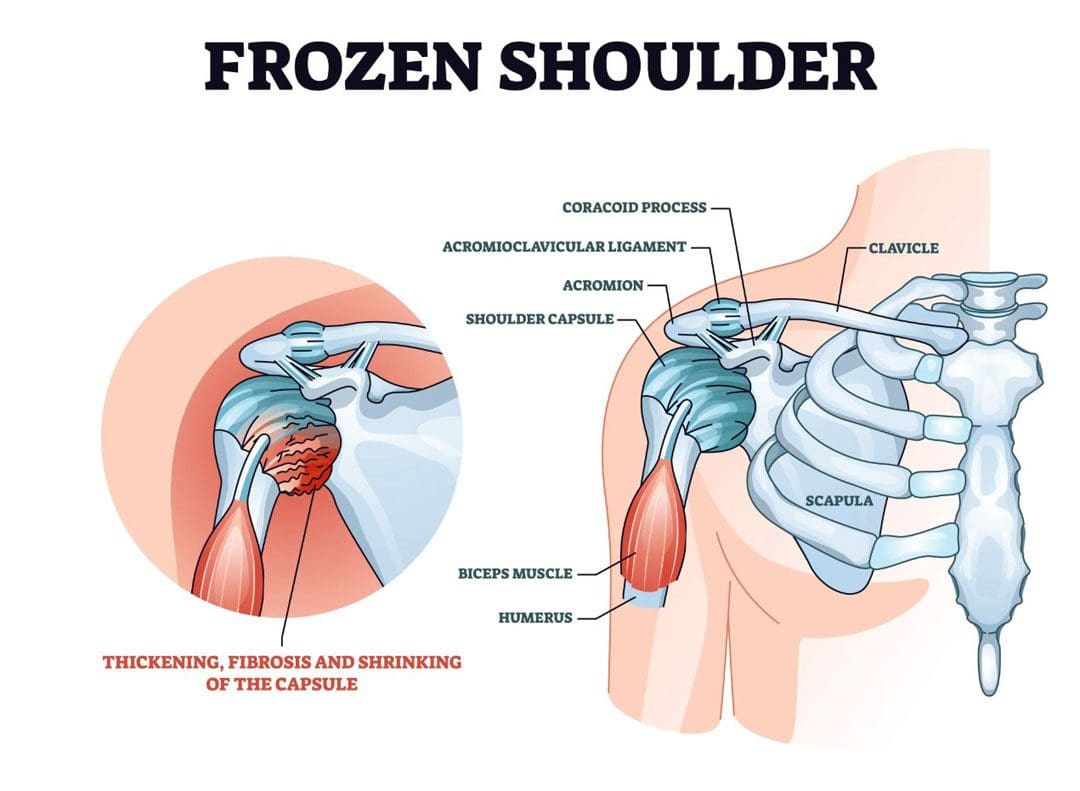
Sleep Importance for Brain Health & TBI Recovery
Discover sleep strategies to improve TBI recovery and promote better health outcomes after a traumatic brain injury.
The Critical Role of Sleep in Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide to Natural Healing
The path to recovery after a brain injury—whether from a severe fall, a sports accident, or an automobile accident—can seem drawn out and unpredictable. After a traumatic brain injury (TBI), sleep is one of the most important resources for brain repair and general health restoration. However, TBI often causes annoying sleep disturbances, which makes rehabilitation much more difficult. Individuals recuperating from traumatic brain injury may have headaches, physical discomfort, insomnia, persistent exhaustion, and memory loss. It’s not just the injury—environmental elements like noise, temperature, and light may make sleep even more difficult. These issues affect the brain, nerves, muscles, and even our emotional states; they don’t affect only one area of the body.
Thankfully, research indicates that getting more sleep might promote faster physical and mental recovery. Acupuncture, physical therapy, massage, chiropractic adjustments, and integrative wellness methods are just a few of the natural, non-surgical therapies that may promote healing and help reestablish regular sleep patterns. People with TBI may discover hope and practical solutions for regaining peaceful nights and stronger days by learning about the critical relationship between sleep and brain health, as well as how our surroundings and various treatments affect rehabilitation. The science behind sleep and TBI will be covered in this article, along with the reasons why sleep is crucial for the body and brain to heal, common symptoms and risk profiles following a brain injury, and safe, research-backed strategies to enhance sleep and aid in recovery so you can continue on your path to improved health.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury and Sleep Disruption
Traumatic brain injury affects millions of people each year, creating a cascade of physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges. The relationship between TBI and sleep is particularly profound, as sleep-wake disturbances are among the most common and debilitating consequences of injury (Sandsmark et al., 2017). Research indicates that approximately 30-85% of individuals who experience a TBI report sleep disturbances, with these problems often persisting for years after the initial injury (Aoun et al., 2019). The brain injury itself triggers multiple mechanisms that disrupt normal sleep architecture. When trauma occurs, the brain undergoes diffuse axonal injury, in which nerve fibers throughout the brain are damaged or torn. This damage particularly affects the arousal and sleep-regulation systems, creating fundamental problems in how the brain controls sleep and wakefulness (Sandsmark et al., 2017). The injury disrupts key brain structures, including the hypothalamus, brainstem, and reticular activating system—all essential components of maintaining healthy sleep-wake cycles.
Beyond the direct structural damage, TBI causes profound hormonal disruptions that further compromise sleep quality. Studies have shown that 95% of patients with acute TBI have low cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin levels, a wake-promoting neurotransmitter (Aoun et al., 2019). When hypocretin levels drop, excessive daytime sleepiness often results. Additionally, traumatic brain injury reduces levels of histamine, another wake-promoting substance, and melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. These hormonal imbalances create a perfect storm for sleep dysfunction that can manifest as insomnia, hypersomnia, or disrupted circadian rhythms.
The Glymphatic System: Sleep’s Critical Waste Removal Function
One of the most important discoveries in recent years has been understanding the glymphatic system and its relationship to sleep and brain health. The glymphatic system serves as the brain’s waste-clearance pathway, removing toxic metabolites and proteins that accumulate during waking hours. This system operates primarily during sleep, when it becomes 80-90% more active compared to the waking state (Aoun et al., 2019). During deep sleep, particularly slow-wave sleep, the brain undergoes critical housekeeping functions. Cerebrospinal fluid flows through the brain tissue, washing away cellular debris, proteins such as beta-amyloid and tau, and other potentially harmful substances that accumulate during daily activities (Piantino et al., 2022). When sleep is disrupted after TBI, this waste-clearance process is impaired. The accumulation of these neurotoxic substances can then potentiate cognitive dysfunction, slow recovery, and potentially increase the risk of long-term neurodegenerative conditions.
The bidirectional relationship between sleep disturbances and TBI symptoms creates a vicious cycle. The brain injury disrupts sleep, impairing glymphatic clearance. This impairment leads to increased accumulation of waste products, worsening cognitive symptoms and brain inflammation, and further disrupting sleep (Piantino et al., 2022). Breaking this cycle through targeted sleep interventions becomes essential for optimal recovery.
Common Sleep Disorders Following Traumatic Brain Injury
Understanding the specific types of sleep disorders that develop after TBI helps guide appropriate treatment strategies. The most common sleep disturbances include insomnia, post-traumatic hypersomnia, sleep-disordered breathing, circadian rhythm disorders, and parasomnias (Viola-Saltzman & Watson, 2012).
- Insomnia represents the most frequently reported sleep complaint after TBI, affecting 25-29% of patients compared to only 6-10% of the general population (Aoun et al., 2019). People with insomnia following brain injury typically experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep throughout the night, or waking too early in the morning. The insomnia often stems from multiple factors, including heightened anxiety about sleep, pain, increased sensitivity to noise and light, and dysfunction in the brain regions that control sleep initiation and maintenance.
- Post-traumatic hypersomnia affects approximately 20-25% of individuals after brain injury, manifesting as excessive daytime sleepiness, longer sleep durations, or an increased need for daytime naps (Aoun et al., 2019). This condition can significantly impair daily functioning, making it difficult to maintain work responsibilities, social activities, or rehabilitation programs. The excessive sleepiness often relates to reduced hypocretin levels and disruption of wake-promoting neurochemical systems.
- Sleep-disordered breathing, including obstructive sleep apnea, occurs in approximately 23% of TBI patients (Aoun et al., 2019). Brain injury can affect the upper airway muscles, contribute to weight gain due to reduced activity, or damage brainstem regions that control breathing during sleep. When breathing becomes repeatedly interrupted throughout the night, oxygen levels drop, sleep quality plummets, and the brain’s recovery process becomes compromised.
- Circadian rhythm disorders develop when the brain’s internal clock becomes disrupted. The suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus serves as the master circadian pacemaker, but brain injury can damage this region or the pathways connecting it to other brain areas (Aoun et al., 2019). When circadian rhythms shift, people may find themselves unable to fall asleep until very late at night, waking up at inappropriate times, or experiencing irregular sleep-wake patterns that make maintaining a consistent schedule nearly impossible.
How Environmental Factors Affect Brain Activity and Sleep
The environment plays a powerful role in either supporting or sabotaging sleep quality, particularly for individuals recovering from traumatic brain injury. People with TBI often develop heightened sensitivities to environmental stimuli, making the sleep environment especially critical for recovery.
- Light exposure represents one of the most potent environmental influences on sleep and circadian rhythms. Light suppresses melatonin production, the hormone that signals the brain that it’s time to sleep. Artificial light from streetlights, electronic devices, and indoor lighting can delay sleep onset and disrupt circadian phase (Environmental Determinants, 2018). For TBI patients who may already have reduced melatonin production, exposure to light at night can compound sleep difficulties. Even small amounts of light pollution have been shown to significantly affect sleep architecture, reducing sleep efficiency and increasing wakefulness after sleep onset.
- Environmental noise creates another major barrier to quality sleep. Traffic sounds, aircraft noise, and urban noise pollution fragment sleep by causing brief arousals throughout the night. Studies have shown that exposure to airplane noise increases the risk of sleeping fewer than 7 hours per night (The Influence of Environmental Factors, 2025). For individuals with TBI, who often experience increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, noise pollution can be particularly disruptive. The brain’s heightened arousal state makes it more difficult to filter out environmental sounds, leading to more frequent awakenings and lighter, less restorative sleep.
- Temperature regulation affects sleep quality by influencing the body’s thermoregulatory system. The ideal sleep environment typically ranges from 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit. People living in warmer climates often experience more difficulty sleeping, especially during summer months when higher temperatures can interfere with the natural drop in core body temperature that facilitates sleep onset (Where You Live, 2023). Following TBI, some individuals develop problems with temperature regulation, making environmental temperature control even more important.
- Indoor air quality influences sleep by affecting breathing and overall comfort. Poor ventilation, allergens, dust, and chemical pollutants can trigger respiratory issues, allergic reactions, or general discomfort that disrupts sleep. Maintaining clean air through proper ventilation, air filtration, and reducing indoor pollution sources supports better breathing and more restful sleep.
Neurological Disorders and Overlapping Risk Profiles
Traumatic brain injury rarely exists in isolation. The complex neurological changes that follow brain injury often create overlapping symptom profiles that affect multiple body systems simultaneously. Understanding these interconnected symptoms helps explain why TBI recovery requires a comprehensive, whole-person approach.
- Headaches represent one of the most common and persistent symptoms following TBI, affecting the majority of individuals during recovery. These headaches can range from tension-type headaches caused by muscle tension and stress to migraine-like headaches with throbbing pain, light sensitivity, and nausea. The relationship between headaches and sleep is bidirectional—poor sleep can trigger or worsen headaches, while severe headaches make falling asleep or staying asleep extremely difficult. Chronic headaches activate pain pathways that increase brain arousal, directly interfering with the relaxation necessary for sleep onset.
- Cognitive issues, including problems with memory, attention, concentration, and executive function, create significant challenges after TBI. Sleep plays an essential role in cognitive functioning, as memory consolidation, learning, and cognitive processing all depend on adequate sleep (Sanchez et al., 2022). When sleep becomes disrupted, cognitive symptoms worsen, creating frustration and anxiety that further impair sleep. Research has shown that better sleep during the hospitalization phase after TBI predicts more favorable long-term cognitive outcomes years later (Sanchez et al., 2022).
- Fatigue affects 43-73% of people following TBI and differs from normal tiredness (Aoun et al., 2019). This pathological fatigue persists despite rest, creating overwhelming exhaustion that makes even simple daily tasks feel impossible. The fatigue relates to the brain’s increased energy demands during healing, disrupted sleep architecture, and neuroinflammation. When fatigue and sleep disturbances coexist, they create a reinforcing cycle where fatigue makes it harder to maintain normal activity levels, disrupting circadian rhythms and further impairing sleep quality.
- Sleep disturbances themselves become both a symptom and a perpetuating factor in TBI recovery. The various forms of sleep disruption—from insomnia to hypersomnia to circadian rhythm shifts—all impair the brain’s ability to heal and regenerate. Poor sleep increases inflammation, impairs immune function, worsens mood and anxiety, and slows cognitive recovery (Zielinski & Gibbons, 2022).
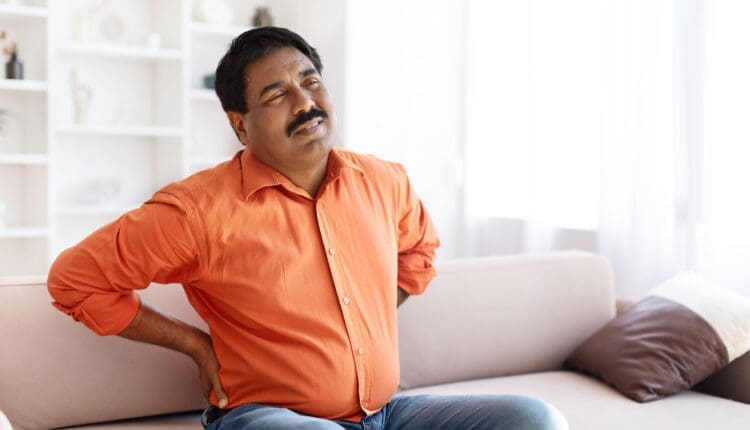
- Muscle instability and musculoskeletal pain frequently develop after TBI due to the accident mechanism, reduced activity during recovery, or changes in muscle tone and coordination. The relationship between musculoskeletal pain and sleep is well-established—pain makes finding comfortable sleep positions difficult and triggers frequent awakenings throughout the night. Simultaneously, poor sleep increases pain sensitivity by impairing the body’s natural pain modulation systems (Sleep Disturbance in Musculoskeletal Conditions, 2023).
These overlapping symptoms create what researchers call a “symptom cluster”—a group of interconnected problems that influence and worsen each other. Addressing only one symptom in isolation rarely produces lasting improvement. Instead, comprehensive treatment approaches that target multiple symptoms simultaneously tend to yield better outcomes.
Sleep Disturbances and the Musculoskeletal System
The connection between sleep quality and musculoskeletal health extends beyond simple pain, keeping someone awake. Poor sleep fundamentally changes how the body processes and responds to pain signals, creating physiological changes that perpetuate both sleep problems and musculoskeletal dysfunction. When sleep becomes disrupted, several neurochemical changes occur that affect pain processing. Sleep deprivation increases inflammatory cytokines—proteins that promote inflammation throughout the body. This heightened inflammatory state sensitizes pain receptors, making normally non-painful stimuli feel painful and amplifying existing pain (Sleep Disorders in Chronic Pain, 2023). Additionally, poor sleep impairs the descending pain-inhibitory pathways—the brain’s natural pain-suppression system—making it more difficult for the body to modulate pain signals.
The coexistence of insomnia and chronic musculoskeletal pain results in greater pain intensity and alterations in sleep homeostasis. Among patients with neuropathic pain, those with poor sleep quality experience more severe pain, more severe depressive states, and worse quality of life than patients with good sleep quality (Sleep Disorders in Chronic Pain, 2023). This creates a vicious cycle where pain disrupts sleep, poor sleep increases pain sensitivity, heightened pain further disrupts sleep, and the cycle continues. Sleep disturbances also affect muscle recovery and tissue repair. During deep sleep, the body releases growth hormone, which promotes tissue healing and muscle regeneration. When sleep quality suffers, this repair process becomes impaired, potentially slowing recovery from injuries and contributing to ongoing musculoskeletal dysfunction. The reduced physical activity that often accompanies both TBI and sleep problems can lead to muscle deconditioning, decreased flexibility, and altered movement patterns that increase injury risk and perpetuate pain.
The Autonomic Nervous System: Understanding the Body’s Control Center
To understand how various treatments improve sleep after TBI, it’s essential to grasp the role of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) in sleep regulation. The ANS controls involuntary body functions, including heart rate, breathing, digestion, and the sleep-wake cycle. It consists of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The sympathetic nervous system governs the “fight, flight, or freeze” response. When activated, it increases heart rate, raises blood pressure, heightens alertness, and prepares the body for action. While this system serves important protective functions, chronic activation—common after TBI due to anxiety, pain, and stress—makes falling asleep and staying asleep extremely difficult.
The parasympathetic nervous system promotes “rest and digest” functions. When activated, it slows heart rate, promotes relaxation, aids digestion, and facilitates sleep. The vagus nerve serves as the primary pathway for parasympathetic signals, connecting the brain to organs throughout the body. Strong vagal tone—the measure of vagus nerve activity—indicates good parasympathetic function and associates with better stress resilience, improved sleep quality, and enhanced overall health (The Vagus Nerve, 2024). After traumatic brain injury, the balance between these two systems often becomes disrupted, with excessive sympathetic activation and reduced parasympathetic activity. This imbalance manifests as difficulty relaxing, heightened anxiety, rapid heart rate, and sleep disturbances. Restoring autonomic balance becomes a key goal of many non-surgical treatment approaches.
Neuroinflammation and Sleep Regulation
Neuroinflammation—inflammation within the brain and central nervous system—plays a central role in both TBI pathophysiology and sleep regulation. When a brain injury occurs, the immune system responds by activating inflammatory processes intended to clear damaged tissue and promote healing. However, when this inflammation becomes excessive or prolonged, it can impair recovery and disrupt normal brain function. Inflammatory cytokines, particularly interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α, directly influence sleep regulation. These molecules can promote sleepiness during acute phases of inflammation, which may explain the excessive sleepiness some people experience immediately after brain injury. However, chronic elevation of these inflammatory markers can disrupt sleep architecture, reduce sleep efficiency, and fragment sleep (Zielinski & Gibbons, 2022).
The relationship between inflammation and sleep is bidirectional. Poor sleep increases inflammatory markers, while elevated inflammation disrupts sleep. This creates another reinforcing cycle that can impede TBI recovery. Inflammation also impairs the glymphatic system’s ability to clear waste products from the brain. The combination of impaired glymphatic function and elevated neuroinflammation creates conditions that slow healing and perpetuate cognitive dysfunction. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation through what scientists call the “inflammatory reflex.” When the vagus nerve detects inflammatory signals, it can activate anti-inflammatory pathways that help modulate the immune response (Zielinski & Gibbons, 2022). This connection between the vagus nerve, inflammation, and sleep helps explain why treatments that stimulate vagal activity can improve both inflammation and sleep quality.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Improving Sleep After TBI
While medications can provide short-term relief for sleep problems, they rarely address the underlying causes of sleep dysfunction and can carry risks of dependency and side effects. Non-surgical treatments offer effective alternatives that target the root causes of sleep disturbances while promoting overall healing and recovery.
Chiropractic Care: Restoring Nervous System Function
Chiropractic care focuses on the relationship between the spine and nervous system, recognizing that spinal misalignments can interfere with nervous system function and overall health. For individuals recovering from TBI, chiropractic care offers multiple benefits, including improvements in sleep quality and neurological recovery. Research has demonstrated that chiropractic adjustments can improve brain function, with studies showing up to a 20% boost following a single adjustment (How Chiropractic Neurology Supports, 2025). These improvements include enhanced cerebrospinal fluid flow, reduced pressure on the nervous system, and improved blood circulation to the brain—all factors critical for TBI recovery. Chiropractic care affects sleep through several mechanisms. By addressing misalignments in the spine, particularly in the upper cervical region, chiropractors help improve nervous system function and reduce interference with sleep-regulating pathways (The Relationship Between Chiropractic Care and Sleep, 2023). Spinal adjustments activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting the relaxation response necessary for falling asleep. Studies have shown significant improvements in light sleep stages and overall quality of life following chiropractic treatment, along with reductions in anxiety, depression, fatigue, and pain—all factors that commonly disrupt sleep after TBI (Neuroplastic Responses to Chiropractic Care, 2024).
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, FNP-BC, has observed in his clinical practice that chiropractic care combined with functional medicine approaches can significantly improve outcomes for patients with TBI and sleep disturbances. His integrated approach addresses not only structural alignment but also nutritional factors, lifestyle modifications, and the underlying causes of nervous system dysfunction. By restoring proper spinal alignment and nervous system function, chiropractic care helps patients achieve better sleep patterns, reduced pain, and improved overall recovery.
Acupuncture: Modulating Neurotransmitters and Autonomic Function
Acupuncture, a key component of traditional Chinese medicine, involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body to influence energy flow and promote healing. Modern research has revealed that acupuncture exerts powerful effects on neurotransmitter systems, autonomic nervous system function, and neuroplasticity—all of which are relevant to improving sleep after TBI. Studies have demonstrated that acupuncture therapy can effectively treat sleep disorders by modulating several key neurotransmitter systems. Acupuncture increases gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an inhibitory neurotransmitter that promotes calmness and sleep, while decreasing glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter that promotes wakefulness (The Effects of Acupuncture on Sleep Disorders, 2023). This shift in the excitatory-inhibitory balance creates conditions more conducive to falling asleep and maintaining sleep throughout the night.
Acupuncture also affects the autonomic nervous system by modulating vagus nerve activity. Research shows that acupuncture can directly influence peripheral nerves and muscles, which in turn modulate autonomic tone and central nervous system activation (Autonomic Activation in Insomnia, 2011). By activating parasympathetic pathways, acupuncture promotes the relaxation response, reduces stress hormone levels, and improves sleep quality. For stroke patients with sleep disorders—conditions that share similarities with TBI—acupuncture combined with conventional treatments produced significant improvements in sleep quality and neurological function (Effect of Acupuncture on Sleep Quality, 2021). The treatment reduced the time needed to fall asleep, increased total sleep duration, improved sleep efficiency, and decreased the frequency and duration of breathing interruptions during sleep. In Dr. Jimenez’s integrative practice, acupuncture serves as a valuable tool for addressing sleep disturbances in TBI patients. The treatment’s ability to reduce pain, decrease anxiety, improve autonomic balance, and directly influence sleep-regulating neurotransmitters makes it particularly effective when combined with other therapeutic modalities.
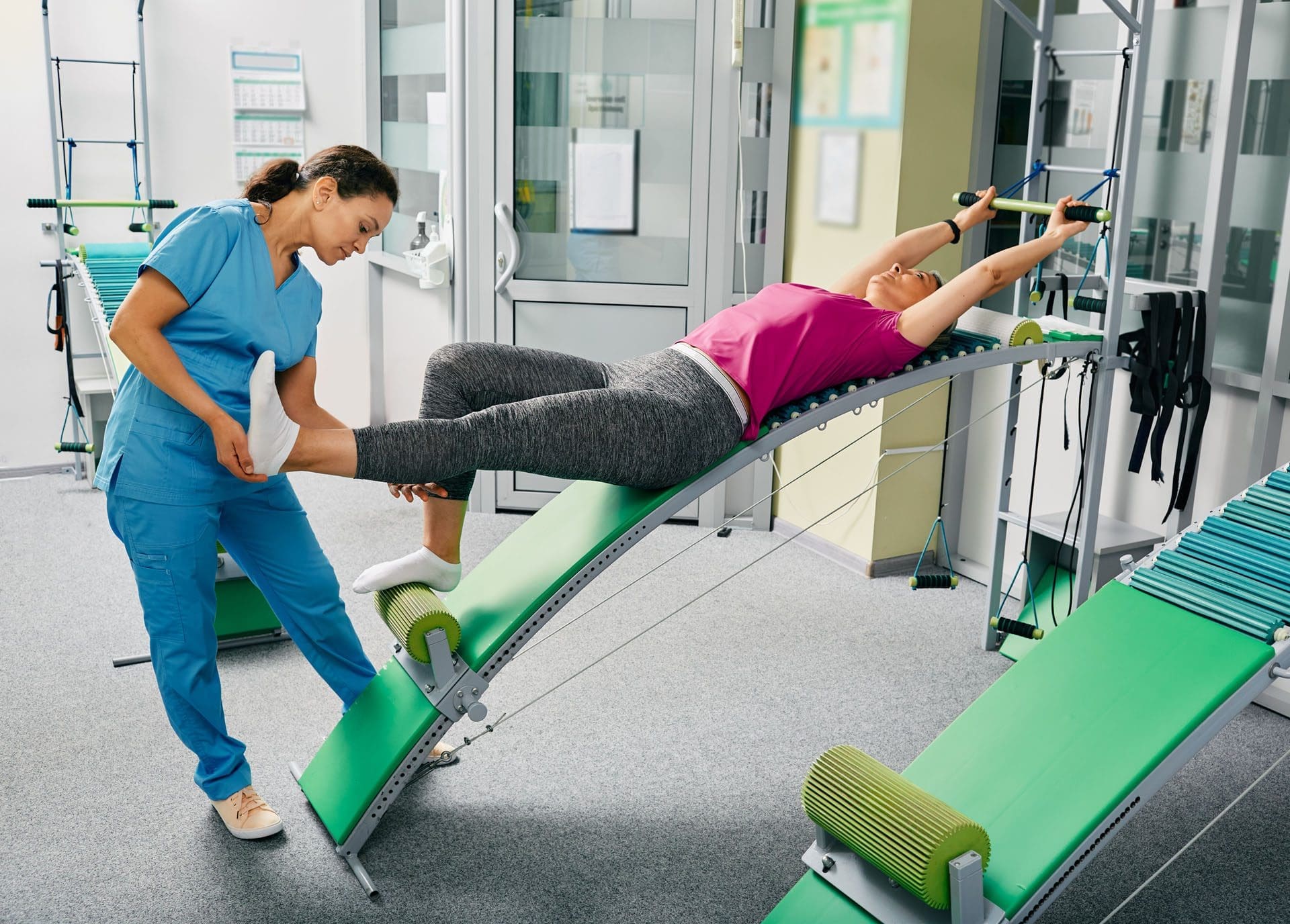
Physical Therapy: Exercise and Movement for Better Sleep
Physical therapy uses targeted exercises, manual techniques, and movement strategies to restore function, reduce pain, and improve overall physical health. For individuals recovering from TBI, physical therapy offers benefits that extend well beyond musculoskeletal improvements, enhancing sleep quality and neurological recovery. Exercise represents one of the most effective non-pharmacological interventions for improving sleep. A meta-analysis demonstrated that exercise interventions resulted in significant improvements in overall sleep quality, subjective sleep perception, and sleep latency—the time needed to fall asleep (Sleep Disturbance in Musculoskeletal Conditions, 2023). Exercise promotes better sleep through multiple mechanisms, including reducing anxiety and depression, regulating circadian rhythms, increasing sleep drive, and promoting deeper, more restorative sleep stages.
Physical therapy also addresses the musculoskeletal pain that commonly disrupts sleep after TBI. Through manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and posture education, physical therapists help reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore normal movement patterns. When pain decreases, sleep quality typically improves as individuals can find comfortable positions and experience fewer pain-related awakenings (How Physical Therapy Supports Better Sleep, 2025). The timing and type of exercise matter for sleep quality. Regular aerobic exercise improves sleep, but exercising too close to bedtime can be stimulating and delay sleep onset. Physical therapists help patients develop appropriate exercise programs that promote sleep without interfering with the ability to fall asleep. Moderate-intensity exercise training has been shown to have significant beneficial effects on both sleep quality and cardio-autonomic function (Sleep Disturbance in Musculoskeletal Conditions, 2023). For TBI patients specifically, research has shown that physical therapy exercises represent a safe and useful strategy for managing sleep disorders in neurorehabilitation (Physical Therapy Exercises for Sleep Disorders, 2021). The combination of improved physical function, reduced pain, better mood, and normalized circadian rhythms creates optimal conditions for restorative sleep.
Massage Therapy: Activating the Parasympathetic Response
Massage therapy involves manipulating soft tissues to promote relaxation, reduce muscle tension, and improve circulation. This hands-on approach offers powerful benefits for sleep quality by directly influencing the nervous system and supporting the body’s natural healing processes. The scientific foundation for massage therapy’s sleep benefits lies in its effects on the autonomic nervous system. Massage activates the parasympathetic nervous system, signaling the body to shift from the stress response to the relaxation response (How Massage Therapy Improves Sleep Quality, 2024). This activation reduces heart rate, lowers blood pressure, decreases cortisol (the primary stress hormone), and increases production of serotonin and dopamine—neurotransmitters associated with mood regulation and relaxation.
Massage therapy supports better sleep by increasing serotonin levels, which serve as a precursor to melatonin. By promoting the production of these sleep-regulating hormones, massage helps the body naturally fall into a healthy sleep cycle (How Massage Therapy Can Improve Sleep Quality, 2024). This natural approach to improving melatonin production can be particularly valuable for TBI patients who may have reduced melatonin levels due to brain injury. Research has demonstrated that massage therapy reduces muscle pain and tension, improves circulation and oxygen flow, and creates overall physical relaxation that facilitates sleep (Massage Positively Influences Daytime Brain Activity, 2025). For individuals with musculoskeletal pain following TBI, massage addresses both the pain itself and the muscle guarding and tension that develop in response to pain.
Studies examining massage therapy in postmenopausal women with insomnia found significant improvements in sleep architecture, including decreased REM latency, reduced time in stage 1 sleep, and increased time in the deeper stages 3 and 4 sleep (The Beneficial Effects of Massage Therapy, 2014). These changes represent meaningful improvements in sleep quality, as deeper sleep stages provide more restorative benefits. In clinical practice, massage therapy is often integrated with other treatment modalities to provide comprehensive care for TBI patients. The combination of massage with chiropractic care, physical therapy, and other approaches creates synergistic effects that enhance overall outcomes.
The Science of Motion- Video
Restoring Communication Between Brain and Body
All of these non-surgical treatments share a common goal: restoring proper communication between the brain and body. Traumatic brain injury disrupts this communication on multiple levels—from direct damage to neural pathways to hormonal imbalances to autonomic dysfunction. By addressing these disruptions through various therapeutic approaches, practitioners help reestablish the connections necessary for healing. The central nervous system coordinates all body functions through intricate networks of neurons that transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. When TBI occurs, this communication system becomes compromised. Chiropractic care addresses structural barriers to nerve transmission; acupuncture modulates neurotransmitter activity; physical therapy restores movement patterns that influence neural feedback; and massage therapy activates sensory pathways that signal safety and relaxation to the brain.
Vagal tone—the activity level of the vagus nerve—serves as a key indicator of how well the brain and body communicate. Higher vagal tone associates with better stress resilience, improved mood, better cognitive function, and enhanced sleep quality (The Vagus Nerve, 2024). Many of the non-surgical treatments discussed here work, in part, by improving vagal tone. Chiropractic adjustments, acupuncture, massage, and certain breathing exercises can all activate the vagus nerve, strengthening the parasympathetic response and improving autonomic balance. The somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary movements and processes sensory information, also plays a role in sleep quality. When musculoskeletal pain or movement dysfunction affects the somatic system, it can create ongoing sensory signals that keep the nervous system in a heightened state of alertness. Treatments that address these somatic issues—through physical therapy, massage, and manual techniques—help quiet these alerting signals and allow the nervous system to transition into sleep states more easily.
Developing an Effective Sleep Routine After TBI
Creating and maintaining a consistent sleep routine represents one of the most important steps for improving sleep quality after traumatic brain injury. A well-designed sleep routine helps regulate circadian rhythms, signals the brain that it’s time for sleep, and creates optimal conditions for restorative rest.
Establish Consistent Sleep and Wake Times
The foundation of good sleep hygiene involves going to bed and waking up at approximately the same time every day, including weekends. This consistency helps program the brain’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep at bedtime and wake up feeling more refreshed (Enhancing Sleep Quality After TBI, 2024). After TBI, when circadian rhythms may be disrupted, this consistency becomes even more critical for reestablishing normal sleep-wake patterns.
Choose a bedtime that allows for 7-9 hours of sleep before your desired wake time. While individual sleep needs vary, most adults require at least seven hours of sleep per night for optimal health and recovery. Avoid the temptation to “sleep in” to make up for poor sleep, as this can further disrupt circadian rhythms and make it more difficult to fall asleep the following night.
Create a Relaxing Pre-Sleep Routine
Dedicate the 60-90 minutes before bedtime to calming activities that help transition from wakefulness to sleep. This wind-down period signals to the brain and body that sleep is approaching, allowing physiological systems to prepare for rest (Sleep After Traumatic Brain Injury, 2025).
Consider incorporating the following elements into your pre-sleep routine:
- Dim the lights throughout your living space in the evening. Bright light suppresses melatonin production, making it harder to feel sleepy. Use soft, warm-toned lighting and avoid bright overhead lights as bedtime approaches.
- Avoid screens from phones, tablets, computers, and televisions for at least 30-60 minutes before bed. The blue light emitted by electronic devices particularly suppresses melatonin and can delay sleep onset by up to two hours (Assessment and Management of Sleep Disturbances, 2024). If you must use devices, enable night mode or a blue light filter, and keep the screen brightness low.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, gentle stretching, or meditation. These activities activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reduce stress hormone levels, and prepare the body for sleep. Even 10-15 minutes of focused relaxation can significantly improve your ability to fall asleep.
- Take a warm bath or shower 60-90 minutes before bed. The subsequent cooling of body temperature after getting out of the bath mimics the natural temperature drop that occurs at sleep onset, helping to trigger sleepiness.
- Engage in quiet, non-stimulating activities like reading a book (preferably a physical book rather than an e-reader), listening to calming music, or journaling. Avoid activities that are mentally or emotionally stimulating, such as work-related tasks, intense discussions, or watching exciting or disturbing content.
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
The bedroom environment significantly influences sleep quality, particularly for individuals with TBI who may have heightened sensory sensitivities.
- Keep the bedroom cool, ideally between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit. A cooler room temperature supports the natural drop in core body temperature that facilitates sleep onset and helps maintain sleep throughout the night (Where You Live, 2023).
- Make the room as dark as possible. Use blackout curtains or shades to block outside light, cover or remove electronic devices with glowing lights, and consider using a sleep mask if complete darkness isn’t achievable. Even small amounts of light can disrupt sleep architecture and reduce sleep quality.
- Minimize noise by using earplugs, white noise machines, or fans to create a consistent background sound that masks disruptive environmental noises. For some individuals, complete silence works best, while others find gentle, consistent sounds more soothing.
- Ensure your bed is comfortable with a supportive mattress and pillows appropriate for your preferred sleep position. If musculoskeletal pain disrupts your sleep, consider using additional pillows for support or trying different sleep positions to reduce pressure on painful areas.
- Use the bedroom only for sleep and intimacy. Avoid working, watching television, or engaging in other wakeful activities in bed. This helps strengthen the mental association between the bedroom and sleep, making it easier to fall asleep when you get into bed.
Manage Daytime Behaviors That Affect Nighttime Sleep
Actions taken during the day significantly impact nighttime sleep quality.
- Get exposure to natural light early in the morning and throughout the day. Sunlight exposure helps regulate circadian rhythms, suppresses daytime melatonin production, and strengthens the contrast between day and night signals to the brain (Assessment and Management of Sleep Disturbances, 2024). Aim for at least 30 minutes of natural light exposure in the morning.
- Exercise regularly, but not within 2-3 hours of bedtime. Regular physical activity improves sleep quality, but exercising too close to bedtime can be stimulating and delay sleep onset (Warding Off Sleep Issues, 2024). Morning or early afternoon exercise provides the best sleep benefits.
- Limit naps to 20-30 minutes and avoid napping after 3:00 PM. While short naps can be refreshing, long or late-day naps can interfere with nighttime sleep. If you’re experiencing excessive daytime sleepiness after TBI, discuss appropriate napping strategies with your healthcare provider, as this may indicate an underlying sleep disorder requiring specific treatment.
- Avoid caffeine for at least 5-6 hours before bedtime. Caffeine has a half-life of 5-6 hours, meaning half of the caffeine consumed remains in your system that long after consumption. For sensitive individuals or those with sleep difficulties, avoiding caffeine after noon may be necessary (Warding Off Sleep Issues, 2024).
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid alcohol close to bedtime. While alcohol may initially make you feel sleepy, it disrupts sleep architecture, reduces REM sleep, and causes more frequent awakenings during the night. Alcohol also affects breathing during sleep and can worsen sleep-disordered breathing.
- Avoid large meals within 2-3 hours of bedtime. Eating too close to bedtime can cause digestive discomfort that interferes with sleep. If you’re hungry before bed, choose a light snack that combines complex carbohydrates with a small amount of protein.
A Questionnaire Example of TBI Symptoms
Address Specific Sleep Problems
Different sleep problems require targeted strategies.
- For difficulty falling asleep, try the “cognitive shuffle” technique or counting backwards by threes from a random number. These activities occupy the mind with neutral content, preventing anxious or racing thoughts that can delay sleep onset. If you don’t fall asleep within 20-30 minutes, get out of bed and engage in a quiet, non-stimulating activity until you feel sleepy.
- For frequent nighttime awakenings, practice staying calm and avoiding clock-watching, which can increase anxiety about sleep. Use the same relaxation techniques you employ before bed to help return to sleep. If awakening relates to pain, work with your healthcare providers to address pain management strategies.
- For early morning awakening, ensure you’re getting adequate light exposure during the day and avoiding light exposure in the evening. This helps shift your circadian rhythm to a more appropriate schedule.
When to Seek Professional Help
While good sleep hygiene provides the foundation for better sleep, it’s not sufficient as a standalone treatment for specific sleep disorders. If you’re implementing these strategies consistently for 2-3 weeks without significant improvement, consult with healthcare providers who specialize in sleep medicine or TBI rehabilitation (Assessment and Management of Sleep Disturbances, 2024).
A professional evaluation can identify specific sleep disorders like sleep apnea, narcolepsy, or circadian rhythm disorders that require targeted treatments. Sleep studies, including polysomnography and multiple sleep latency testing, provide objective measurements of sleep architecture and can reveal problems not apparent from self-report alone.
The Role of Functional Medicine in TBI and Sleep Recovery
Functional medicine takes a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to health, seeking to identify and address the root causes of illness rather than simply managing symptoms. For individuals recovering from TBI with sleep disturbances, functional medicine offers valuable insights and treatment strategies that complement other therapeutic interventions. Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s clinical approach exemplifies the principles of functional medicine applied to TBI and sleep disorders. As both a chiropractor and board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner with training in functional and integrative medicine, Dr. Jimenez conducts detailed assessments that evaluate personal history, current nutrition, activity behaviors, environmental exposures, genetic factors, and psychological and emotional elements that may contribute to sleep problems.
This comprehensive evaluation often reveals multiple contributing factors that conventional approaches might miss. For example, nutrient deficiencies in magnesium, vitamin D, or B vitamins can significantly impact sleep quality and neurological recovery. Chronic inflammation driven by dietary factors, environmental toxins, or gut health problems can impair both sleep and healing. Hormonal imbalances, blood sugar dysregulation, and mitochondrial dysfunction can all contribute to the fatigue, cognitive problems, and sleep disturbances that follow TBI. By identifying these underlying issues, functional medicine practitioners can create personalized treatment plans that address multiple factors simultaneously. This might include nutritional interventions to correct deficiencies and reduce inflammation, dietary modifications to support stable blood sugar and gut health, targeted supplementation to support mitochondrial function and neurological healing, stress management strategies to balance the autonomic nervous system, and environmental modifications to reduce toxic exposures and optimize the sleep environment. The integration of functional medicine with chiropractic care, physical therapy, acupuncture, and other modalities creates a truly comprehensive approach to TBI recovery. Rather than viewing sleep problems as an isolated issue, this integrated perspective recognizes sleep as one component of overall health that both affects and is affected by multiple body systems.
The Science of Recovery: Why Comprehensive Care Matters
The evidence supporting non-surgical, integrative approaches to TBI and sleep disorders continues to grow. Research consistently demonstrates that addressing sleep problems after TBI can improve multiple outcomes, including cognitive function, pain levels, mood and anxiety, quality of life, and overall recovery trajectories (Wickwire, 2020). Studies examining sleep quality during the acute hospitalization phase after TBI have found that better sleep during this critical period predicts more favorable long-term cognitive outcomes years later (Sanchez et al., 2022). Specifically, less fragmented sleep, more slow-wave sleep, and higher spindle density during hospitalization are associated with better memory and executive function at long-term follow-up. Importantly, these sleep measures were better predictors of cognitive outcomes than traditional injury severity markers, highlighting sleep’s critical role in recovery.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) has emerged as a highly effective treatment for TBI-related sleep problems, with 70-80% of patients experiencing lasting benefit and approximately 50% achieving complete resolution of insomnia (Perspective: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, 2023). CBT-I teaches skills and strategies that address the perpetuating factors maintaining insomnia, including dysfunctional beliefs about sleep, behaviors that interfere with sleep, and cognitive processes that increase arousal at bedtime. The combination of non-surgical treatments—chiropractic care, acupuncture, physical therapy, and massage therapy—with behavioral interventions like CBT-I and functional medicine approaches creates optimal conditions for recovery. Each modality addresses different aspects of the complex pathophysiology underlying TBI and sleep disturbances. Together, they work synergistically to restore nervous system function, reduce inflammation, improve autonomic balance, address pain and musculoskeletal dysfunction, optimize nutritional status, and reestablish healthy sleep-wake cycles.
Conclusion: Hope for Recovery Through Holistic Healing
Although the effects of traumatic brain injury and the resulting sleep problems may be overwhelming, there are effective therapies that can assist the brain’s amazing healing ability and greatly enhance quality of life. Understanding the intricate connections between inflammation, sleep, brain damage, autonomic function, and general health empowers people to actively participate in their own healing and make well-informed choices about their treatment. In addition to promoting general neurological healing, the non-surgical methods covered in this article—physical therapy, massage therapy, acupuncture, and chiropractic care—offer safe and efficient ways to enhance sleep quality. By treating pain and musculoskeletal dysfunction, lowering inflammation, enhancing autonomic balance, reestablishing a healthy brain-body connection, and restoring appropriate nervous system function, these therapies are effective.
Establishing individualized sleep schedules and practicing regular sleep hygiene habits lay the groundwork for improved sleep. Professional advice from medical professionals with training in integrative and functional medicine, such as Dr. Alexander Jimenez, may help people address the underlying causes of their sleep issues rather than just treating their symptoms. TBI recovery is seldom linear, and sleep issues may last for months or even years. Nonetheless, significant progress may be achieved with perseverance, patience, and all-encompassing treatment that treats the patient as a whole rather than just specific symptoms. The brain’s amazing neuroplasticity, or capacity to create new neural pathways and connections, lasts a lifetime. People may use this neuroplasticity to aid in recovery and take back their life after traumatic brain injury by establishing the best possible healing circumstances via restful sleep, a healthy diet, suitable treatments, and encouraging surroundings.
References
- Aoun, R., Rawal, H., Attarian, H., & Sahni, A. (2019). Impact of traumatic brain injury on sleep: An overview. Nature and Science of Sleep, 11, 131-140. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S182158
- Effect of acupuncture on sleep quality and neurological function in stroke patients with sleep apnea syndrome. (2021). BioMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8121144/
- Enhancing sleep quality after traumatic brain injury: Strategies for recovery. (2024, January 16). Flourish Supportive Living. https://flourishsupportiveliving.com/enhancing-sleep-quality-after-traumatic-brain-injury/
- How chiropractic neurology supports brain healing. (2025, July 23). HML Functional Care. https://hmlfunctionalcare.com/how-chiropractic-neurology-supports-brain-healing/
- How massage therapy improves sleep quality. (2025, April 20). Total Health Systems. https://totalhealthsystems.com/how-massage-therapy-improves-sleep-quality/
- How physical therapy supports better sleep & reduces pain. (2025, August 18). Bay Area Physical Therapy. https://bayarea-pt.com/how-physical-therapy-supports-better-sleep-reduces-pain/
- Landvater, J., Kim, S., Caswell, K., Kwon, C., Odafe, E., Roe, G., Tripathi, A., Vukovics, C., Wang, J., Ryan, K., Cocozza, V., Brock, M., Tchopev, Z., Tonkin, B., Capaldi, V., Collen, J., Creamer, J., Irfan, M., Wickwire, E. M., Williams, S., & Werner, J. K. (2024). Traumatic brain injury and sleep in military and veteran populations: A literature review. NeuroRehabilitation, 55(3), 245-270. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-230380
- Massage positively influences daytime brain activity and reduces sleep-onset latency. (2025, July 27). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11308652/
- Neuroplastic responses to chiropractic care: Broad impacts on pain, mood, sleep, and quality of life. (2024, November 6). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11563899/
- Perspective: Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia is a promising intervention for mild traumatic brain injury. (2023, October 2). Brain Injury Association of New Jersey. https://bianj.org/perspective-cognitive-behavioral-therapy-for-insomnia-is-a-promising-intervention-for-mild-traumatic-brain-injury/
- Physical therapy exercises for sleep disorders in a rehabilitation setting: A systematic review and meta-analysis. (2021, September 4). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8416054/
- Piantino, J. A., Iliff, J. J., & Lim, M. M. (2022). The bidirectional link between sleep disturbances and traumatic brain injury symptoms: A role for glymphatic dysfunction? Biological Psychiatry, 91(5), 478-487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.06.025
- Poulsen, I., Langhorn, L., Egerod, I., & Aadal, L. (2021). Sleep and agitation during subacute traumatic brain injury rehabilitation: A scoping review. Australian Critical Care, 34(1), 76-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aucc.2020.05.006
- Sanchez, E., Blais, H., Duclos, C., Arbour, C., Van Der Maren, S., El-Khatib, H., Baril, A. A., Bernard, F., Carrier, J., & Gosselin, N. (2022). Sleep from acute to chronic traumatic brain injury and cognitive outcomes. Sleep, 45(8), zsac123. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsac123
- Sandsmark, D. K., Elliott, J. E., & Lim, M. M. (2017). Sleep-wake disturbances after traumatic brain injury: Synthesis of human and animal studies. Sleep, 40(5), zsx044. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx044
- Sleep after traumatic brain injury. (2025, April 2). Cumbria, Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust. https://cntw.nhs.uk/resource-library/sleep-after-traumatic-brain-injury/
- Sleep disturbance in musculoskeletal conditions: Impact and management strategies. (2023, January 4). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9816969/
- Sleep disorders in chronic pain and its neurochemical mechanisms: A narrative review. (2023, May 31). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10248687/
- The beneficial effects of massage therapy for insomnia in postmenopausal women. (2014, September 15). Sleep Medicine Research, 5(2), 51-54. https://doi.org/10.17241/smr.2014.5.2.51
- The effects of acupuncture on sleep disorders and its underlying mechanism: A literature review of rodent studies. (2023, August 7). Frontiers in Neuroscience, 17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1243029
- The glymphatic system: A beginner’s guide. (2015, May 6). PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4636982/
- The influence of environmental factors on sleep and waking up. (2025, July 1). Pillow App. https://pillow.app/blog/the-influence-of-environmental-factors-on-sleep-and-waking-up/
- The relationship between chiropractic care and sleep. (2023, December 10). Dr. Craig Henry Chiropractic. https://drcraighenry.com/the-relationship-between-chiropractic-care-and-sleep/
- The vagus nerve: A key player in your health and well-being. (2024, October 15). Mass General Brigham. https://www.massgeneral.org/news/article/vagus-nerve-key-player-health-well-being
- Viola-Saltzman, M., & Watson, N. F. (2012). Traumatic brain injury and sleep disorders. Neurologic Clinics, 30(4), 1299-1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2012.08.008
- Warding off sleep issues after brain injury. (n.d.). Kessler Foundation. https://kesslerfoundation.org/research/kessler-foundation-research-center/warding-off-sleep-issues-after-brain-injury
- Where you live may affect how well you sleep. (2023, March 23). Sleep Education. https://sleepeducation.org/where-you-live-may-affect-how-well-you-sleep/
- Wickwire, E. M. (2020). Why sleep matters after traumatic brain injury. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 16(Suppl 1), 5S-6S. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.8872
- Zielinski, M. R., & Gibbons, A. J. (2022). Neuroinflammation, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 12, 853096. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.853096