heal naturally by addressing the causes of inflammation and injury. Benefits include:
- Pain Relief: Adjustments and acupuncture can help reduce pain without relying heavily on medications.
- Improved Function: Exercise and chiropractic care restore mobility.
- Prevention: Early treatment of inflammation reduces the risk of chronic conditions like arthritis.
For example, a patient with chronic neck pain from a car accident might receive adjustments, massage, and exercises to reduce inflammation and prevent long-term issues (El Paso Back Clinic, n.d.).
Conclusion
Inflammation is essential for healing, but can become harmful when chronic. Acute inflammation helps fight infections and repair injuries, while chronic inflammation can lead to serious diseases. Environmental factors, such as a poor diet, stress, or toxins, can trigger chronic inflammation. However, non-surgical treatments like exercise, chiropractic care, and integrative therapies can effectively manage it.
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s integrative approach demonstrates how these treatments work together to reduce inflammation, support detoxification, and promote healing. By addressing the root causes of injuries and inflammation, his clinic helps patients recover and maintain long-term health. Adopting healthy habits, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, can further support these treatments and help keep inflammation in check.
References
Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 45(5), 1105–1115. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28540310/
DifferenceBetween.net. (n.d.). Difference between acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/health/difference-between-acute-inflammation-and-chronic-inflammation/
El Paso Back Clinic. (n.d.). Chronic inflammation & chiropractic. https://elpasobackclinic.com/chronic-inflammation-chiropractic/
Furman, D., Campisi, J., Verdin, E., Carrera-Bastos, P., Targ, S., Franceschi, C., … Slavich, G. M. (2019). Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nature Medicine, 25(12), 1822–1832. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31806905/
Gleeson, M., Bishop, N. C., Stensel, D. J., Lindley, M. R., Mastana, S. S., & Nimmo, M. A. (2011). The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Exercise: Mechanisms and Implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Nature Reviews Immunology, 11(8), 607–615. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22429824/
Harvard Health. (2020). Understanding acute and chronic inflammation. https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/understanding-acute-and-chronic-inflammation
Irwin, M. R., Olmstead, R., & Carroll, J. E. (2016). Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biological Psychiatry, 80(1), 40–52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26140821/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). Dr. Alexander Jimenez – El Paso chiropractor. https://dralexjimenez.com/
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). LinkedIn profile. https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Kavoussi, B., & Ross, B. E. (2007). The neuroimmune basis of anti-inflammatory acupuncture. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 6(3), 251–257. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17761638/
Li, Y. H., Wang, F. Y., Feng, C. Q., Yang, X. F., & Sun, Y. H. (2014). Massage therapy for fibromyalgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One, 9(2), e89304. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24586677/
Liu, Y. Z., Wang, Y. X., & Jiang, C. L. (2017). Inflammation: The common pathway of stress-related diseases. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 316. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28676747/
Mostafalou, S., & Abdollahi, M. (2017). Pesticides: An update of human exposure and toxicity. Archives of Toxicology, 91(2), 549–599. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27604863/
Shmerling, R. H. (2020). How acute inflammation turns chronic. Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/how-acute-inflammation-turns-chronic
West, K. A., Anderson, S. E., McAlindon, T. E., & Bannuru, R. R. (2021). Yoga for osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 29(7), 913–921. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33798607/