Sustainable Weight Loss: Nutrition and Chiropractic

Lasting Results
Losing weight in a healthy way means making changes that you can keep up for a long time. At ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine in El Paso, TX, a recommended, sustainable weight-loss nutrition plan focuses on a moderate, consistent caloric deficit, prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods over restrictive dieting. This approach helps you cut calories without feeling hungry all the time. Key components include filling half your plate with vegetables, choosing lean proteins, consuming high-fiber carbohydrates, and limiting processed, sugary items to ensure long-term, healthy weight loss (Mayo Clinic, 2023a). Instead of quick fixes, this plan aims for slow, steady progress, like losing 1 to 2 pounds per week, which is safer and more likely to stick (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2023).
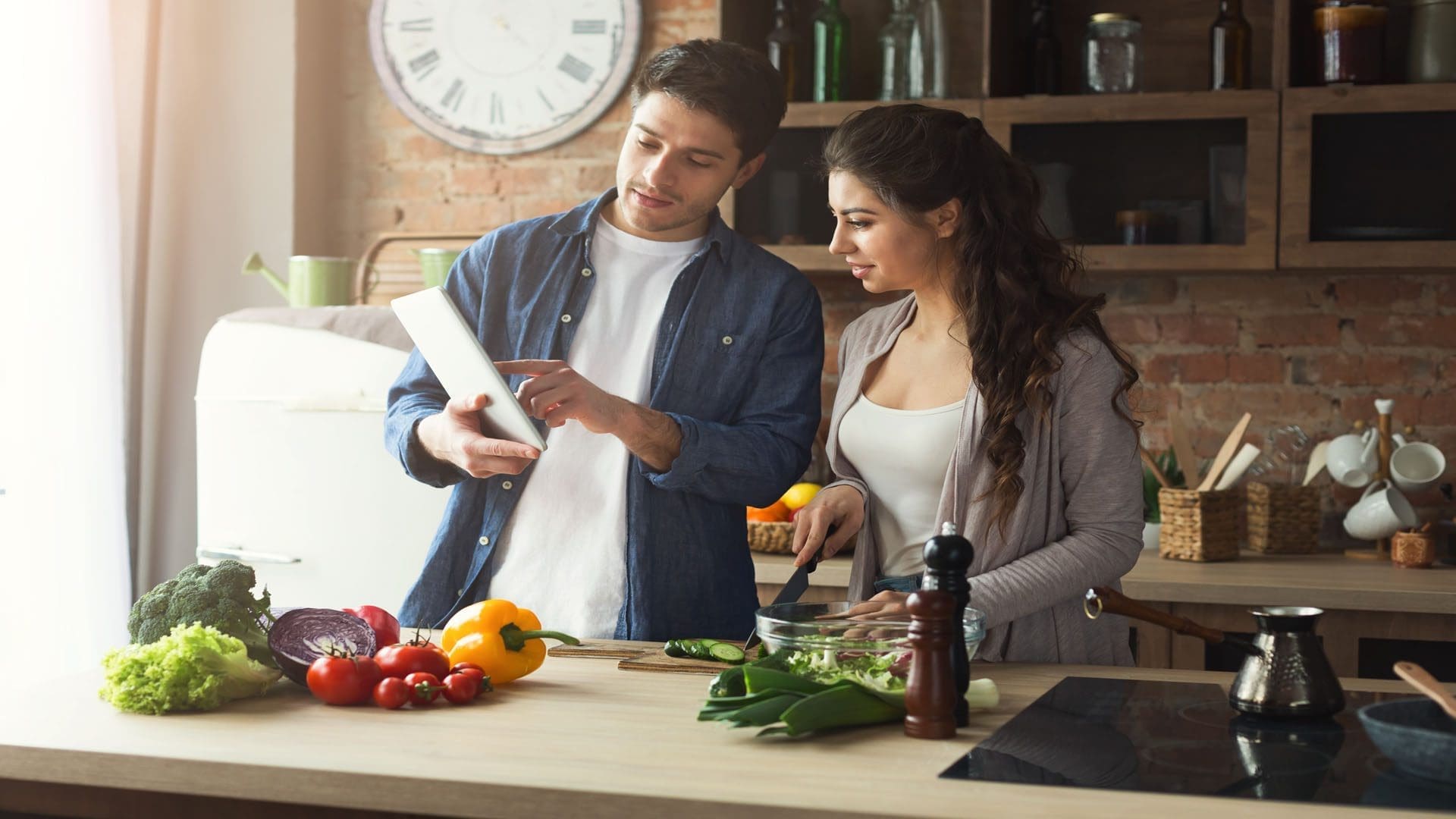
A big part of the above strategy is eating balanced meals. For example, a recommended nutrition plan for weight loss at ChiroMed focuses on a balanced, nutrient-dense diet rich in lean proteins, fiber, vegetables, and healthy fats, alongside consistent meal timing and adequate hydration to create a sustainable calorie deficit. Drinking plenty of water helps control hunger and keeps your body working well (Hoag Medical Group, n.d.). Eating at regular times can stop overeating and keep your energy steady throughout the day.
Here are some key food choices for a sustainable plan offered through ChiroMed’s nutrition counseling:
- Vegetables: Fill half your plate with options like broccoli, spinach, or carrots. They are low in calories but high in vitamins.
- Lean proteins: Pick chicken, fish, eggs, or beans. These help you feel full and build muscle.
- High-fiber carbs: Go for whole grains like oats or brown rice. Fiber slows digestion and helps with blood sugar control.
- Healthy fats: Add avocados, nuts, or olive oil in small amounts. They support heart health without adding too many calories.
- Limit sugary items: Cut back on soda, candy, and baked goods. These can lead to quick weight gain and energy crashes.
By focusing on these, you create a calorie deficit naturally, without counting every bite (UCSF Health, n.d.). Studies show that diets high in whole foods lead to better long-term results because they reduce inflammation and improve gut health (Bischoff et al., 2021).
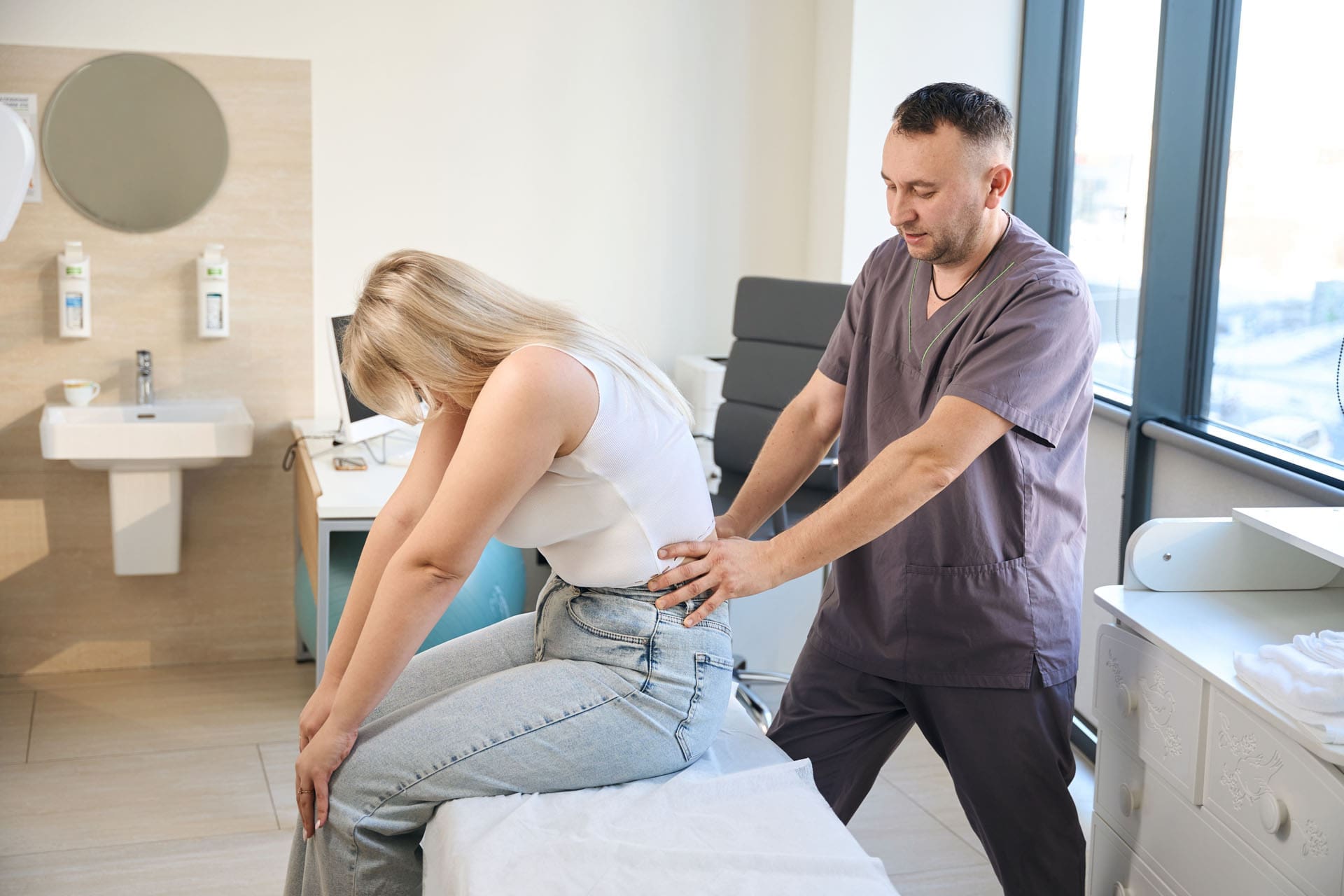
At ChiroMed, an integrative chiropractic clinic, this is supported by personalized nutritional counseling, inflammation-reducing dietary plans, metabolic testing, and guidance on supplements, all while addressing structural alignment to improve physical activity capacity. Located at 11860 Vista Del Sol Dr, Suite 128 in El Paso, TX, ChiroMed’s team looks at your whole body, not just the diet. For instance, if your back hurts, it might keep you from exercising, so addressing it with chiropractic care can make weight loss easier (Sierra, n.d.).
A recommended weight loss plan at ChiroMed focuses on a sustainable, calorie-controlled diet rich in whole foods, lean protein, fiber, and hydration, aiming for 1–2 pounds of fat loss per week. The clinic, led by Dr. Alex Jimenez and his team, offers a comprehensive, tailored plan that includes nutritional advice, tests to assess how your metabolism works, and sometimes special programs like Ideal Protein to support your diet and address any hormonal or inflammatory issues. This means testing your metabolism to see how your body burns calories and, if needed, suggesting supplements.
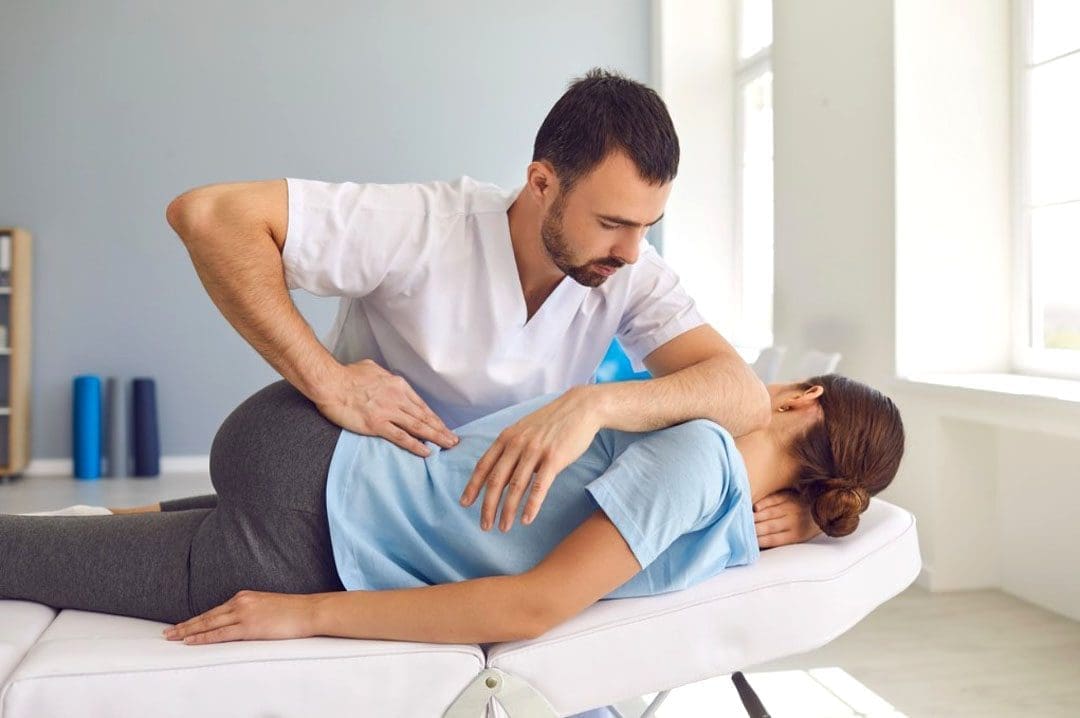
Integrating nutritional counseling with chiropractic adjustments
ChiroMed addresses both metabolic and structural components, often making weight loss more effective and sustainable. Adjustments can improve your posture and reduce pain, allowing you to move more and burn more calories (The Glen Chiro, n.d.). Plus, better alignment might help with digestion, as poor spine health can affect your gut (Jimenez, n.d.), leading to improved nutrient absorption and overall digestive health.
Dr. Alex Jimenez, who has led ChiroMed since 1996, shares clinical observations from his practice in El Paso, Texas. With over 30 years of experience, he notes that combining chiropractic care with nutrition helps patients address root causes such as hormonal imbalances and inflammation. For example, he recommends anti-inflammatory foods and personalized plans, such as ketogenic or Mediterranean diets, to reset blood sugar and support weight management (Jimenez, n.d.). In his clinic, tools such as body composition analysis help tailor diets, leading to improved energy and long-term success. He emphasizes consistency, like weekly meal plans, and integrates functional medicine to address gut health, which can influence weight (Jimenez, 2026a).
From insights shared on platforms like LinkedIn, Dr. Jimenez observes that food serves as medicine in functional approaches, working even better alongside chiropractic adjustments. He points out the gut-brain-spine connection, where poor posture affects digestion and weight control. For sustainable results, he suggests beginner-friendly plans with whole foods and detox strategies to boost metabolism (Jimenez, 2026b). ChiroMed’s blog also covers weight loss motivation and strategies for long-term success, aligning with these observations.
To put these recommendations into action at ChiroMed, start with simple steps:
- Track your meals: Use an app to see your calorie intake without stress.
- Stay hydrated: Aim for 8-10 glasses of water a day.
- Add movement: Walk or do light exercises, especially after adjustments.
- Get tested: Metabolic tests at the clinic can show whether hormones, which are chemical messengers in the body, are out of balance.
- Use supplements wisely: Things like probiotics might help reduce inflammation, but only under guidance from ChiroMed’s team, as improper use can lead to adverse effects or imbalances in gut health.
Research backs this up. One study found that balanced macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbs—help with satiety and blood sugar control, making weight loss easier (Clinically, n.d.). Another tip is to eat protein at every meal, as it curbs hunger (Healthline, 2023).
At ChiroMed, services go beyond diets. They provide coaching on lifestyle changes, like stress reduction, which affects hormones and weight. For instance, high stress can lead to cortisol spikes, which can cause fat storage. Resolving spinal problems may improve your sleep quality and reduce your stress levels (Beard Family Chiropractic, n.d.).
Real results come from whole foods. Focus on nutrient-dense options to fuel your body right (Hope Brain & Body Recovery Center, n.d.). Avoid crash diets; they often fail because they ignore sustainability (Mayo Clinic, 2023b).
In summary, a successful weight-loss plan at ChiroMed combines smart eating with expert chiropractic support. By choosing whole foods and getting integrated care, you address both diet and body mechanics. Dr. Jimenez’s work at ChiroMed shows how this holistic way leads to lasting health. Contact ChiroMed at +1 (915) 412-6680 or visit https://chiromed.com/ to start your journey, especially if you have health issues (MedlinePlus, 2023).
References
Beard Family Chiropractic. (n.d.). Nutrition for weight management
Chiropractic Health and Wellness. (n.d.). Holistic approach to weight loss
Clinikally. (n.d.). Simple and effective tip to successful weight loss
Get Well Northville. (n.d.). Chiropractor nutritional counseling vs traditional diet plans
Healthline. (2023). How to lose weight as fast as possible
Hoag Medical Group. (n.d.). What is the best kind of diet to lose weight?
Hope Brain & Body Recovery Center. (n.d.). Functional medicine weight loss
Jimenez, A. (n.d.). ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare in El Paso, TX
Mayo Clinic. (2023a). Weight loss: Choosing a diet that’s right for you
Mayo Clinic. (2023b). Mayo Clinic diet meal plans
Robinhood Integrative Health. (n.d.). Integrative health diet plans
Sierra, L. (n.d.). Nutrition and chiropractic care: A holistic approach to wellness
The Glen Chiro. (n.d.). Holistic chiropractic care: Nutrition integration
UCSF Health. (n.d.). Guidelines for losing weight
U.S. Coast Guard. (2021). What is a healthy weight loss eating plan anyway?