Effective Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) El Paso, TX
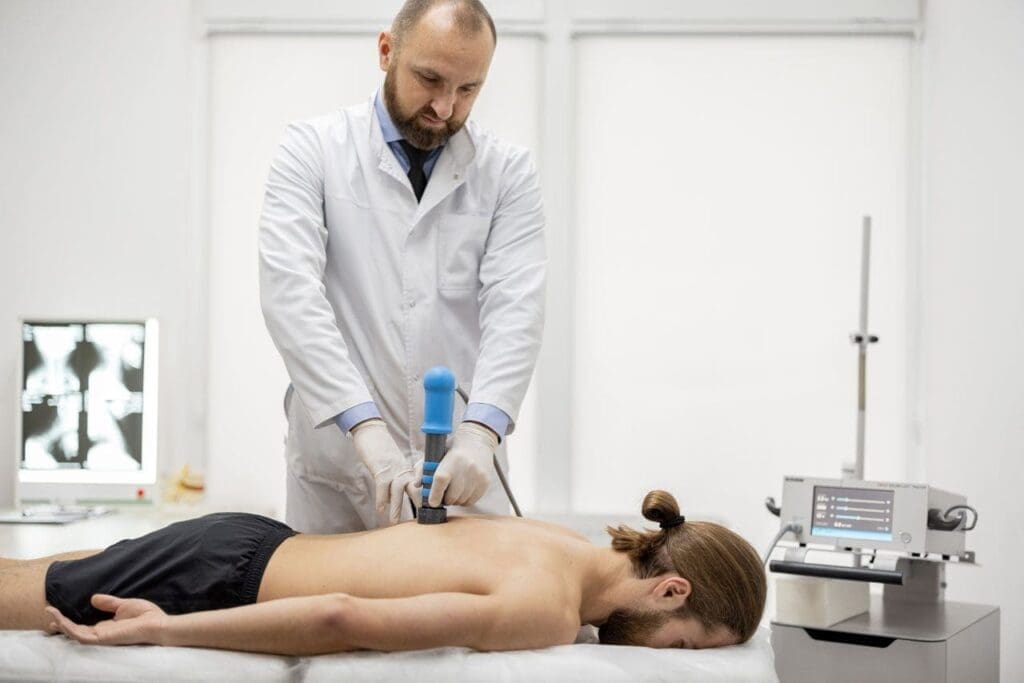
ESWT for Musculoskeletal Healing
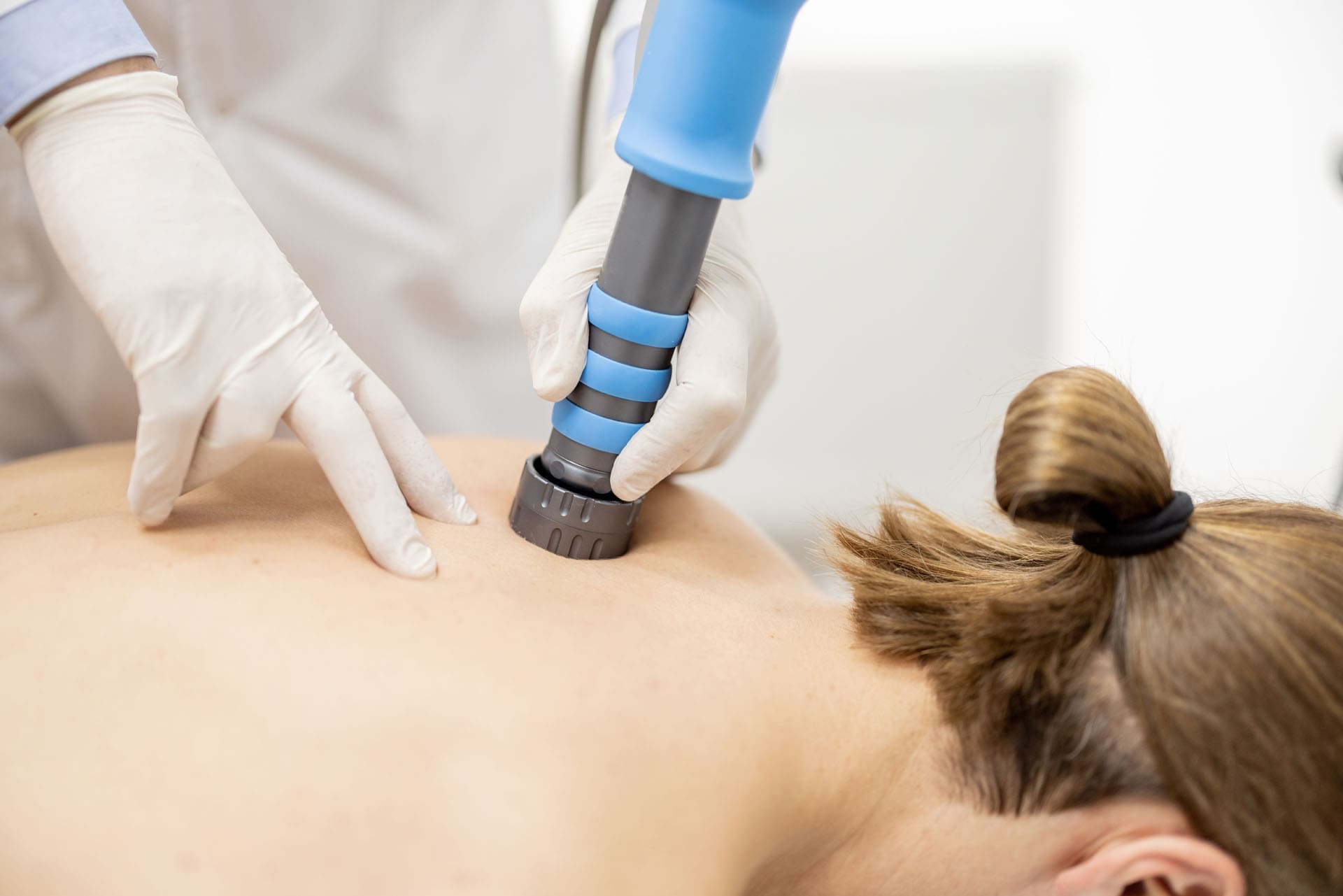
Shockwave therapy is gaining popularity for those struggling with pain from injuries or ongoing conditions. However, not every shockwave device delivers the same results. Weak radial tools or basic massage devices fall short compared to true shockwave therapy. Effective shockwave therapy, called Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), uses powerful, focused sound waves to cause tiny tissue injuries that kickstart the body’s natural healing deep within. ESWT provides specific energy levels, measured in mJ/mm², to spark repair processes. It reaches 4-6 cm into the body and is often FDA-approved for certain treatments. For genuine regenerative healing, Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSW) is essential, delivering high-energy waves rather than the shallower radial pressure waves.
True ESWT is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy acoustic waves to aid in the healing of muscles, tendons, and bones. It reduces inflammation, dissolves scar tissue, and relieves pain in conditions like tendinitis or long-term back problems. At integrative clinics like ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine in El Paso, TX, ESWT can be added to other therapies to speed recovery. ChiroMed, led by Dr. Alex Jimenez, combines chiropractic adjustments with holistic approaches to deliver a complete, surgery-free solution that addresses both tissue repair and body alignment.
What Is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)?
ESWT means Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy, where “extracorporeal” indicates it’s done outside the body without any cuts. The process sends strong sound waves into the affected spot. These waves make small traumas that prompt the body to heal itself, boosting blood flow, cell growth, and pain reduction over time (UCHealth, n.d.; Physis Rehab, n.d.).
Unlike radial devices that generate spreading pressure waves with limited depth, ESWT concentrates energy. Radial tools may mimic a deep massage but lack the regenerative power. Real ESWT employs systems such as electrohydraulic or electromagnetic systems to target areas precisely and penetrate deeper (SoftWave TRT, n.d.; Mayo Clinic, n.d.).
Key points about ESWT:
- ESWT is non-invasive, requiring neither surgery nor injections.
- Treatments take 10 to 20 minutes.
- Typically, 3 to 6 sessions are needed.
- There is minimal recovery time required for daily activities.
- The FDA has approved this treatment for conditions such as heel pain (Mayo Clinic, n.d.; Spring Chiropractic, n.d.).
At ChiroMed in El Paso, this aligns with their holistic model, combining ESWT with chiropractic care for better pain management outcomes.
Differences Between Focused and Radial Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapies vary, mainly between focused and radial types. Understanding this helps clarify why focused therapy excels in deep repair.
Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSW) delivers waves to a pinpoint area at specific depths, reaching up to 12 cm deep with intense energy. It’s ideal for bone or deep tendon problems, creating pressure peaks that encourage the formation of new blood vessels and cell repair (Physis Rehab, n.d.; HTX Urology, n.d.).
Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSW) spreads waves from the applicator, strongest at the skin and only 3 to 4 cm deep. It’s more pressure than a true shockwave, suitable for surface tension but not deep healing. Many marketed devices are radial and do not deliver the promised results (SoftWave TRT, n.d.; Mayo Clinic, n.d.).
- Focused: Deeper reach, higher energy, suited for chronic issues.
- Radial: Shallower, milder, and better for light muscle relief.
- Choose focused for activating stem cells and growth (Your Chiropractor, n.d.; Bell District Spine and Rehab, n.d.).
Experts caution against low-cost home radial devices, which may cause injury if misused. Opt for FDA-approved focused options for safety (HTX Urology, n.d.). ChiroMed emphasizes evidence-based tools in its integrative care.
How ESWT Promotes Healing
ESWT uses sound waves to positively stimulate tissues. The energy causes microtrauma that signals repair, enhancing blood supply with oxygen and nutrients. It reduces swelling and clears scar tissue, thereby relieving discomfort (UCHealth, n.d.; Physis Rehab, n.d.).
It triggers body responses by releasing signals for stem cells and growth factors, forming new vessels and mending tissues. In tendinitis, it remodels collagen to strengthen tendons (Your Chiropractor, n.d.; Bell District Spine and Rehab, n.d.).
Benefits:
- Fast pain relief, often after the first treatment.
- Improved range of motion.
- Enduring effects for months or years.
- Avoids medications or operations.
- Success up to 80-90% for some ailments (Physis Rehab, n.d.; Spring Chiropractic, n.d.).
Great for stubborn injuries, ESWT revives healing where it stalled (UCHealth, n.d.). At ChiroMed, this aligns with their focus on root-cause fixes for chronic pain.
Integrating ESWT in ChiroMed’s Approach
ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine in El Paso excels in blending therapies. Founded in 1996, it combines conventional and alternative methods to create personalized plans. Chiropractic aligns the spine, while ESWT heals soft tissues, creating a full non-surgical strategy (Go Holistiq, n.d.; Bell District Spine and Rehab, n.d.).
For back pain, adjustments correct structure, and ESWT eases muscle inflammation. This accelerates recovery from injuries or tendinitis (Uemura Chiropractic, n.d.; Thriving Life Wellness Center, n.d.).
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, leads with expertise in chronic pain, sciatica, and functional medicine. His observations stress non-invasive care for root causes, avoiding drugs or surgery. At ChiroMed, he integrates therapies such as acupuncture and nutrition, with potential ESWT, for musculoskeletal health (Jimenez, n.d.; ChiroMed, n.d.).
Clinics like ChiroMed combine ESWT with laser or ultrasound for enhanced results. Shockwave clears scars, and laser curbs inflammation (MedRay Laser, n.d.; Firgeleski Chiropractic Center, n.d.).
Integration perks:
- Quicker pain relief.
- Lasting mobility gains.
- Tailored patient plans.
- No medication side effects.
- Boosts total wellness (Go Holistiq, n.d.; Village Chiros, n.d.).
ChiroMed’s team, including therapists, collaborates for optimal care at their Vista Del Sol location.
Clinical Applications and Benefits at ChiroMed
ESWT treats various issues, like heel pain by removing spurs, or elbow tendinitis by strengthening tissues. It also aids bone healing after fractures (Mayo Clinic, n.d.; Bell District Spine and Rehab, n.d.).
In ChiroMed’s chiropractic focus, it handles neck, back, shoulder, and knee pains. Patients report less discomfort and better function quickly. It’s cost-effective and low-risk (Spring Chiropractic, n.d.; Thriving Life Wellness Center, n.d.).
Dr. Jimenez’s work on sciatica and injuries supports ESWT in complex cases, promoting fast, natural recovery (Jimenez, n.d.).
Overall advantages:
- It lessens the need for surgery.
- Enhances daily life.
- Succeeds where others fail.
- Safe, with few limitations, such as avoiding tumor areas (Mayo Clinic, n.d.; Physis Rehab, n.d.).
In summary, ESWT at clinics like ChiroMed provides strong, non-invasive healing. With focused therapy and integrative care under Dr. Jimenez, El Paso patients achieve lasting relief. Contact ChiroMed for custom advice.
References
Bell District Spine and Rehab. (n.d.). How Shockwave Therapy Enhances Chiropractic Services.
ChiroMed. (n.d.). ChiroMed – Integrated Medicine Holistic Healthcare in El Paso, TX.
Firgeleski Chiropractic Center. (n.d.). Combination Therapy.
Go Holistiq. (n.d.). The Power of Combining Chiropractic Treatment and Shockwave Therapy.
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Shockwave treatment: A new wave for musculoskeletal care.
MedRay Laser. (n.d.). Medray’s Dual Laser & Shockwave Therapy | Integrative Healing System.
Physis Rehab. (n.d.). Shockwave Therapy Benefits: A Complete Guide for Pain & Injury Recovery.
SoftWave TRT. (n.d.). SoftWave vs Shockwave Explained.
Spring Chiropractic. (n.d.). Shockwave Therapy & Treatments Available at Spring Chiropractic.
Thriving Life Wellness Center. (n.d.). Service: Shockwave Therapy.
UCHealth. (n.d.). Shockwave therapy can help those who have chronic injuries.
Uemura Chiropractic. (n.d.). Understanding Shockwave Therapy for Chronic Pain.
Village Chiros. (n.d.). How is Shockwave Therapy Used in Chiropractic Care?.
Your Chiropractor. (n.d.). How StemWave and SoftWave ESWT Heal Your Body.