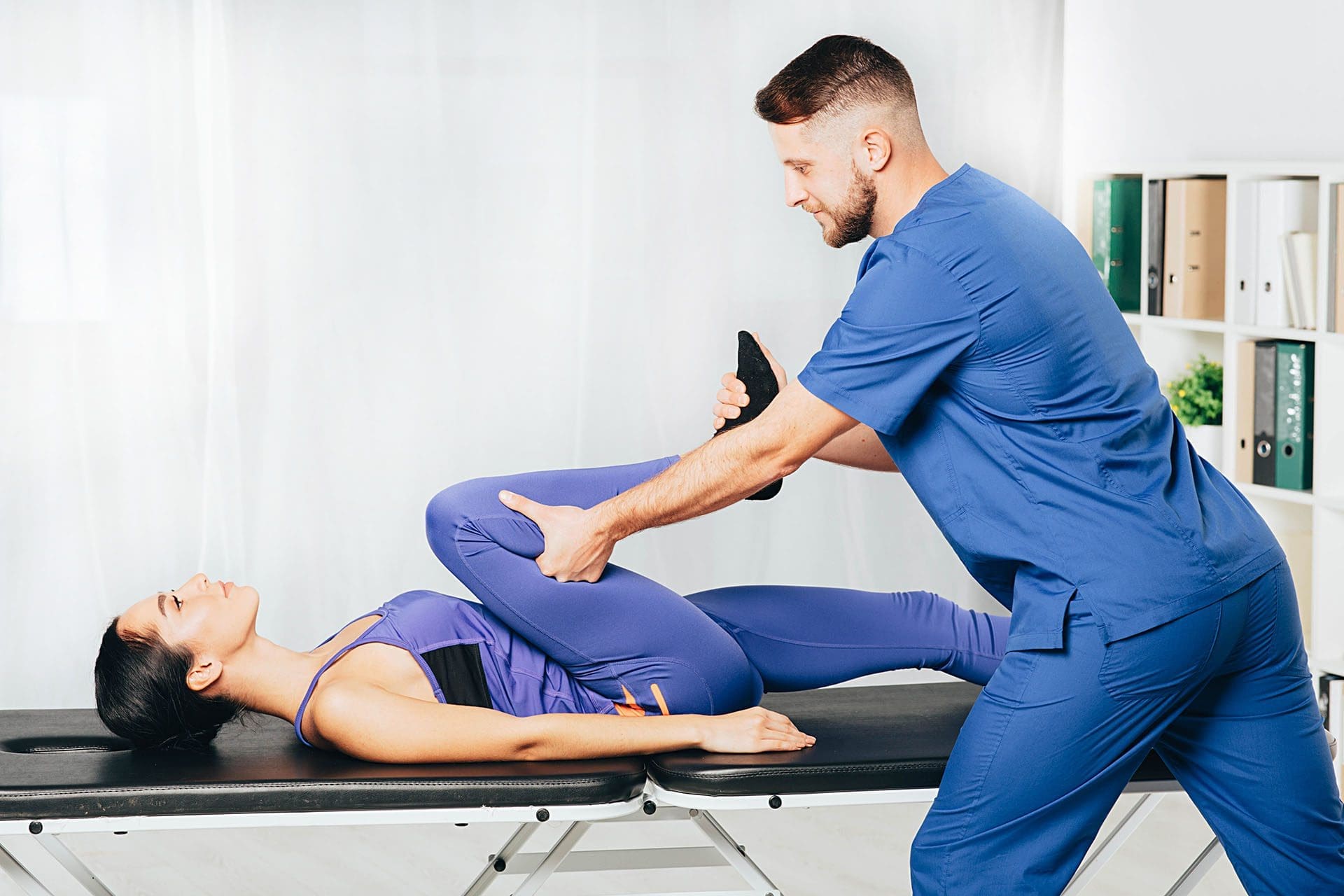
ChiroMed’s Guide to Iliac Crest Pain Relief
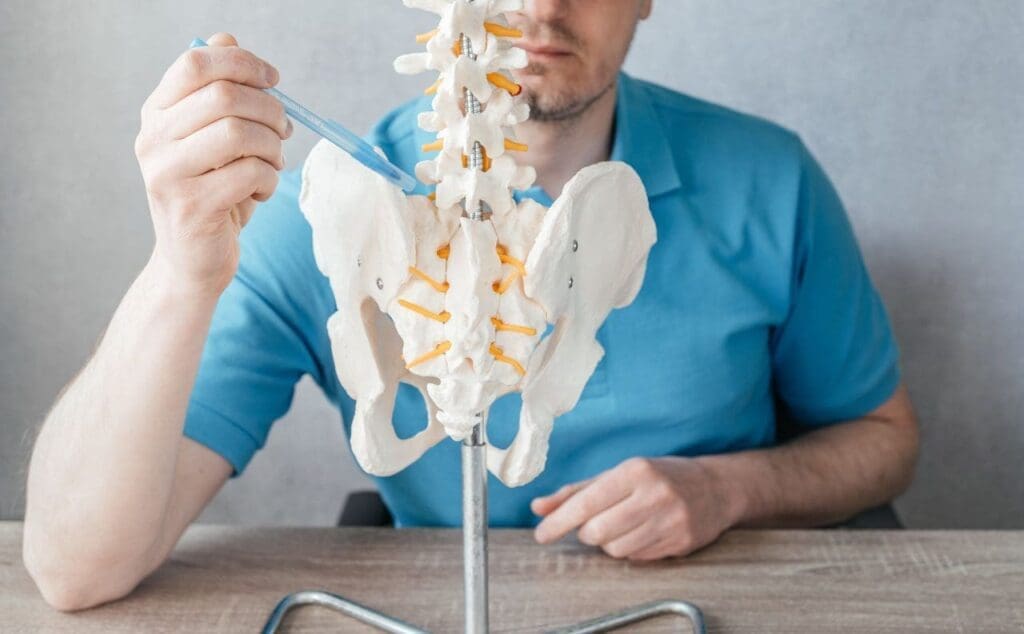
Comprehensive Care at ChiroMed for Iliac Crest Pain Syndrome
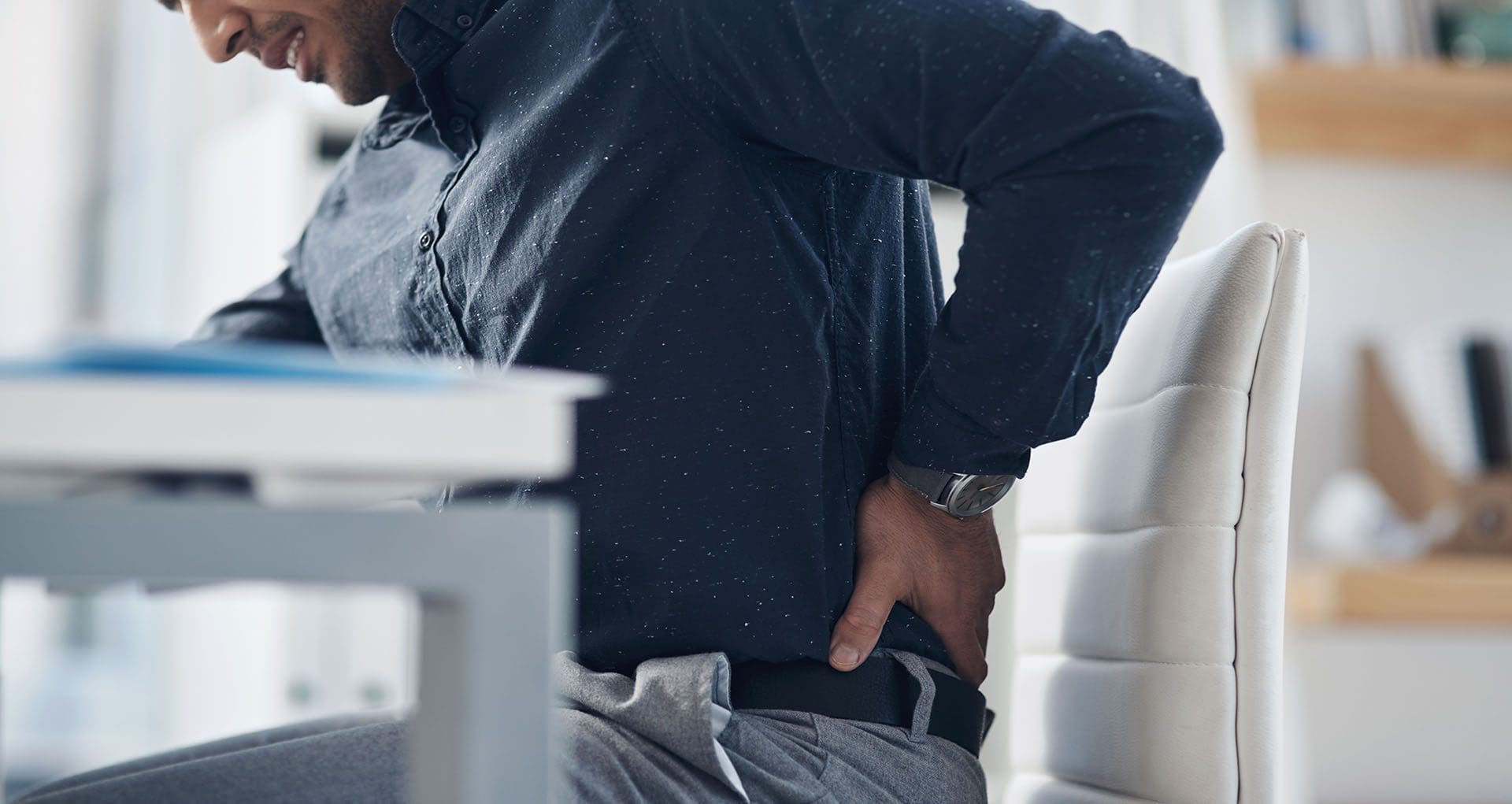
At ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare in El Paso, TX, we specialize in treating iliac crest pain syndrome, a condition causing chronic low back pain that often stems from the iliac crest—the top ridge of the pelvis. Injuries of the iliolumbar ligament, which connects the lumbar spine to the pelvis and provides stability, frequently cause this pain (Verywell Health, 2023). Our team, led by Dr. Alexander Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, combines chiropractic care with integrative therapies to address the root causes of this condition, offering personalized solutions for lasting relief.
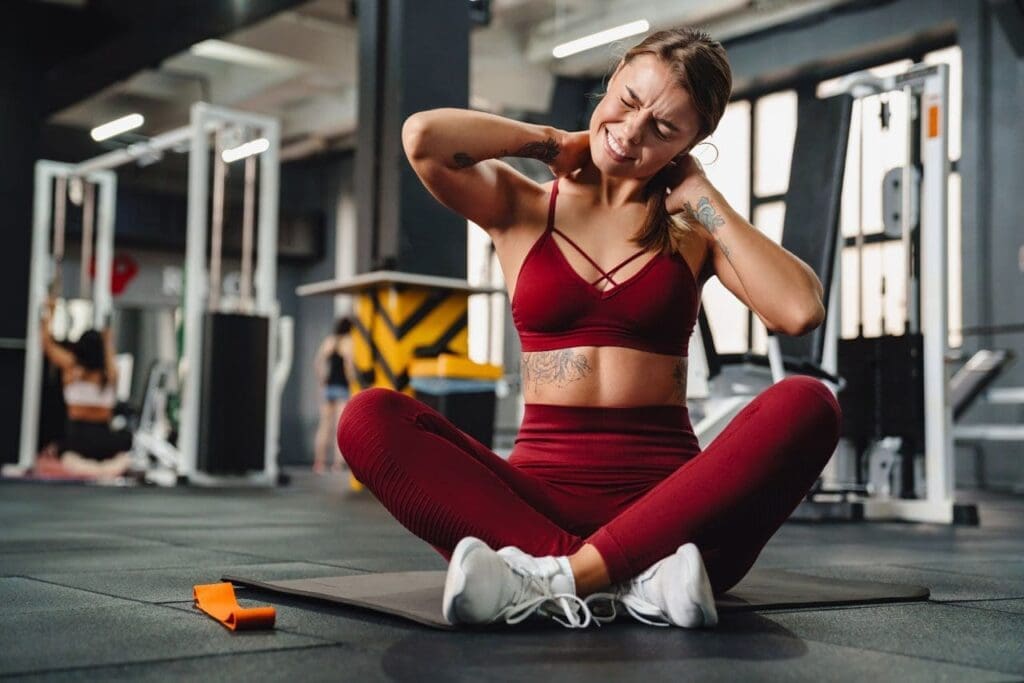
Iliac crest pain can happen due to overuse, injuries, or weak core and back muscles, which puts stress on ligaments and joints like the sacroiliac (SI) joint. Muscle spasms in the lower back, such as in the quadratus lumborum, can worsen the pain by creating instability or imbalances, pulling on the iliac crest (Physio-Pedia, 2023a). At ChiroMed, we use a holistic approach, blending chiropractic adjustments, massage therapy, acupuncture, and targeted exercises to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent future issues.
Our clinic’s mission is to create individualized treatment plans that go beyond symptom relief. By combining conventional and alternative medicine, we help patients—whether recovering from sports injuries, work accidents, or motor vehicle collisions—achieve optimal health (ChiroMed, 2023). With advanced diagnostics and a team of licensed professionals, including Dr. Jimenez and therapists like Helen Wilmore and Kristina Castle, we ensure comprehensive care tailored to your needs.
References ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare. (2023). About us. https://www.chiromed.com/ Medical News Today. (2023). What to know about iliac crest pain. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319695 Physio-Pedia. (2023a). Quadratus lumborum syndrome. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Quadratus_Lumborum_Syndrome Verywell Health. (2023). Iliac crest definition. https://www.verywellhealth.com/iliac-crest-definition-3120351
Dr. Alexander Jimenez’s Expertise in Injury Recovery
Dr. Alexander Jimenez, a board-certified chiropractor and family nurse practitioner, brings a unique dual-scope approach to treating iliac crest pain syndrome at ChiroMed. With over 25 years of experience since graduating from the University of Vermont in 1999, Dr. Jimenez specializes in helping patients recover from work, sports, personal, and motor vehicle injuries (Jimenez, 2023a). His ability to combine chiropractic expertise with medical diagnostics makes him a trusted provider in El Paso for complex cases.
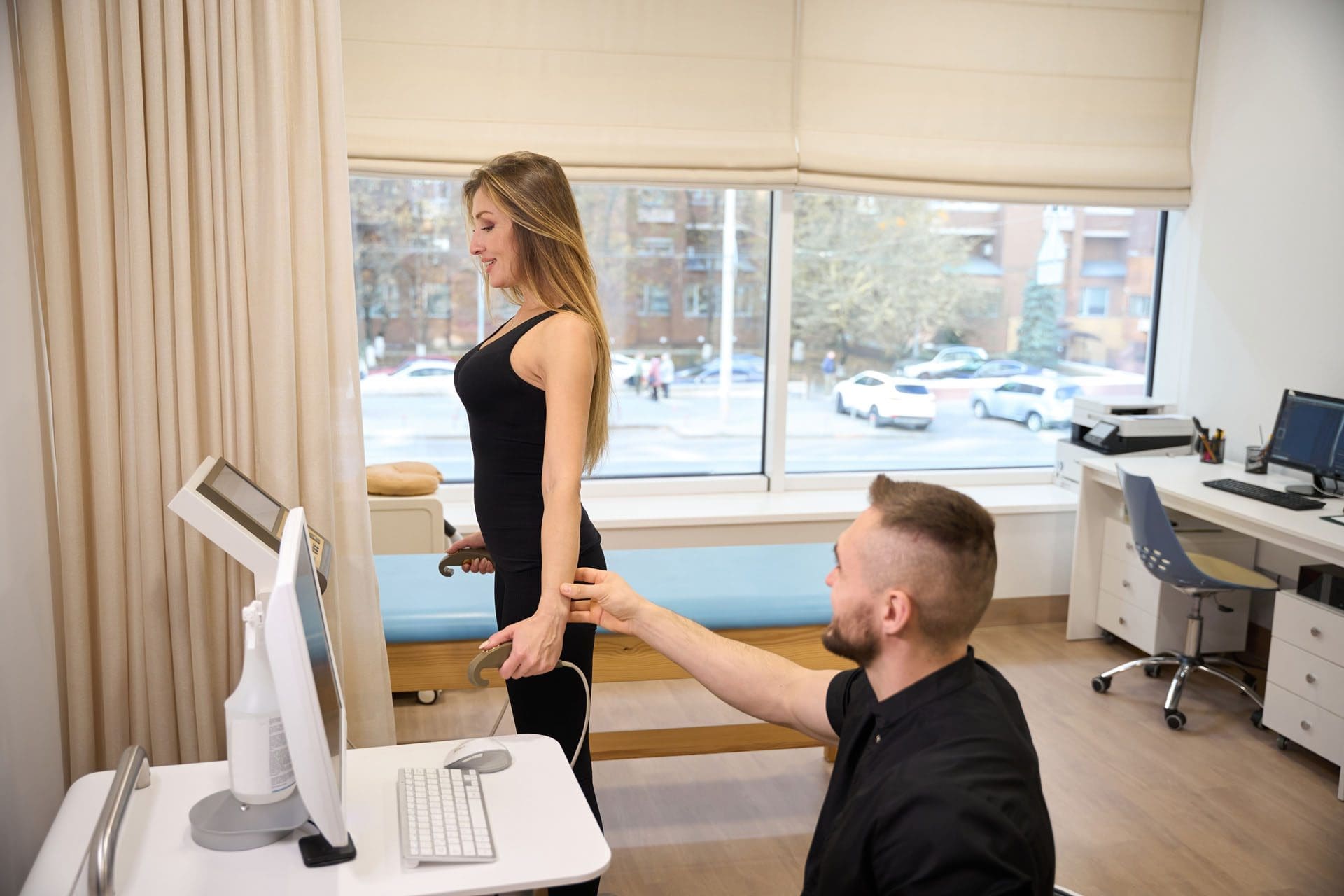
Dr. Jimenez uses advanced imaging, like X-rays or MRIs, to identify the exact cause of pain, whether it’s a strained iliolumbar ligament, SI joint dysfunction, or a herniated disc contributing to muscle spasms (Jimenez, 2023b; Precision Pain Care, 2023). His diagnostic process involves a thorough physical exam to detect misalignments or muscle imbalances, followed by a tailored treatment plan. For example, a patient with pain from a car accident might receive spinal adjustments to realign the pelvis, paired with exercises to strengthen supporting muscles.
Beyond treatment, Dr. Jimenez excels in handling the legal side of personal injury cases. He provides detailed clinical reports that connect a patient’s injury to their symptoms, aiding in insurance claims or legal proceedings (Jimenez, 2023c). This is especially valuable for motor vehicle or workplace injuries, where accurate documentation is critical. By addressing both the medical and legal aspects, Dr. Jimenez ensures patients can focus on recovery while navigating complex processes.
References Jimenez, A. (2023a). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://dralexjimenez.com/ Jimenez, A. (2023b). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/ Jimenez, A. (2023c). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://www.whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaLL6qY3rZZiMGQ0S32u/364 Precision Pain Care. (2023). How a herniated disc in your upper back causes pain, numbness, and weakness. https://www.precisionpaincarerehab.com/blog/how-a-herniated-disc-in-your-upper-back-causes-pain-numbness-and-weakness-27693.html
Integrative Therapies for Iliac Crest Pain Relief
ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare in El Paso, TX, takes a comprehensive approach to treating iliac crest pain syndrome by combining chiropractic care with integrative therapies like massage, acupuncture, and targeted exercises. This condition, which is usually caused by an injury to the iliolumbar ligament or problems with the sacroiliac (SI) joint, leads to ongoing low back pain that can spread to the hips or groin. Our integrative methods focus on addressing these root causes to provide lasting relief and improve overall wellness.
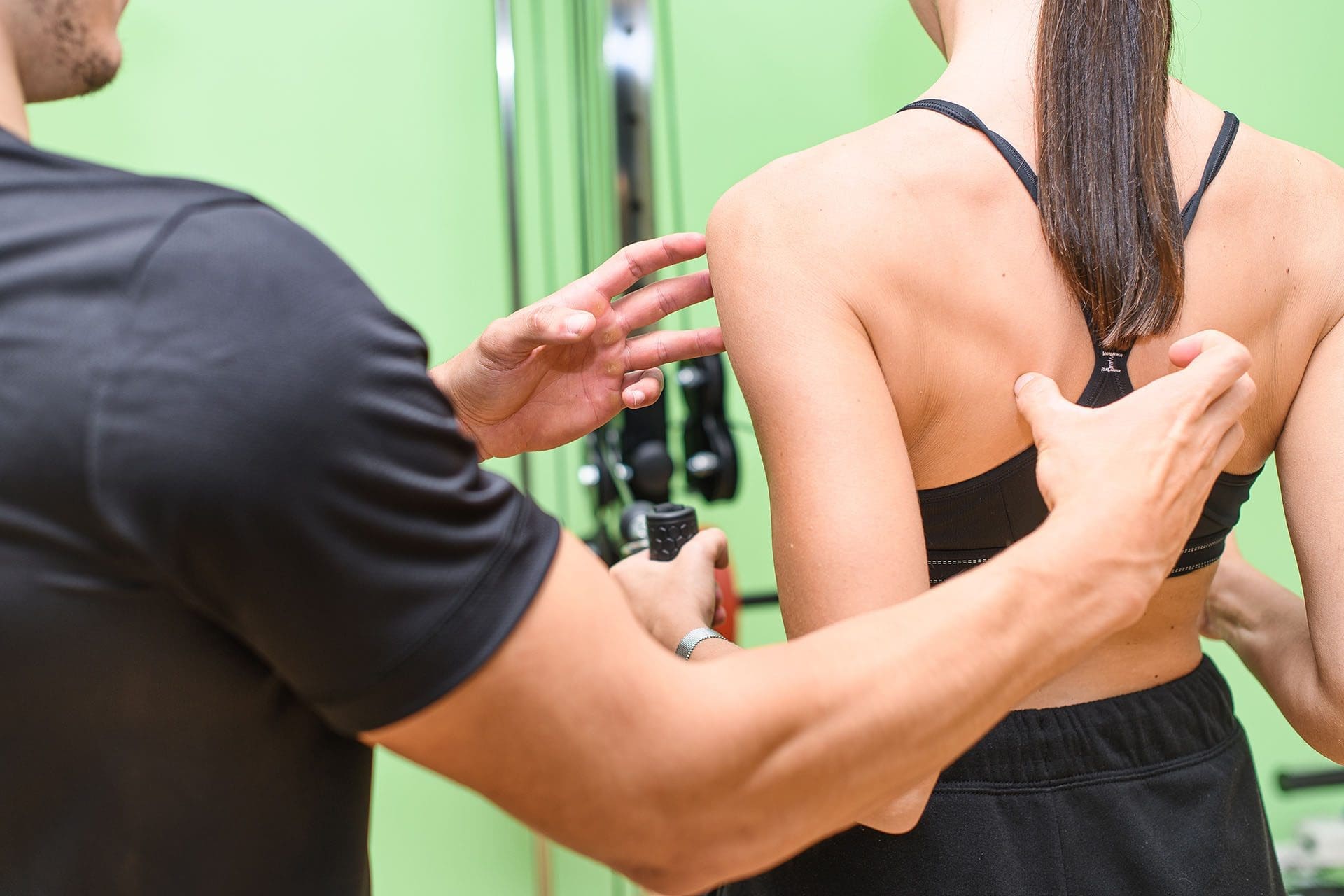
Chiropractic adjustments are central to our treatment plans. These gentle, hands-on techniques realign the spine and pelvis, reducing pressure on the SI joint and iliac crest. By correcting misalignments, we restore proper joint function, which can immediately ease pain and improve mobility (Miami Chiropractors, 2023a). For example, if a misaligned SI joint is straining the iliolumbar ligament, adjustments help redistribute weight and reduce stress on the affected area.
Massage therapy, provided by our licensed therapist Helen Wilmore, complements chiropractic care by relieving muscle spasms in the lower back, such as in the quadratus lumborum. These spasms often worsen iliac crest pain by creating instability or pulling on ligaments (Physio-Pedia, 2023a). Massage improves blood flow, relaxes tight muscles, and reduces inflammation, helping break the cycle of pain and tension (Binns Family Chiropractic, 2023).
Acupuncture, another key service at ChiroMed, targets specific points to reduce inflammation and stimulate the body’s natural pain-relief mechanisms. Studies indicate that acupuncture can effectively treat SI joint pain, often associated with iliac crest issues (Healthline, 2023). Our team also incorporates targeted exercises, like hip stretches and core strengthening, to stabilize the pelvis and prevent further strain on ligaments (WebMD, 2023). These exercises are tailored to each patient’s needs, ensuring they rebuild strength without aggravating the injury.
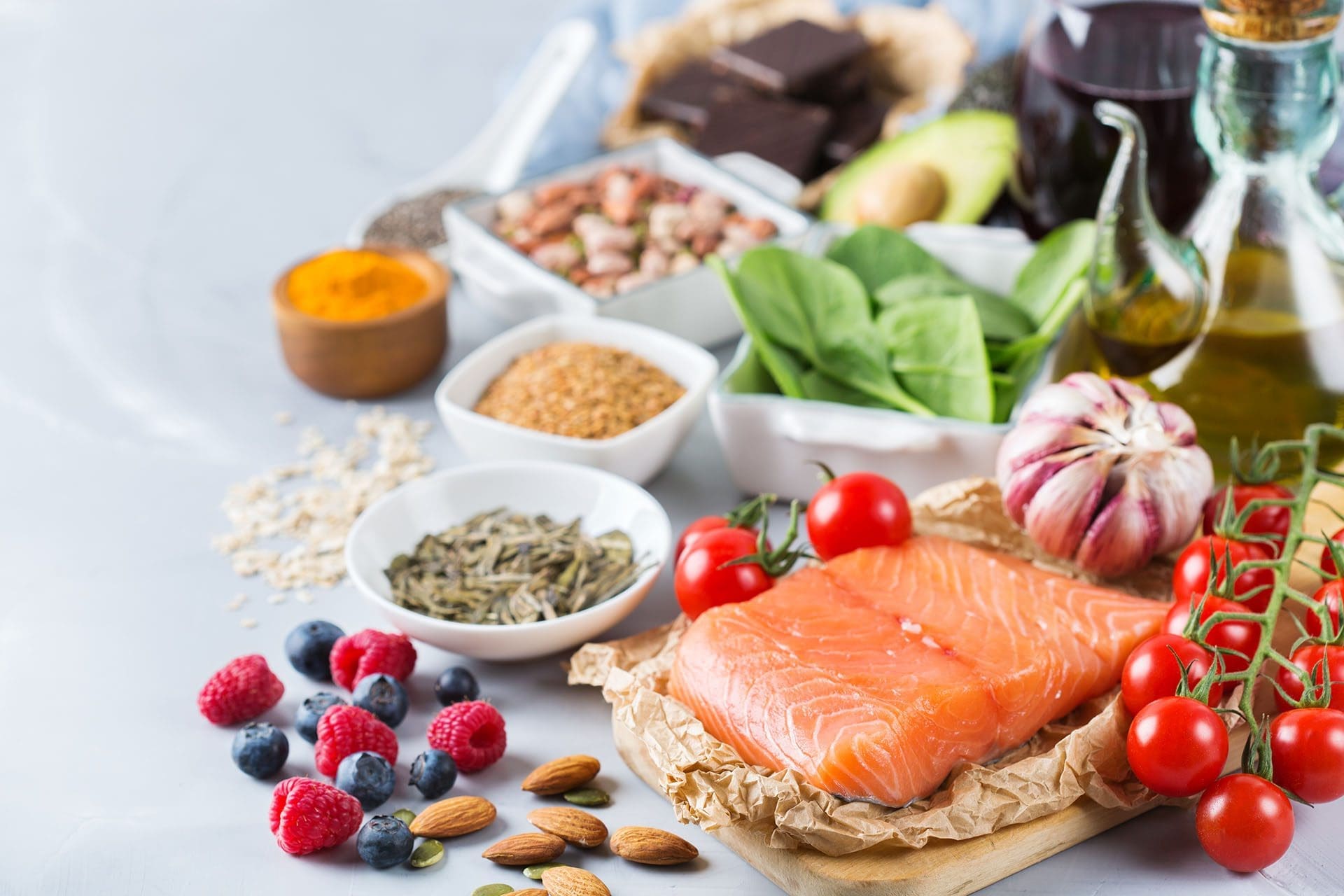
Integrative medicine at ChiroMed also includes nutrition counseling and naturopathy to support overall health. For instance, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can reduce swelling around the iliac crest, while stress management techniques help prevent muscle tension (NCCIH, 2023). This combination of therapies—chiropractic, massage, acupuncture, exercise, and nutrition—addresses structural, muscular, and inflammatory aspects of iliac crest pain syndrome, promoting natural healing and long-term recovery.
References Binns Family Chiropractic. (2023). 7 benefits of chiropractic care for sacroiliac joint problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/ Healthline. (2023). Acupuncture for SI joint pain. https://www.healthline.com/health/acupuncture-for-si-joint-pain Miami Chiropractors. (2023a). How chiropractic care can help relieve chronic hip pain. https://www.miami-chiropractors.com/how-chiropractic-care-can-help-relieve-chronic-hip-pain/ NCCIH. (2023). Chronic pain and complementary health approaches: Usefulness and safety. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/chronic-pain-and-complementary-health-approaches-usefulness-and-safety Physio-Pedia. (2023a). Quadratus lumborum syndrome. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Quadratus_Lumborum_Syndrome Verywell Health. (2023). Iliac crest definition. https://www.verywellhealth.com/iliac-crest-definition-3120351 WebMD. (2023). Causes of iliac crest pain and exercises to reduce pain and ache. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/causes-of-iliac-crest-pain-and-exercises-to-reduce-pain-and-ache
Comprehensive Rehabilitation at ChiroMed
ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare offers a well-rounded rehabilitation program for iliac crest pain syndrome, designed to address a wide range of injuries while promoting natural healing and preventing long-term complications. Located in El Paso, TX, our clinic integrates chiropractic care, physical therapy, and complementary therapies to create personalized treatment plans that restore optimal function (ChiroMed, 2023).
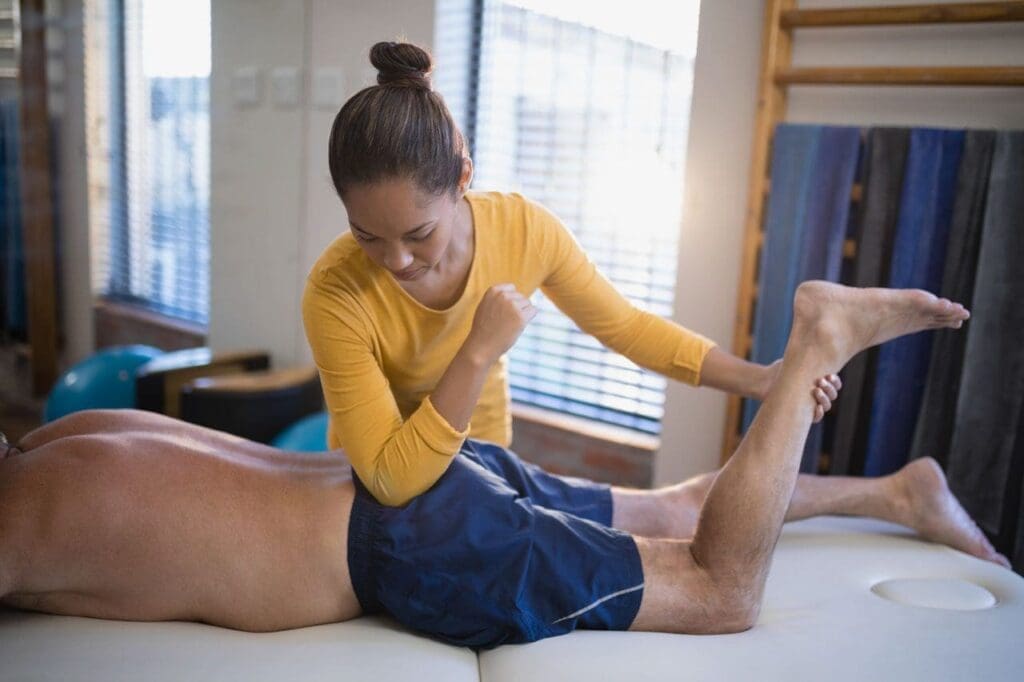
The rehabilitation process begins with a thorough assessment by our team, including Dr. Alexander Jimenez and physical therapists like Kristina Castle. We use diagnostic tools such as X-rays or MRIs to identify issues like iliolumbar ligament injuries, SI joint dysfunction, or herniated discs that may contribute to pain (Physio-Pedia, 2023b; Precision Pain Care, 2023). This detailed evaluation allows us to design a treatment plan that targets the specific cause of each patient’s discomfort.
Chiropractic adjustments are a cornerstone of our approach, correcting misalignments in the spine and pelvis to reduce strain on the iliac crest and surrounding ligaments (Gonstead Chiropractic Center, 2023). These adjustments improve joint mobility and alleviate pressure, often providing immediate relief. To support this, our physical therapists guide patients through targeted exercises to strengthen core and back muscles, which helps stabilize the pelvis and prevent future injuries (WebMD, 2023). For example, a patient recovering from a work-related injury might perform hip stretches to improve flexibility while building core strength to support the lower back.
Massage therapy and acupuncture further enhance recovery by addressing muscle tension and inflammation. Massage, performed by our experienced staff, relaxes tight muscles and improves circulation, while acupuncture reduces pain and swelling, particularly in the SI joint (Healthline, 2023). Our integrative approach also incorporates naturopathy and nutrition counseling to support overall health, addressing factors like poor diet or stress that can worsen pain (NCCIH, 2023).
This comprehensive strategy is especially effective for patients with injuries from sports, work, or motor vehicle accidents. By using different treatments together, we address the physical, muscle, and inflammation issues related to iliac crest pain syndrome, which helps lower the chances of long-term problems like arthritis or ongoing pain. Our team works closely with other healthcare providers to ensure our treatments complement conventional medical care, creating a seamless plan tailored to each patient.
At ChiroMed, we believe in empowering patients to achieve long-term wellness. Our comfortable clinic environment and experienced staff, including licensed therapists and chiropractors like Anthony Wills, make recovery a positive experience (ChiroMed, 2023). Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain or recovering from an injury, our goal is to help you return to your daily activities with improved strength, mobility, and overall health.
References ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare. (2023). About us. https://www.chiromed.com/ Dr. Justin Dean. (2023). Iliac crest pain. https://drjustindean.com/iliac-crest-pain/ Gonstead Chiropractic Center. (2023). Overcoming sacroiliitis with chiropractic care. https://gonsteadchiropracticcenter.com/blog/b/overcoming-sacroiliitis-with-chiropractic-care Healthline. (2023). Acupuncture for SI joint pain. https://www.healthline.com/health/acupuncture-for-si-joint-pain NCCIH. (2023). Chronic pain and complementary health approaches: Usefulness and safety. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/chronic-pain-and-complementary-health-approaches-usefulness-and-safety Physio-Pedia. (2023b). Iliolumbar ligament. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Iliolumbar_ligament Precision Pain Care. (2023). How a herniated disc in your upper back causes pain, numbness, and weakness. https://www.precisionpaincarerehab.com/blog/how-a-herniated-disc-in-your-upper-back-causes-pain-numbness-and-weakness-27693.html WebMD. (2023). Causes of iliac crest pain and exercises to reduce pain and ache. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/causes-of-iliac-crest-pain-and-exercises-to-reduce-pain-and-ache
Understanding Iliac Crest Pain Syndrome
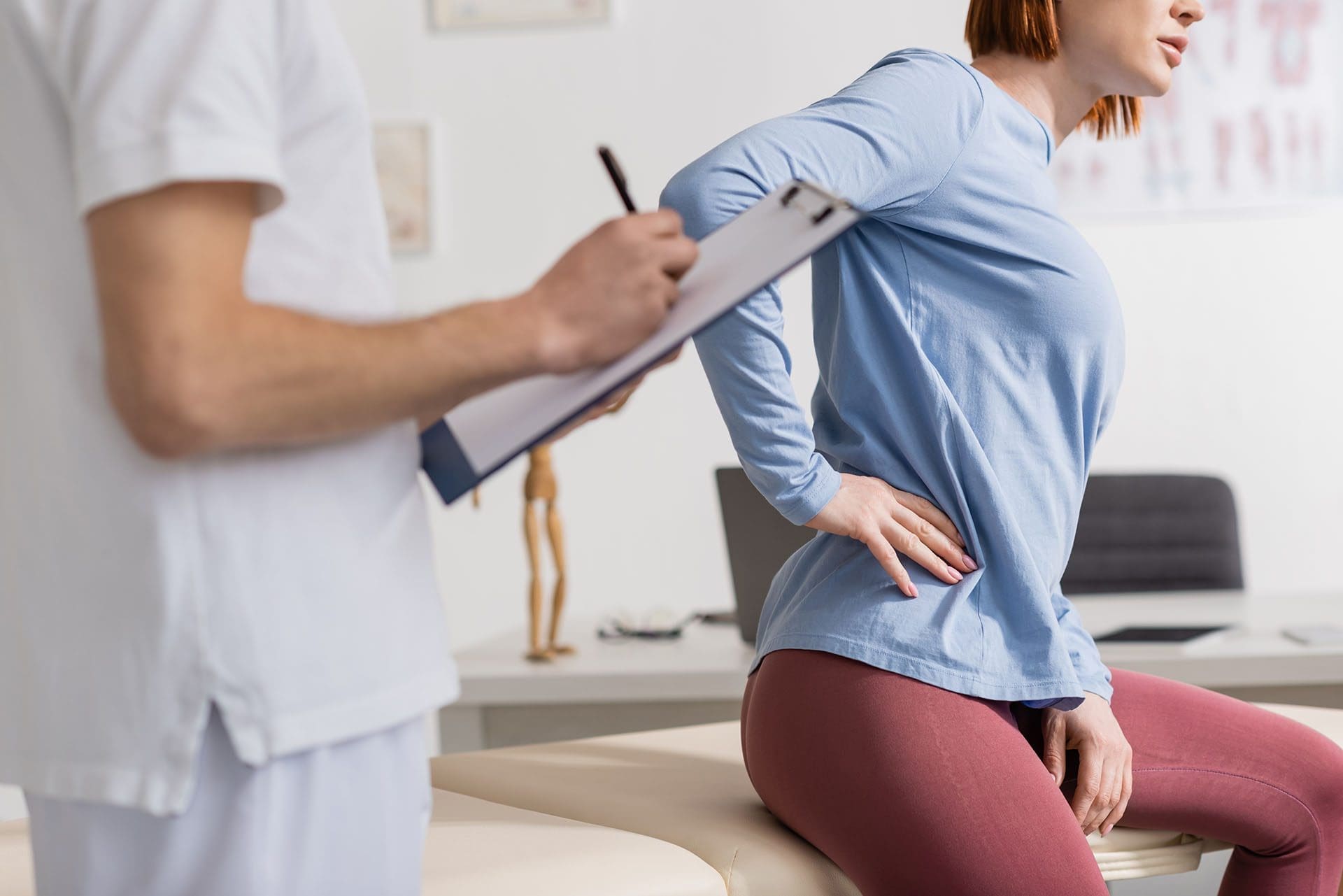
Iliac crest pain syndrome is a condition that causes persistent lower back pain, often originating from the iliac crest, the curved top edge of the pelvis. This pain is commonly triggered by an injury to the iliolumbar ligament, which links the lumbar spine to the pelvis, helping stabilize the lower back (Physio-Pedia, 2023b). Causes include overuse from activities like running or heavy lifting, direct trauma from falls or accidents, and weak core or back muscles that fail to support the pelvis properly (Medical News Today, 2023).
Muscle spasms, particularly in the quadratus lumborum, can intensify the pain by creating instability or imbalances that strain the ligaments around the iliac crest (Physio-Pedia, 2023a). For instance, a sudden injury might cause muscles to tighten, pulling on the iliac crest and worsening discomfort. Symptoms include a dull ache or sharp pain along the iliac crest, tenderness when pressed, and pain that may spread to the hips, lower back, or abdomen (Aesthetics and Medical Lasers, 2023). Left untreated, this can lead to a cycle of pain and spasms that disrupts daily life.
At ChiroMed, we understand how debilitating this condition can be. Our team uses advanced diagnostics to pinpoint the cause, whether it’s a ligament injury, SI joint dysfunction, or related muscle issues. By addressing these underlying factors, we create targeted treatment plans to relieve pain and restore function, helping patients return to their normal activities (ChiroMed, 2023).
References Aesthetics and Medical Lasers. (2023). Iliac crest pain syndrome. https://aestheticsandmedicallasers.com/iliac-crest-pain-syndrome/ ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare. (2023). About us. https://www.chiromed.com/ Medical News Today. (2023). What to know about iliac crest pain. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319695 Physio-Pedia. (2023a). Quadratus lumborum syndrome. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Quadratus_Lumborum_Syndrome Physio-Pedia. (2023b). Iliolumbar ligament. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Iliolumbar_ligament
Conclusion: Your Path to Recovery with ChiroMed
Iliac crest pain syndrome can make everyday activities challenging, but at ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare in El Paso, TX, we’re dedicated to helping you find relief and reclaim your life. By using chiropractic care along with other treatments like massage, acupuncture, and specific exercises, we tackle the main reasons for your pain, such as a strained iliolumbar ligament, SI joint issues, or muscle imbalances (ChiroMed, 2023 Our team, led by Dr. Alexander Jimenez, uses advanced diagnostics and personalized plans to ensure effective, natural healing.
Whether you’re recovering from a sports injury, work accident, or motor vehicle collision, our comprehensive approach promotes long-term wellness and prevents complications. We work closely with other healthcare providers to complement conventional treatments, ensuring a plan that fits your unique needs (ChiroMed, 2023). Visit us at our comfortable clinic, or contact us at [email protected] or +1 (915) 412-6680 to start your journey to better health.
References
Aesthetics and Medical Lasers. (2023). Iliac crest pain syndrome. https://aestheticsandmedicallasers.com/iliac-crest-pain-syndrome/
Binns Family Chiropractic. (2023). 7 benefits of chiropractic care for sacroiliac joint problems. https://binnsfamilychiropractic.com/7-benefits-of-chiropractic-care-for-sacroiliac-joint-problems/
ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare. (2023). About us. https://www.chiromed.com/
Dr. Justin Dean. (2023). Iliac crest pain. https://drjustindean.com/iliac-crest-pain/
Gonstead Chiropractic Center. (2023). Overcoming sacroiliitis with chiropractic care. https://gonsteadchiropracticcenter.com/blog/b/overcoming-sacroiliitis-with-chiropractic-care
Healthline. (2023). Acupuncture for SI joint pain. https://www.healthline.com/health/acupuncture-for-si-joint-pain
Jimenez, A. (2023a). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://dralexjimenez.com/
Jimenez, A. (2023b). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://www.linkedin.com/in/dralexjimenez/
Jimenez, A. (2023c). Dr. Alex Jimenez. https://www.whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaLL6qY3rZZiMGQ0S32u/364
Medical News Today. (2023). What to know about iliac crest pain. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319695
Miami Chiropractors. (2023a). How chiropractic care can help relieve chronic hip pain. https://www.miami-chiropractors.com/how-chiropractic-care-can-help-relieve-chronic-hip-pain/
Miami Chiropractors. (2023b). The role of chiropractic adjustments in relieving hip pain. https://www.miami-chiropractors.com/the-role-of-chiropractic-adjustments-in-relieving-hip-pain/
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2023). Chronic pain and complementary health approaches: Usefulness and safety. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/chronic-pain-and-complementary-health-approaches-usefulness-and-safety
Physio-Pedia. (2023a). Quadratus lumborum syndrome. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Quadratus_Lumborum_Syndrome
Physio-Pedia. (2023b). Iliolumbar ligament. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Iliolumbar_ligament
Precision Pain Care. (2023). How a herniated disc in your upper back causes pain, numbness, and weakness. https://www.precisionpaincarerehab.com/blog/how-a-herniated-disc-in-your-upper-back-causes-pain-numbness-and-weakness-27693.html
Spinal Backrack. (2023). Iliac crest pain syndrome: Causes and treatment. https://www.spinalbackrack.com/iliac-crest-pain-syndrome-causes-and-treatment/
Verywell Health. (2023). Iliac crest definition. https://www.verywellhealth.com/iliac-crest-definition-3120351
WebMD. (2023). Causes of iliac crest pain and exercises to reduce pain and ache. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/causes-of-iliac-crest-pain-and-exercises-to-reduce-pain-and-ache